| Title |
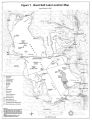
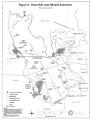
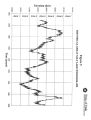
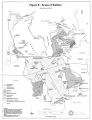
Great Salt Lake, Draft Comprehensive Management Plan |
| Creator |
Great Salt Lake Planning Team, Utah Department of Natural Resources |
| Publisher |
Digitized by J. Willard Marriott Library, University of Utah |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Digitization Specifications |
Original scanned on Epson Expression 10000XL Flatbed Scanner and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed tiff and converted to pdf with embedded text. Compound objects generated in ContentDM. |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights Management |
Digital Image Copyright 2009 University of Utah, All Rights Reserved |
| Scanning Technician |
Seungkeol Choe |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s68w3cpm |
| Setname |
wwdl_documents |
| ID |
1141408 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s68w3cpm |