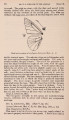
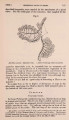
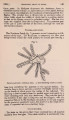
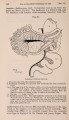
| Title |
Proceedings of the general meetings for scientific business of the Zoological Society of London 1896 |
| Call Number |
QL1 .Z7; Record ID 997682580102001 |
| Date |
1896 |
| Publisher |
Digitized by J. Willard Marriott Library, University of Utah |
| Subject |
Zoology; Periodicals |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Collection Name |
Rare Books Collection |
| Holding Institution |
Rare Books Division, Special Collections, J. Willard Marriott Library, University of Utah |
| Rights |
 |
| Scanning Technician |
Jason VanCott |
| Digitization Specifications |
Original scanned on Kirtas 2400 with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. Display image generated in Kirtas Technologies' OCR Manager as multiple page PDF. |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s6f227ct |
| Setname |
uum_rbc |
| ID |
265931 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6f227ct |