| Title |
Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals |
| Call Number |
QP401 .D3; Record ID 99335160102001 |
| Date |
1872 |
| Description |
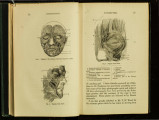
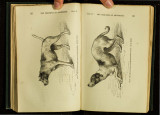
Darwin, Charles (1809-1882). The expression of the emotions in man and animal. London: J. Murray, 1872 First edition QP401 D3 Edition of seven thousand copies. |
| Creator |
Darwin, Charles, 1809-1882 |
| Publisher |
Digitized by J. Willard Marriott Library, University of Utah |
| Subject |
Emotions; Instinct; Psychology, Comparative |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Identifier |
XQP401D3.pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Collection Name |
Rare Books Collection |
| Holding Institution |
Rare Books Division, Special Collections, J. Willard Marriott Library, University of Utah |
| Rights |
 |
| Scanning Technician |
Cedar Gonzalez |
| Digitization Specifications |
Original scanned with Hasselblad H2D 39 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi tifs. Display images created in Adobe Photoshop Lightroom 4 and generated in Adobe Acrobat ProX as multiple page PDF. |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s6s21b6j |
| Setname |
uum_rbc |
| ID |
282029 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6s21b6j |