| Title |
Partial Third Nerve Palsy and Ocular Neuromyotonia From Displacement of Posterior Communicating Artery Detected by High-Resolution MRI |
| Creator |
Cruz, Franz Marie; Blitz, Ari M; Subramanian, Prem S |
| Affiliation |
Wilmer Eye Institute (FMZ, PSS), The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland; Division of Neuroradiology (AMB), The Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland |
| Abstract |
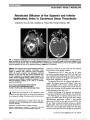
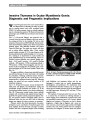
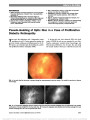
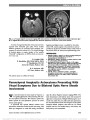
Ocular neuromyotonia is an unusual condition in which sustained, undesired contraction of one or more extraocular muscles occurs after normal muscle activation. Although most commonly reported after paraseller cranial irradiation for tumor, chronic nonaneurysmal vascular compression of the third nerve can produce partial ocular motor nerve paresis and ocular neuromyotonia. A 75-year-old woman presented with intermittent left-gaze-evoked binocular diplopia. She had an incomplete right third nerve palsy but became symptomatically diplopic and esotropic upon sustained left gaze. High-resolution brain magnetic resonance imaging showed displacement of the right posterior communicating artery and contact with the right third nerve. Gaze-evoked diplopia resolved with carbamazepine, but a partial third nerve paresis remained. |
| Subject |
Older people; Anticonvulsants; Carbamazepine; Circle of Willis; Diplopia; Female; Humans; Isaacs Syndrome; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Oculomotor Nerve Diseases; Treatment Outcome |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Publication Type |
Journal Article |
| Collection |
Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library: Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology Archives: https://novel.utah.edu/jno/ |
| Publisher |
Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins |
| Holding Institution |
Spencer S. Eccles Health Sciences Library, University of Utah |
| Rights Management |
© North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society |
| Setname |
ehsl_novel_jno |
| ID |
227483 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6gr03wb/227483 |