Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
Filters: Collection:ehsl_novel_wfh
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 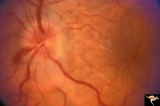 | A101 Disc Swelling due to Intraocular Hypotension | Ocular hypotension following lens replacement surgery. Retinal/macular folds. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Disc edema. Disease/ Diagnosis: Intraocular hypotension. Clinical: Low intraocular pressure or intraocular hypotension. | Image |
| 2 | 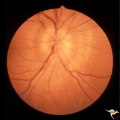 | A201 Disc Swelling with Big Blind Spot Syndrome | Blind spot larger than could be explained by visible edema. Subretinal white dots probably indicate margin of blind spot. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Unknown. Disease/ Diagnosis: Big blind spot syndrome. Clinical: symptoms: photosias, blurred vision signs: Disc swelling; white spots in t... | Image |
| 3 | 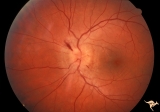 | A202 Disc Swelling with Big Blind Spot Syndrome | Blind spot larger than could be explained by visible disc edema. Reference: Fletcher WA, Imes RK, Goodman D, Hoyt WF. Acute idiopathic blind spot enlargement. A big blind spot disc edema. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988 Jan;106(1):44-9. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Unknown. Disease/ Diagnosis: Big ... | Image |
| 4 |  | A203 Disc Swelling with Big Blind Spot Syndrome | Slight inferior swelling in patient with grossly enlarged blind spot. 66 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Unknown. Disease/ Diagnosis: Big blind spot syndrome. Clinical: symptoms: photopsias; blurred vision signs: disc swelling; white dots in the retina; enlarged blind spot on... | Image |
| 5 | 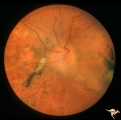 | A301a Disc Swelling, Chorioretinal Disease | a and b same eye. Bad chorioretinal scars with disc swelling. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unknown. | Image |
| 6 | 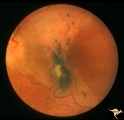 | A302b Disc Swelling, Chorioretinal Disease | Bad chorioretinal scars with disc swelling. Temporal extent of chorioretinal scarring. A and B are the same eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unknown. | Image |
| 7 |  | A303 Disc Swelling, Chorioretinal Disease | Neovascular net. Disc swelling with peripapillary neo-vascularization with subretinal hemorrhage. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. | Image |
| 8 | 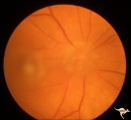 | A401Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Vitreopapillary haze. Cone of vitreous that has obscured the disc. Uveitis patient. Anatomy: Optic disc; Vitreous. Pathology: Vitreal contact with the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Vitreal traction on the disc? Clinical: Visual blurring in uveitis?¼igns: disc swelling; disc obscuration. | Image |
| 9 | 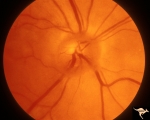 | A402a Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Posterior vitreous detachment with vitreo papillary adherence to the optic disc. See fluorescein angiogram A43b. Anatomy: Optic disc; Vitreous. Pathology: Posterior vitreous detachment with vitreo papillary adherence to the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Disc swelling due to vitreo papilary adheren... | Image |
| 10 | 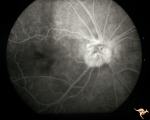 | A403b Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Fluorescein angiogram shows fluorescein leaking around entire disc where attachment of vitreous exists. Refers to A402a. Anatomy: Optic disc; Vitreous. Pathology: Disc swelling due to posterior vitreal detachment. Disease/ Diagnosis: Disc swelling due to posterior vitreal detachment. Clinical: float... | Image |
| 11 | 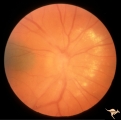 | A404 Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Disc elevation (swelling) and vitritis. Posterior vitreous detachment with vitritis. Incidental choroidal nevus. Anatomy: Optic disc; Vitreous; Retina. Pathology: Posterior vitreal detachment, disc swelling, and vitritis-horoidal nevus. Disease/ Diagnosis: Vitreal detachment from optic disc; choroid... | Image |
| 12 | 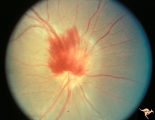 | A405 Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Prepapillary hemorrhage. Partial posterior vitreous detachment in myopic Asian patient. Reference: Katz B, Hoyt WF. Intrapapillary and peripapillary hemorrhage in young patients with incomplete posterior vitreous detachment. Signs of vitreopapillary traction. Ophthalmology. 1995 Feb;102(2):349-54. ... | Image |
| 13 | 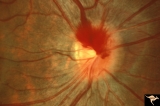 | A406 Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Prepapillary hemorrhage. Partial posterior vitreous detachment in myopic Asian patient. Reference: Katz B, Hoyt WF. Intrapapillary and peripapillary hemorrhage in young patients with incomplete posterior vitreous detachment. Signs of vitreopapillary traction. Ophthalmology. 1995 Feb;102(2):349-54. A... | Image |
| 14 | 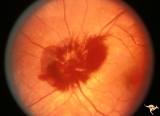 | A407 Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Prepapillary hemorrhage. Partial posterior vitreous detachment in myopic patient. Reference: Katz B, Hoyt WF. Intrapapillary and peripapillary hemorrhage in young patients with incomplete posterior vitreous detachment. Signs of vitreopapillary traction. Ophthalmology. 1995 Feb;102(2):349-54. Anatomy... | Image |
| 15 | 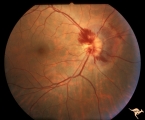 | A408 Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Prepapillary hemorrhage. Partial posterior vitreous detachment in myopic Asian patient. Reference: Katz B, Hoyt WF. Intrapapillary and peripapillary hemorrhage in young patients with incomplete posterior vitreous detachment. Signs of vitreopapillary traction. Ophthalmology. 1995 Feb;102(2):349-54. A... | Image |
| 16 | 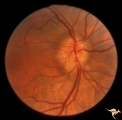 | A501 Disc Swelling, Pre-Ischemic Swelling | Pre AION swelling. Asymptomatic on October 8, 1985. Same patient as A5_2b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Pre AION, Pre ischemic swelling. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 17 | 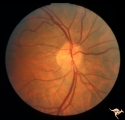 | A502 Disc Swelling, Pre-Ischemic Swelling | Pre AION swelling. Cleared after 8 days. October 16, 1985. Disc swelling resolved. arterioles at 6:00 and 12:30 have focal narrowing. Patient did not lose vision. Same patient as A5_1a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal. Disease/ Diagnosis: Resolved pre-AION swelling; Resolved pre ischemic swel... | Image |
| 18 | 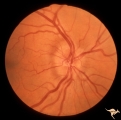 | A503 Disc Swelling, Pre-Ischemic Swelling | Pre-ischemic swelling. March 22, 1983. Same patient as A5_4d. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Pre-AION; Pre-ischemic swelling. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 19 | 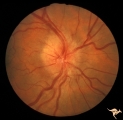 | A504 Disc Swelling, Pre-Ischemic Swelling | AION with altitudinal visual loss. July 7, 1983. Same patient as A5_3c. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Altitudinal visual field loss due to AION. | Image |
| 20 |  | B101 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Pallid swelling in course of acute AION. 48 year old man who developed disc swelling after a flu like illness, then developed AION. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss after flu-like illness. | Image |
| 21 |  | B102 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Ischemic swelling. March 2, 1978. Same patient as B1_03. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Diabetic with optic disc swelling and visual loss. | Image |
| 22 | 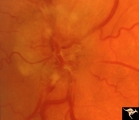 | B103 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Ischemic swelling. 50 year old woman, 12 days after a viral illness. Nasal nerve fiber layer bundle visual field defect. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss after viral illness. | Image |
| 23 | 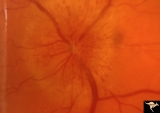 | B104 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Ischemic swelling. 57 year old man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 24 | 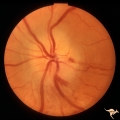 | B105 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Pallid ischemic swelling. 48 year old woman, flight attendant. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 25 | 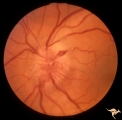 | B106 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Red ischemic swelling. 49 year old man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
