| Title |
False Negative Hydroxyamphetamine Test in Horner Syndrome Caused by Acute Internal Carotid Artery Dissection |
| Creator |
Moster, ML; Galiani, D; Garfinkle, W |
| Affiliation |
Department of Neurosensory Sciences, Albert Einstein Medical Center, Philadelphia, USA. mmoster@aol.com |
| Abstract |
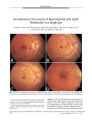
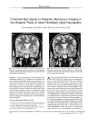
A patient with Horner syndrome from internal carotid artery dissection initially had a false negative hydroxyamphetamine test. Two months later, the ophthalmic signs had disappeared but the hydroxyamphetamine test was positive. This case illustrates that hydroxyamphetamine testing may be falsely negative in acute Horner syndrome because norepinephrine stores in oculosympathetic postganglionic terminals have not yet been depleted. However, the hydroxyamphetamine test may be positive even after the ophthalmic signs of Horner syndrome have disappeared. |
| Subject |
Adult; Anisocoria/physiopathology; Carotid Arteries/surgery; Dissection/adverse effects; False Negative Reactions; Hemorrhage/physiopathology; Horner Syndrome/diagnosis; Horner Syndrome/etiology; Humans; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Male; Warfarin/therapeutic use; p-Hydroxyamphetamine/diagnostic use |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Publication Type |
Journal Article |
| Collection |
Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library: Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology Archives: https://novel.utah.edu/jno/ |
| Publisher |
Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins |
| Holding Institution |
Spencer S. Eccles Health Sciences Library, University of Utah |
| Rights Management |
© North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society |
| Setname |
ehsl_novel_jno |
| ID |
225253 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6fr32qh/225253 |