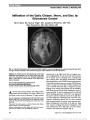
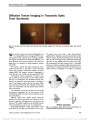
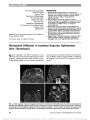
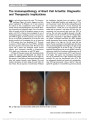
| OCR Text |
Show The Heidenhain Variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease-A Case Series Sarah E. Parker, MD, Meena Gujrati, MD, John H. Pula, MD, Sarah N. Zallek, MD, Jorge C. Kattah, MD Background: To study the neuro-ophthalmologic character-istics of patients with the visual variant of Creuztfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) predominantly affecting the occipital and parietal lobes, known as the Heidenhain variant (HvCJD). The initial symptoms and findings may overlap with other posterior cerebral degenerative disorders. We reviewed our experience with HvCJD including clinical course and results of neuroimaging, electroencephalography (EEG), and cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF) studies. Neuropathological postmortem findings were reviewed when available to confirm the clinical impression. Methods: Retrospective study of HvCJD patients examined in the past 15 years at a single tertiary referral university hospital. Rapid rate of visual and neurological deterioration and abnormal diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) were char-acteristic for HvCJD. Results: Three patients displayed abnormalities in DWI, EEG, and CSF and had rapid clinical progression, leading to a clinical diagnosis of HvCJD. None underwent diagnostic cerebral biopsy. In 2 patients, the diagnosis of sporadic CJD was confirmed by postmortem neuropathologic, immunohis-tochemical, and genetic studies. Conclusions: The gold standard for establishing the diag-nosis of HvCJD is based on the characteristic histopatho-logic findings and molecular confirmation. Concern with potential iatrogenic CJD, related to surgical instrumentation or operating room prion contamination, has limited the availability of confirmatory brain biopsy. Our case series illustrates how the combination of clinical neuroimaging and EEG studies and 14:3:3 protein and other neuronal protein marker levels can lead to the diagnosis of HvCJD. Immuno-histochemical analysis and genetic testing at a specialized prion research center will assist in identifying the sporadic variant and genetic forms of CJD. Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology 2014;34:4-9 doi: 10.1097/WNO.0b013e3182916155 © 2013 by North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society Introduction Posterior cortical degeneration (PCD) is the final common outcome from myriad etiologies with differing patho-physiologic mechanisms. Although several different histolog-ical subtypes have been identified, the essential feature of PCD is neuronal degeneration centered in the occipital, pos-terior temporal, and parietal lobes. The initial clinical man-ifestations of PCD suggest topographic localization but do not provide etiologic specificity. The Heidenhain variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (HvCJD) is characterized by occipital and posterior parieto-temporal cortex neuronal loss induced by the mutant prion protein PrPSC. HvCJD is one cause of PCD, which is typ-ically difficult to diagnose, rapidly progressive and accounts for approximately one-third of all Creuztfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) cases (1-9). METHODS Three patients with HvCJD evaluated at the University of Illinois between 1998 and 2012 were included in our study. The institutional review board determined that this project did not meet the definition of human subject research according to federal regulations, given that all 3 patients died before the initiation of this retrospective investigation. Concern about instrument and/or surgical suite contam-ination as possible sources of iatrogenic CJD (10) obstructed acquisition of a diagnostic brain biopsy at our institution. We pursued alternative diagnostic options. Elevation of the 14:3:3 Departments of Neurology (SEP, JHP, SZ, JCK) and Neuropathology (MG), Illinois Neurologic Institute, University of Illinois, Peoria, Illinois. Supplemental digital content is available for this article. Direct URL citations appear in the printed text and are provided in the full text and PDF versions of this article on the journal's Web site (www.jneuro-ophthalmology.com). John Farrel, MD, from the Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases consulted in Case 1. Address correspondence to Jorge C. Kattah, MD, Department of Neurology, Illinois Neurologic Institute, University of Illinois; E-mail: kattahj@uic.edu 4 Parker et al: J Neuro-Ophthalmol 2014; 34: 4-9 Original Contribution Copyright © North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. and other neuronal proteins as a CJD marker could lead to a misdiagnosis of HvCJD in PCD patients with or without associated dementia. We applied diagnostic criteria proposed by Kropp et al (6) that are endorsed by the World Health Organization and the American Academy of Neurology 14:3:3 protein evidence-based guideline (2). These criteria include disease duration less than 2 years and a compatible aggregate of clinical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), serial electroencephalography (EEG) data, and elevated cerebrospi-nal fluid (CSF) 14:3:3 and/or other neuronal proteins (2-5). Postmortem tissue examination with immunohistochemical staining and genetic testing confirmed sporadic CJD in 2 of our patients. Case Reports All patients were referred to our Neuro-Ophthalmology Unit with visual disturbances. One patient was transferred from an outside facility with progressive cortical blindness and advanced encephalopathy. The other 2 patients presented at an earlier stage of disease: 1 with an isolated visual field defect and 1 with a visual field defect, dyschromatopsia, and visual hallucina-tions. These latter 2 patients developed rapid neurological deterioration occurring over the ensuing 4 weeks. Case 1 A 73-year-old Caucasian cattle farmer with diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and essential tremor noted episodic painless diplopia and blurry vision. He had previously received panretinal photocoagulation for diabetic retinopathy in both eyes. At that time, his symptoms were believed due to the diabetic complications of retinopathy and ocular motor paresis. Three weeks later, he reported "progressive fading vision" and that he "could not talk right." Computed tomog-raphy and MRI of the brain were reported to be normal. Over the next 2 weeks, his visual loss progressed. He could not visually recognize objects or people, although he could recognize them by touch or hearing their voices. We initially evaluated the patient 2 months after the onset of symptoms. At that time, he could not perform any activities of daily living. His visual acuity could not be assessed. Pupils reacted sluggishly to light and optokinetic response was absent. Ophthalmoscopic examination showed bilateral optic disc pallor and evidence of panretinal photo-coagulation. He had no family history of dementia or medical procedures that would have placed him at risk for iatrogenic CJD. During his hospitalization, the patient slept most of the time, with weak arousals, and developed startle myoclonus. MRI of the brain showed ribbon-like gyriform hyper-intensities in the occipital lobes due to restricted diffusion. No abnormalities were noted in the basal ganglia. He had 2 EEGs: the first showed diffuse slowing and intermittent generalized spike and wave complexes. Three days later, a second EEG showed generalized triphasic wave complexes at a 1 Hz frequency (Fig. 1). Laboratory testing showed low serum thiamine and vitamin B12 levels. CSF 14:3:3 and neuron-specific enolase levels were increased. Following an advanced directive, his family elected to withdraw care. Ten weeks after the onset of visual symptoms, he expired. Examination before death in the hospital revealed a mute, akinetic cortically blind patient. Autopsy performed by the National Prion Disease Pathol-ogy Surveillance Center at Case Western Reserve University showed spongiform encephalopathy. Immunoblot revealed abnormal protease-resistant prion protein (PrPSc), known as PrP 27-30, confirming the diagnosis of sporadic CJD. Genetic testing showed homozygosity for methionine in codon 129. Case 2 A 74-year-old Caucasian woman with chronic bronchitis and bilateral hearing loss secondary to otosclerosis com-plained of blurred vision and difficulty with balance. Visual acuity was 20/25 in each eye with reduced color vision bilaterally. Pupillary reactions and eye movement were normal, and the fundi were unremarkable. Automated visual field testing demonstrated a left homonymous hemi-anopia (Fig. 2). Neurological examination including vestib-ular testing was normal. EEG showed focal slowing in the right parietal region, and brain MRI revealed increased signal in the cortical gyri of the right tempo-parietal junction. No abnormalities were noted in the cerebellum or basal ganglia. Two weeks later, neuropsychometric testing showed deficits involving multiple cognitive domains. The patient had short- and long-term memory loss and impairment of orientation, attention, and concentration. She had decreased ability to learn new information, impaired verbal compre-hension and arithmetic skills, and decreased left sensory perception. She had bilateral visual field defects, difficulty with left hand-eye coordination, spasm of fixation, and optic ataxia. One week later, she was still able to walk without assistance but progressive difficulty with her vision rendered her unable to get around her home or feed herself without assistance. On examination, she was cortically blind. Six weeks after initial evaluation, the patient was admitted to hospital because she was unable to care for herself. She was in a mute akinetic state with reactive pupils but without response to visual threat. There was left beat nystagmus in primary gaze alternating with periods of left gaze deviation that could be overcome with head turn (See Supplemental Digital Content, Video, http://links.lww.com/WNO/A73). A few days later, she developed startle and spontaneous myoclonus. EEG showed 1-Hz periodic sharp wave discharges preceding the myoclonus, characteristic of CJD. MRI revealed right temporo-parietal gyriform hyperintensity on T2 and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery image (FLAIR) sequences, CSF demonstrated elevated protein of 75 mg/dL (normal: 35-45 mg/dL) but no other abnormalities. The 14: 3:3 protein was not tested. She was discharged home with hospice care and died about 12 weeks after the onset of her first visual symptoms. An autopsy was not performed. Parker et al: J Neuro-Ophthalmol 2014; 34: 4-9 5 Original Contribution Copyright © North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. Case 3 A 77-year-old Caucasian woman, retired surgical nurse, with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, atrial fibrillation, ulcerative colitis, and osteoporosis reported a 2-week history of multicolored visual hallucina-tions and intermittent distortion of images. Visual acuity was 20/60, right eye, and 20/100, left eye. Pupils reacted normally to light and accommodation. She could not read the Ishihara color plates but was able to name individual colors. A right homonymous hemianopia was detected by confrontation technique but the patient could not perform formal visual field testing. Ophthalmoscopic and biomicro-scopic examinations were normal. There was diffuse slowing of background activity on EEG and a visual evoked potential testing showed prolonged P100 latencies. There was an area of increased gyriform signal in the left striate cortex on brain MRI without abnormalities in the basal ganglia or cerebellum (Fig. 3). Single-photon emis-sion computed tomography (SPECT) scan showed decreased perfusion in the left posterior parietal-occipital region. Within 2 weeks of presentation, the patient developed visual agnosia, prosopagnosia, impaired short-term memory, speech problems, confusion, and mild right-sided clumsi-ness. On admission, the Folstein Mini Mental Status Examination score was 4/30 (normal: 30/30). She was still able to recite the Lord's Prayer with no mistakes. She had a 2-fold increase in CSF 14:3:3, and neuronal-specific enolase level was also increased (82.5 ng/mL; normal: ,35 ng/mL). A follow-up examination 7 weeks after initial presentation demonstrated startle myoclonus. She was unre-sponsive but arousable and had a right hemiparesis and right Babinski sign. She died approximately 8 weeks after the onset of her visual symptoms. Autopsy showed spongiform encephalopathy, neuro-nal loss, and gliosis, affecting primarily the occipital cortex and cerebellum (Fig. 4). These findings were con-sistent with the diagnosis of CJD. Western blot prion (PrP) gene and immunohistochemical examination of the brain confirmed the diagnosis of sporadic CJD with homozygozity for methionine in codon 129. Given her occupation history as a surgical nurse for 50 years, there was an investigation into the possibility of an iatrogenic mechanism, but no exposure link to a CJD source was identified. FIG. 1. Case 1. Electroencephalogram shows synchronous sharp wave discharges (1 Hz) that coincided with generalized myoclonic jerks. 6 Parker et al: J Neuro-Ophthalmol 2014; 34: 4-9 Original Contribution Copyright © North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. DISCUSSION In 1998, Benson et al (11) described PCD as an unusual neurodegenerative disorder involving the posterior parietal and occipital lobes. Neuropathologic findings in PCD include senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, typical for Alz-heimer disease in the majority of cases (7-9). Less frequently, subcortical gliosis as a variant of Pick disease and spongiform changes, neuronal loss and gliosis due to prion infection were reported (9). However, epidemiologic data are lacking. Clin-ical findings in PCD and HvCJD include combinations of visual field defects, cortical blindness, dyschromatopsia, visual agnosia, alexia, prosopagnosia, palinopsia, optical anosognosia, Balint and Gertsmann syndrome (12-16). Between 1998 and 2012, we evaluated 10 patients with PCD; 3 had sporadic HvCJD who were followed until their death. We are uncertain about the etiology in the remaining 7 patients who developed either a slowly progressive FIG. 2. Case 2. Automated visual fields reveal an incongruous left homonymous hemianopia. FIG. 3. Case 3. A. Diffusion-weighted imaging demonstrates gyriform areas of increased signal intensity in the left parieto-occipital cortex. B. ADC map confirms presence of restricted diffusion. Parker et al: J Neuro-Ophthalmol 2014; 34: 4-9 7 Original Contribution Copyright © North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. dementia (evolving over several years) and are still alive or were lost to follow-up. The largest published series of the HvCJD included 34 pathologically confirmed cases over a 51-month period (6). This study from the University of Göttingen in Germany is the geographic base of the "German National Creutzfeldt- Jakob Disease Surveillance Study." Clinical findings were available in 25 cases and consisted of a combination of visual loss and higher visual deficits as found in previous studies. The rate of neurological deterioration was faster in the HvCJD group compared with other CJD variants and did not correlate with location or extent of neuropathologic findings. Homozygosis for methionine in codon 129, iden-tified in 2 of our patients, was noted as a possible genetic indicator of an aggressive clinical course. We evaluated our patients by applying the diagnostic criteria used by Kropp et al (6) and endorsed by the World Health Organization (Table 1). Neuroimaging findings showed subtle increased intensity in the parieto-occipital region on T2 and FLAIR images only in case 2. Yet all 3 patients had striking visual deficits on examination. Therefore, HvCJD should be considered in any patient with visual field loss and a normal MRI or when imaging abnormalities fail to explain the clinical findings (15). Our imaging protocol included diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) sequences (12,16). Restricted diffusion involving the gyri of the parieto-occipital cortex was observed in 2 of our cases (Fig. 3). The third patient (Case 2) was evaluated before the incorporation of DWI sequences in the MRI protocol at our institution. DWI was the most helpful ancillary test supporting the diagnosis of HvCJD, and to our knowledge, other PCD variants usually are not associated with DWI changes. Initial EEG results showed nonspecific focal or general-ized slowing, but follow-up EEG showed periodic sharp waves (Fig. 2) characteristic of CJD in later stages, correlat-ing with the presence of myoclonus. SPECT scanning con-firmed occipital hypoperfusion in one of our cases and should be part of PCD evaluation. SPECT largely has been replaced by PET that demonstrates focal cerebral hypome-tabolism in PCD (13,17). An important characteristic observation suggesting HvCJD in our patients was rapid clinical deterioration. The initial HvCJD diagnosis in Case 1 was supported by progressive neurological deterioration over 10 weeks after the onset of visual symptoms. Our other 2 patients were evaluated at an earlier stage of disease and were scheduled for additional testing over several days. Both patients failed to keep their 2-week follow-up appointments, and contact with their families revealed that they experienced rapid neurological deterioration with inability to perform activities of daily living. This prompted us to perform house calls to complete neurological evaluation and discussion with the family. Markers of massive neuronal loss (14:3:3 protein and neuronal-specific enolase) were elevated in 2 of our cases. These markers are deemed highly specific and sensitive (1). Their value must be interpreted with caution in individual cases, as increased neuronal protein levels (false positives) may be found in other rapidly progressive dementias and potential PCD mimics including autoimmune and paraneo-plastic encephalitis, nonconvulsive status epilepticus, intra-vascular lymphoma, and vasculitis (2,5). Although characteristic histopathology of CJD remains the gold standard in establishing the diagnosis, the risk of instrument or surgical suite prion contamination during brain biopsy has limited the availability of brain biopsy (10). Until a specific serum or CSF prion marker is available, the premortem diagnosis of HvCJD in a patient with PCD continues to rely on close clinical monitoring, neuroimaging testing, serial EEG, and elevated CSF markers (18,19). We FIG. 4. Case 3. Brain autopsy specimen reveals spongiform degeneration with neuronal loss and reactive gliosis (hematoxylin and eosin, ·400). TABLE 1. Diagnostic criteria for Heidenhain variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease Definite Pathologic evidence of spongiform degeneration, gliosis, neuronal loss in posterior, temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes Probable Visual impairment: blurred vision, visual field defect, cortical blindness Rapidly progressive dementia (,2 years) Myoclonus Cerebellar, pyramidal, or extrapyramidal tract signs Akinetic mutism EEG with periodic sharp wave complexes MRI: increased cortical signal in parieto-occipital region (DWI) Elevation of neuronal destruction markers in CSF Possible Same criteria as "probable" without EEG findings Adapted from Kropp et al. (6) EEG, electroencephalogram; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; DWI, diffusion-weighted imaging; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid. 8 Parker et al: J Neuro-Ophthalmol 2014; 34: 4-9 Original Contribution Copyright © North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. strongly recommend that specimens be sent to the National Prion Research Center at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, OH, and similar prion research centers for confirmatory, cerebral histopathology, immunohistochemi-cal staining of abnormal protease-resistant prion protein, and genetic testing. This testing protocol establishes the diagnosis of sporadic, variant, and genetic forms of CJD and hopefully will prevent delay in establishing the correct diagnosis (20). In vitro, anti-prion agents have been found effective in controlling prion growth and progression. Unfortunately, these agents have failed to cure or slow CJD infection in humans (21-23). ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The National Prion Disease Pathology Surveillance Center at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH, performed histopathologic, genetic, and immunologic studies in 2 of our patients. REFERENCES 1. Hsich G, Kenney K, Gibbs CJ, Lee KH, Harrington MG. The 14-3-3 brain protein in cerebrospinal fluid as a marker for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:924-930. 2. Muayqil T, Gronseth G, Camicioli R. Evidence-based guideline: diagnostic accuracy of CSF 14:3:3 protein in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease: report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology Published Ahead of Print. Neurology. 2012;79:1499-1506. 3. Chapman T, McKeel DW Jr, Morris JC. Misleading results with the 14-3-3 assay for the diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology. 2000;55:1396-1397. 4. Aksamit AJ, Cerebrospinal fluid 14-3-3 protein: variability of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, laboratory standards, and quantitation. Arch Neurol. 2003;60:803-804. 5. Saiz A, Graus F, Dalmau J, Pifarre A, Marin C, Tolosa E. Detection of 14-3-3 brain protein in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with paraneoplastic neurological disorders. Ann Neurol. 1999;46:774-777. 6. Kropp S, Shulz-Schaeffer WJ, Finkenstaedt M, Riedeman C, Windl O, Steinhoff B, Zerr I, Kretzchamar H, Poser S. The Heidenhain variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Neurol. 1999;56:55-61. 7. Berthier ML, Leiguarda R, Starkstein SE, Sevlever G, Taratuto AL. Alzheimer's disease in a patient with posterior cortical atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991;54:1110-1111. 8. Levine DN, Lee JM, Fisher CM. The visual variant of Alzheimer's disease: a clinicopathologic case study. Neurology. 1993;43:305-313. 9. Victoroff J, Ross W, Benson F, Verity A, Vinters H. Posterior cortical atrophy. Neuropathologic correlations. Arch Neurol. 1994;51:269-274. 10. Brown P, Wolff A, Gajdusek DC. A simple and effective method for inactivating virus infectivity in formalin-fixed tissue samples from patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology. 1990;40:887-890. 11. Benson DF, Davis RJ, Snyder BD. Posterior cortical atrophy. Arch Neurol. 1988;45:789-793. 12. Vargas ME, Kupersmith MJ, Savino PJ, Petito F, Frohman PF, Warren FA. Homonymous field defect as the first manifestation of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995;119:497-504. 13. Prasad S, Lee EB, Woo JH, Alavi A, Galetta SL. MRI and positron emission tomography findings in Heidenhain variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neuroophthalmol. 2010;30: 260-262. 14. Purvin V, Bonnin J, Goodman J. Palinopsia as a presenting manifestation of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1989;9:242-246;discussion 247-248. 15. Brazis PW, Lee AG, Graff-Randorf N, Desai MP, Eggenberger ER. Homonymous visual field defects in patients without corresponding structural lesions on neuroimaging. J Neuroophthalmol. 2000;20:92-96. 16. Cornelius JR, Boes CJ, Ghearing G, Leavitt JA, Kumar N. Visual symptoms in the Heidenhain variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease. J Neuroimaging. 2009;19:283-287. 17. Clarencon F, Gutman F, Giannesini C, Penicaud A, Galanaud D, Kerrou K, Marro B, Talbot JN. MRI and FDG PET/CT findings in a case of probable Heidenhain variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neuroradiol. 2008;35:240-243. 18. Atarashi R, Sano K, Satoh K, Nishida N. Real-time quaking-induced conversion: a highly sensitive assay for prion detection. Prion. 2011;5:150-153. 19. McGuire LI, Poden AH, Orru CD, Wilhan JM, Appelford NE, Mallison G, Andrews M, Head MW, Caughey B, Will RG, Knight RS, Green AJ. Real time-quaking induced conversion analysis of cerebrospinal fluid in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease. Ann Neurol. 2012;72:278-285. 20. Peterson RW, Torres-Chae CC, Kuo AL, Ando T, Nguyen EA, Wong K, Dearmond SJ, Hamna A, Garcia P, Johnson DY, Miller BL, Geschwind MD. Differential diagnosis of Jacob- Creutzfeldt disease. Arch Neurol. 2012;69:1578-1582. 21. Otto M, Cepek l, Ratka P, Doehlinger S, Boekhoff L, Wiltfang J, Irle E, Pengand G, Eller-Lenz B, Wndl O, Kretscner HA, Poser S, Prange H. Efficacy of flupirtine on cognitive function in patients with CJD: a double-blind study. Neurology. 2004;62:714-718. 22. Geschwind MD. Clinical trials for prion disease: difficult challenges, but hope for the future. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8: 304-306. 23. Collinge J, Gorham M, Hudson F, Kennedy A, Keogh G, Pal S, Rosser M, Rudge P, Siddique O, Spyer M, bThomas D, Walker S, Webb T, Wroe S, Darbyshire J. Safety and efficacy of quinacrine in human prion disease (PRION-1 study): a patient-preference trial. Lancet Neurol. 2009;8:334-344. Parker et al: J Neuro-Ophthalmol 2014; 34: 4-9 9 Original Contribution Copyright © North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. |