| OCR Text |
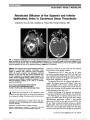
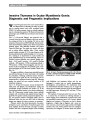
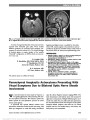
Show Partial Third Nerve Palsy and Ocular Neuromyotonia From Displacement of Posterior Communicating Artery Detected by High-Resolution MRI Franz Marie Cruz, MD, Ari M. Blitz, MD, Prem S. Subramanian, MD, PhD Abstract: Ocular neuromyotonia is an unusual condition in which sustained, undesired contraction of one or more extraocular muscles occurs after normal muscle activation. Although most commonly reported after paraseller cranial irradiation for tumor, chronic nonaneurysmal vascular compression of the third nerve can produce partial ocular motor nerve paresis and ocular neuromyotonia. A 75-year-old woman presented with intermittent left-gaze-evoked binocular diplopia. She had an incomplete right third nerve palsy but became symptomatically diplopic and esotropic upon sustained left gaze. High-resolution brain magnetic resonance imaging showed displacement of the right posterior communicating artery and contact with the right third nerve. Gaze-evoked diplopia resolved with carbamaze-pine, but a partial third nerve paresis remained. Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology 2013;33:263-265 doi: 10.1097/WNO.0b013e31829eb397 © 2013 by North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society A75-year-old healthy woman developed a sense that her eyes "were not moving together" but denied diplopia. Her symptoms became more bothersome, including onset of mild right upper eyelid ptosis, following uncomplicated right cataract surgery. Seven months later, she reported in-termittent binocular diplopia that occurred when she would look straight ahead after prolonged left gaze. Examination at that time showed variable ocular alignment and high eyelid creases bilaterally. Acetylcholine receptor antibody titers and thyroid function testing were normal. Magnetic reso-nance imaging (MRI) of the brain and MRA of the head and neck failed to disclose a cause for the patient's symp-toms. When she developed anisocoria, she was referred for neuro-ophthalmological evaluation. Visual acuity was 20/20 bilaterally. The right pupil was 1.5 mm larger than the left and constricted more slowly to both direct and consensual light stimulation. There was no relative afferent pupillary defect. There was 1.5 mm ptosis of the right upper lid, and ocular motility of the right eye showed mild deficits in adduction, elevation, and depression (Fig. 1). Ductions of the left eye were full. Following sus-tained gaze to the left, the right eye remained in adduction. At this time, the right eye could not be fully abducted and depression and elevation also were reduced (Fig. 2A, B). Also with sustained left gaze, elevation of the ptotic right eyelid was noted, and anisocoria was reduced (see Supplemental Digital Content, Video, http://links.lww.com/WNO/A79). Prolonged down gaze resulted in progressive elevation of the right upper lid with resolution of right lid ptosis (Fig. 2C). FIG. 1. Ocular motility shows a partial right third nerve palsy with pupillary involvement. Wilmer Eye Institute (FMZ, PSS), The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland; Division of Neuroradiology (AMB), The Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland. Supported in part by an unrestricted grant to the Wilmer Eye Institute from Research to Prevent Blindness, Inc, New York, NY. The authors report no conflicts of interest. Supplemental digital content is available for this article. Direct URL citations appear in the printed text and are provided in the full text and PDF versions of this article on the journal's Web site (www.jneuro-ophthalmology.com). Address correspondence to Prem S. Subramanian, MD, PhD, Wilmer Eye Institute, Johns Hopkins Hospital, 600 North Wolfe Street, Baltimore, MD 21287; E-mail: psubram1@jhmi.edu Cruz et al: J Neuro-Ophthalmol 2013; 33: 263-265 263 Photo Essay Section Editor: Timothy J. McCulley, MD Copyright © North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. The patient was diagnosed with a partial right pupil-involving third nerve palsy and ocular neuromyotonia. MRI with attention to the third nerve revealed displacement of the right posterior communicating artery and contact with the cisternal segment of the right third nerve (Fig. 3A, B). The patient was prescribed carbamazepine, 200 mg twice daily, with complete resolution of ocular neuromyotonia. The partial third nerve palsy was unchanged. When the patient stopped carbamazepine 3 months later, the ocular neuromyotonia returned; it resolved again 2 days after car-bamazepine was resumed. Ocular neuromyotonia is an acquired disorder charac-terized by paroxysmal neuronal discharges resulting in brief continuous contractions of extraocular muscles. It is a rare cause of episodic binocular diplopia. It most commonly involves the third nerve, followed by the fourth and sixth nerves (1) and may occur in a setting of chronic ocular motor nerve cranial nerve palsy (2). Lid and pupil synkineses with third nerve involvement may occur (1,2). Ocular neuromyo-tonia may occur spontaneously (3) or following prolonged gaze in the direction of action of the involved extraocular muscle (2,3). It also has been reported following alcohol consumption (2). It is a delayed consequence of cranial irradiation, particu-larly to the parasellar region. Less common causes include Graves dysthyroid orbitopathy (4), cavernous sinus disease (5,6), and neurovascular compression by an arterial aneurysm (2,7) or a dolichoectatic basilar artery (8). On occasion, no specific cause is identified (3). To our knowledge, ocular neu-romyotonia and partial pupil-involving third nerve paresis re-sulting from displacement of the posterior communicating artery and contact with the third nerve have not been reported. Evaluation of patients with ocular neuromyotonia requires neuroimaging (2,9). If a structural abnormality is not iden-tified with conventional brain MRI techniques, one should consider additional MRI sequences, including fast-imaging employing steady-state acquisition (FIESTA), constructive interference in the steady-state (CISS), and volumetric inter-polated breath-hold examination (VIBE). FIESTA and CISS provide high spatial resolution sequences capable of depicting the entire course of the cranial nerves including segments that are not visible using traditional techniques (10). Inoue et al (11) used FIESTA in a patient with ocular neuromyotonia to identify vascular compression of the third nerve at its root exit zone. The patient had no evidence of third nerve palsy. VIBE was designed to shorten acquisition time, enhance image contrast, and decrease image artifact. Its application includes imaging of the lungs, liver, and brain (12). FIG. 2. Following sustained left gaze, the patient develops an esotropia and deficits in elevation (A), and depression (B, C) of the right eye. FIG. 3. High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of the brain with attention to the skull base. A. On precontrast coronal constructive interference in the steady state images, the right posterior communicating artery (long arrow) contacts the right cisternal third nerve (short arrow). The left posterior communicating artery (dashed long arrow) does not contact the third nerve (arrowhead). B. On postcontrast axial volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination images, the right cisternal third nerve (short arrow) is seen adjacent to the right posterior communicating artery (long arrow) and demonstrates enhancement when compared with the left third nerve (arrowhead). 264 Cruz et al: J Neuro-Ophthalmol 2013; 33: 263-265 Photo Essay Copyright © North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. Possible pathophysiologic mechanisms of ocular neuro-myotonia include unstable motor nerve membranes, ephaptic transmission across adjacent nerves, and abnormal extracel-lular potassium concentration (2,3). We believe that ephaptic transmission rather than aberrant regeneration of the third nerve is the mechanism for the progressive eyelid elevation during sustained down gaze seen in our patient. This is also supported by our patient's excellent response to treatment with carabamazepine, a membrane-stabilizing agent. REFERENCES 1. Choi KD, Hwang JM, Park SH, Kim JS. Primary aberrant regeneration and neuromyotonia of the third cranial nerve. J Neuroophthalmol. 2006;26:248-250. 2. Ezra E, Spalton D, Sanders MD, Graham EM, Plant GT. Ocular neuromyotonia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1996;80:350-355. 3. Shults WT, Hoyt WF, Behrens M, MacLean J, Saul RF, Corbett JJ. Ocular neuromyotonia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986;104:1028-1034. 4. Chung SM, Lee AG, Holds JB, Roper-Hall G, Cruz OA. Ocular neuromyotonia in Graves dysthyroid orbitopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997;115:365-370. 5. Jacob M, Vighetto A, Bernard M, Tilikete C. Ocular neuromyotonia secondary to a cavernous sinus meningioma. Neurology. 2006;66:1598. 6. Harrison AR, Wirtschafter JD. Ocular neuromyotonia in a patient with cavernous sinus thrombosis secondary to mucormycosis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997;124:122-123. 7. Park HY, Hwang JM, Kim JS. Abducens neuromyotonia due to internal carotid artery aneurysm. J Neurol Sci. 2008;270: 205-208. 8. Tilikete C, Vial C, Niederlaender M, Bonnier PL, Vighetto A. Idiopathic ocular neuromyotonia: a neurovascular compression syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2000;69:642-644. 9. Salchow DJ, Wermund TL. Abducens neuromyotonia as the presenting sign of an intracranial tumor. J Neuroophthalmol. 2011;31:34-37. 10. Sheth S, Branstetter BF IV, Escott EJ. Appearance of normal cranial nerves on steady-state free precession MR images. Radiographics. 2009;29:1045-1055. 11. Inoue T, Hirai H, Shimizu T, Tsuji M, Shima A, Suzuki F, Matsuda M. Ocular neuromyotonia treated by microvascular decompression: usefulness of preoperative 3D imaging: case report. J Neurosurg. 2012;117:1166-1169. 12. Wetzel SG, Johnson G, Tan AGS, Cha S, Knopop EA, Lee VS, Thomasson D, Rofsky NM. Three-dimensional, T1-weighted gradient-echo imaging of the brain with a volumetric interpolated examination. AJNR. 2002;23:995-1002. Cruz et al: J Neuro-Ophthalmol 2013; 33: 263-265 265 Photo Essay Copyright © North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. |