| Title |
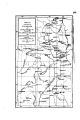
Annual Report upon the Geographical and Geological Surveys and Explorations West of the 100th Meridian, in Nevada, Utah, Colorado, New Mexico, and Arizona |
| Subject |
Indians of North America; Maps.; Discoveries in geography; Indians of North America--Colonial Period,--ca. 1600-1775; Indians of North America-Colonization; Indigenous peoples--North America |
| Keywords |
Native Americans |
| Publisher |
Digitized by J. Willard Marriott Library, University of Utah |
| File Name |
AnnualReportGeographicalandGeologicalSurveys.pdf |
| Tribe |
Navajo; Ute |
| Language |
eng |
| Description |
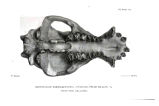
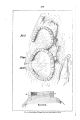
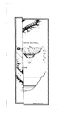
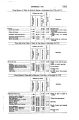
Appendix EE of the Annual Report of the Chief of Engineers for 1873.: ill., maps ; 23 cm. 1873. |
| Type |
Image/StillImage |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Rights |
Digital Image Copyright University of Utah |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s69w39zp |
| Creator |
Wheeler, George M. (George Montague), 1842-1905 |
| Spatial Coverage |
Utah; Colorado; New Mexico; Nevada; Arizona |
| Setname |
uaida_main |
| ID |
356108 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s69w39zp |