| OCR Text |
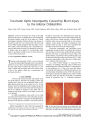
Show ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Bilateral Visual Loss Complicating Liposuction in a Patient with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension Mario Luiz Ribeiro Monteiro, MD, Frederico Castelo Moura, MD, and Leonardo Provetti Cunha, MD Abstract: A 34- year- old obese woman developed blurred vision in both eyes soon after large- volume liposuction of the dorsum and gluteus region bilaterally associated with abdominal dermolipectomy. An ophthalmic examination revealed severe bilateral visual loss and pallid optic disc edema. The patient gave a history of transient obscurations of vision in the past. Neuroimaging studies were non-revealing, but a lumbar puncture disclosed a markedly elevated intracranial pressure. The patient was diagnosed as having had bilateral ischemic optic neuropathy superimposed on pre- existing idiopathic intracranial hypertension ( IIH). Acetazolamide treatment was used. Some visual improvement occurred, and optic disc edema evolved into severe optic disc pallor. This case shows that visual loss from optic disc infarction may be a devastating complication of high- volume liposuction in patients with underlying IIH. Because liposuction is frequently performed on obese patients, physicians should screen for signs and symptoms of IIH before undertaking this procedure. ( J Neuro- Ophthalmol 2006; 26: 34- 37) Liposuction is the most commonly performed plastic surgical operation in the United States ( 1,2). Although it is considered a safe procedure, especially after the introduction of the tumescent technique ( 3,4), serious local and systemic complications have been reported ( 5,6). Visual loss after liposuction is a very uncommon occurrence. In 2000, Minagar et al ( 7) were the first to report a case of ischemic optic neuropathy ( ION) after liposuction. Foroozan and Varon ( 8) and Sibgarullah et al ( 9) recently reported two more cases. We examined a patient who had developed acute bilateral visual loss soon after liposuction and was found to have idiopathic intracranial hypertension ( IIH). We believe this to be the first reported case of a patient with IIH to develop optic nerve- related visual loss following liposuction. Division of Ophthalmology, Hospital das Clinicas of the University of Sao Paulo Medical School, Sao Paulo, Brazil. Address correspondence to Mario Luiz R. Monteiro, MD, Av Angelica 1757, conj. 61., 01227- 200 Sao Paulo, Brazil; E- mail: mlrmonteiro@ terra. com. br CASE REPORT A 34- year- old woman with a history of obesity ( height 1,60 m; weight 80 Kg; body mass index = 31,20) underwent liposuction of the dorsum and gluteus region bilaterally associated with abdominoplasty. Preoperatively she had the following measurements: blood pressure 110/ 70, pulse 72, fasting blood sugar 97 mg/ dl, and hemoglobin 13.1 g/ dl. During the procedure, which was performed under spinal- epidural anesthesia and sedation, 5,500 mL of fat was removed. After surgery the patient remained somnolent for several hours, but upon awakening the following day she complained of headache and blurred vision in both eyes. She was promptly examined, but because her temperature, blood pressure ( 105 X 60 mm Hg), pulse rate ( 109/ min), respiration rate ( 16/ min), and clinical examination seemed to be within the normal range, the symptoms were initially attributed to the effects of blood loss during surgery. Five days after surgery, we examined the patient. When questioned about previous ocular symptoms, she reported that several months before surgery, she had started experiencing transient visual obscurations in both eyes, each episode lasting a few seconds and usually triggered by postural changes such as bending over or rising. She had not consulted an ophthalmologist about these symptoms and denied having headaches or double vision. Her most recent eye examination had been performed ten years previously and was reported as unremarkable. General clinical and neurologic examinations were within normal limits. Best- corrected visual acuity was hand movements OU External eye examination, extraocular movements, and slit lamp examination were normal. Pupils were equal in size and reacted sluggishly to light, but no relative afferent pupillary defect was observed. The intraocular pressure by applanation was 16 mm Hg bilaterally. Ophthalmoscopy showed bilateral pallid optic disc edema with a splinter hemorrhage OD ( Fig. 1). The remainder of the fundus examination was normal. Brain MRI and magnetic resonance venography ( MRV) were normal. Lumbar puncture revealed clear and colorless cerebrospinal fluid ( CSF) with an opening pressure of 59 cm H20. The CSF formula was normal. 34 J Neuro- Ophthalmol Vol. 26, No. 1, 2006 Copyright © Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. Visual Loss after Liposuction in a Patient with LLH J Neuro- Ophthalmol, Vol. 26, No. 1, 2006 FIG. 1. Two weeks after liposuction surgery, bilateral pallid optic disc edema is present. 120 105 90 75 60 120 105 90 75 60 240 255 270 285 3 0 0 / \ 240 255 270 285 300^ FIG. 2. Two weeks after surgery, Goldmann visual fields show residual islands of vision in the temporal fields bilaterally. FIG. 3. Six weeks after surgery, bilateral optic disc pallor is present together with a ring of gliosis around the optic discs indicating that papilledema had been long- standing. 35 Copyright © Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. J Neuro- Ophthalmol, Vol. 26, No. 1, 2006 Ribeiro Monteiro et al She received a diagnosis of IIH and was treated with acetazolamide 250 mg orally QID and dexamethasone orally 4 mg/ d. Headaches decreased and visual acuity improved to finger counting at 20 cm OU. Go Idmann perimetry showed only a residual island of vision in the temporal field with V/ 4e and I/ 4e isopters bilaterally ( Fig. 2). A second lumbar puncture on the ninth day of treatment revealed an opening pressure of 16 cm H20. Medical treatment was maintained, and six weeks after surgery, visual acuity had improved to finger counting OD and 20/ 200 OS. Papilledema had diminished and was eventually replaced by bilateral optic disc pallor OU. A peripapillary hypo- pigmented ring suggested long- standing papilledema ( Fig. 3). Dexamethasone was eventually discontinued and the acetazolamide dose reduced to 500 mg/ d. A third lumbar puncture performed two months after surgery disclosed an opening pressure of 20 cm H20. DISCUSSION Liposuction surgery is a procedure that can help sculpt the body by removing unwanted fat from specific areas, including the abdomen, hips, buttocks, thighs, knees, upper arms, chin, cheeks, and neck. It is today the most commonly performed aesthetic procedure worldwide ( 1,2). Although considered a safe procedure, local and systemic adverse outcomes, such as pulmonary fat embolism, infection, pituitary apoplexy, deep venous thrombosis, fluid overload, and death have been reported ( 10- 12). The safety of liposuction has improved since the introduction of the tumescent technique, designed to remove approximately 1,500 mL of localized fat for cosmetic purposes in non-obese subjects. However, technical improvements have led to an increase in the volume removed by way of liposuction, and unfortunately the procedure is now frequently used in obese patients. Large- volume liposuction (> 3000 mL of aspirate) may be associated with a relatively high rate of morbidity and mortality due to hemodynamic complications. Patients are exposed to prolonged interventions, fluid shifts, and infusion of high doses of epinephrine and lidocaine added to the wetting solution for their analgesic and hemostatic effects. Increased intraoperative cardiac index, heart rate, and mean pulmonary arterial pressure associated with intraoperative low body temperatures have been documented ( 1). After surgery, an increased cardiac work has been observed in patients with high- volume liposuction possibly associated with epinephrine administration and hemo-dilution related to the procedure ( 1). Hemodilution in the postoperative period is probably the result of fluid shift from the operative field and blood loss during surgery given that 25% to 30% of the aspirate may consist of blood ( 11,12). Visual loss after liposuction has been reported only three times ( 7- 9). Minagar et al ( 7) described a 47- year- old woman who underwent liposuction of the abdomen, thighs, and arms and developed postoperative hypotension and anemia. Visual loss developed in the OD on the second postoperative day, and pallid optic disc edema was noted upon ophthalmoscopy. The left optic disc had a normal-sized physiologic cup. Brain MRI and magnetic resonance angiography were normal. The authors believed that the patient had had postoperative anterior ischemic optic neuropathy ( AION) precipitated by acute blood loss and hypotension. Sigbarullah et al ( 9) reported a very similar patient suffering from unilateral AION developing two days after liposuction, when her hematocrit was only 23.5%. Foroozan and Varon ( 8) reported a patient who developed bilateral AION after high- volume liposuction. The patient also developed pulmonary embolism and dural venous sinus thrombosis. The examination disclosed bilateral pallid optic disc edema and hemorrhage. Transverse sinus thrombosis was suggested by MRV but no intracranial pressure measurements were reported. Severe anemia with a hemoglobin of 7.0 g/ dl and hematocrit of 21.6% was documented in the postoperative period. In these three cases, visual loss was most likely precipitated by severe postoperative anemia resulting in AION. Our patient differs from these previously reported cases in that her visual loss was due to bilateral AION in the setting of chronic papilledema in IIH. Hypotension owing to large- volume liposuction likely led to infarction in a disc made vulnerable by being crowded and under increased CSF pressure. Although anemia was not documented in blood samples drawn nine days after surgery, we believe red blood cell loss, transient hemodilution, and hypotension may have contributed to visual loss. Since liposuction is frequently considered in the treatment of obese patients and obesity is a known predisposing factor for IIH, physicians should consider inquiring about transient visual obscurations and screening for papilledema before proceeding with liposuction on such patients. REFERENCES 1. Kenkel JM, Lipschitz AH, Luby M, Kallmeyer I, Sorokin E, Appelt E, et al. Hemodynamic physiology and thermoregulation in liposuction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2004; 114: 503- 13. 2. American Society of Plastic Surgeons. 2001 Procedural Statistics Report. Arlington Heights, IL: American Society of Plastic Surgeons; 2001. 3. Klein JA. The tumescent technique for local anesthesia improves safety in large- volume liposuction. Plast Reconstr Surg 1993; 92: 1085- 98. 4. Klein JA. The tumescent technique: anesthesia and modified liposuction technique. Dermatol Clin 1990; 8: 425- 37. 36 © 2006 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Copyright © Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. Visual Loss after Liposuction in a Patient with LLH J Neuro- Ophthalmol, Vol. 26, No. 1, 2006 5. Rao RB, Ely SF, Hoffman RS. Deaths related to liposuction. N Engl J Med 1999; 340: 1471- 5. 6. Grazer FM, de Jong RH. Fatal outcomes from liposuction: census survey of cosmetic surgeons. Plast Reconstr Surg 2000; 105: 436^ 6. 7. Minagar A, Schatz NJ, Glaser JS. Liposuction and ischemic optic neuropathy. Case report and review of literature. J Neurol Set 2000; 181: 132- 6. 8. Foroozan R, Varon J. Bilateral anterior ischemic optic neuropathy after liposuction. J Neuroophthalmol 2004; 24: 211- 3. 9. Sibgatullah M, Kupersmith MJ, Zerykier A, Volpe S. Ischemic optic neuropathy after liposuction: case report and review. Neuro-ophthalmology 2005; 29: 91- 3. 10. Matarasso A, Hutchinson OH. Liposuction. JAMA 2001; 285: 266- 8. 11. Albin R, de Campo T. Large- volume liposuction in 181 patients. Aesthetic Plast Surg 1999; 23: 5- 15. 12. Courtiss EH, Choucair RJ, Donelan MB. Large- volume suction lipectomy: an analysis of 108 patients. Plast Reconstr Surg 1992; 89: 1068- 82. 37 Copyright © Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. |