| Title |
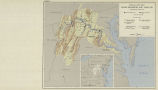
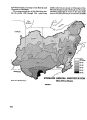
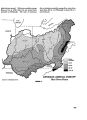
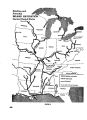
Ten rivers in America's future, from volume 2, the Report of the President's Water Resources Policy Commission |
| Creator |
United States. Water Resources Policy Commission |
| Subject |
Rivers; Water resources development; Water-supply; Hydraulic engineering |
| Spatial Coverage |
United States |
| Publisher |
U.S. Government Printing Office |
| Date |
1950 |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Digitization Specifications |
Digitized by Backstage Library Works. Pages were scanned at 400 ppi on Fujitsu fi-5650C sheetfed scanner as 8-bit grayscale or 24-bit RGB uncompressed TIFF images. For ContentDM access the images were resampled to 750 pixels wide and 120 dpi and saved as JPEG (level 8) in PhotoShop CS with Unsharp Mask of 100/.3. Foldout pages larger than 11" x 14" were captured using a BetterLight Super 8K-2 digital camera back on a 4x5 view camera (100mm Schneider APO lens). Oversize images were resampled to 1500 pixels wide. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) by ABBYY FineReader 7.0 with manual review. |
| Resource Identifier |
http://content.lib.utah.edu/cgi-bin/docviewer.exe?CISOROOT=/wwdl-doc&CISOPTR=1448 |
| Language |
eng |
| Relation |
Western Waters Digital Library |
| Rights Management |
Digital Image Copyright 2005, Marriott Library, University of Utah. All Rights Reserved. |
| Contributing Institution |
J. Willard Marriott Library, University of Utah, 295 S 1500 E, Salt Lake City, UT 84112-0860 |
| Source Physical Dimensions |
Book 801 p. ; 26 cm. |
| Scanning Technician |
Backstage Library Works, 1180 S. 800 E., Orem, UT 84097 |
| Call Number |
LC: HD1694.A5 |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s6r210r8 |
| Setname |
wwdl_documents |
| ID |
1140007 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6r210r8 |