| OCR Text |
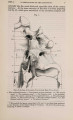
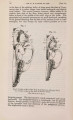
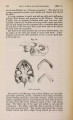
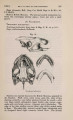
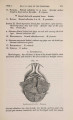
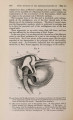
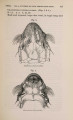
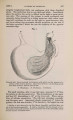
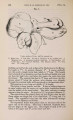
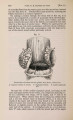
Show 1869.] MYOLOGY OF MENOBRANCHUS LATERALIS. 463 muscular mass, and, passing forwards, is inserted into the flexor surface of the femur just below the great trochanter, in close contiguity both to the insertion of the adductor and to the origin of the biceps. The ilio-caudal (figs. 9 & 10, 27. C) is exceedingly large relatively, and thick, forming the bulk of the lateral caudal muscular mass below the lateral furrow. It is inserted into the whole length of the ilium and its annexed rib. Fig. 9. Superficial muscles of dorsal (extensor) surface of right pelvic limb, and of outer side of posterior part of trunk and anterior part of tail. E. L. B. Extensor longus digitorum. Ex. 0. External oblique. F. C. Femoro-caudal. Gr. Gracilis. G. Mx. Gluteus mayimus. I. Iliacus. II. C. Ilio-caudal. P. Peroneus. B. F. Eector femoris. S. Sartorius. S. M. Semimembranosus. S.T. Semitendinosus. T.A. Tibia is anticus. Gracilis (figs. 8, 9, 10, 11, & 12, G). This muscle arises from the middle (antero-posterior) line of the ventral surface of the pelvic shield. It does not, however, extend forwards for nearly the whole length of this elongated shield, but only as far forwards as a line would be situated which should join the acetabula. It is inserted into the postero-peroneal surface of the upper half of the tibia. The adductor (figs. 8 & 11, A) is very much larger than in Menopoma, as it springs from the middle of the pelvic shield for its whole length, so that rather more appears superficially in front of the gracilis than is concealed beneath the latter. It is inserted into about the upper half of the flexor surface of the femur between the insertions of the iliacus and femoro-caudal. Semitendinosus (figs. 8, 9, 10, & 11, S.T). This small muscle takes origin from the junction of the semimembranosus with tbe gracilis, and not from bone or cartilage. Its insertion is the outside of the flexor digitorum, near the pes. |