| Title |
N2O Formation in Selective Non-Catalytic NOx Reduction Process |
| Creator |
Muzio, L. J.; Martz, T. D.; Montgomery, T. A.; Quarturcy, Q. C.; Cole, J. A.; Kramlich, J. C. |
| Publisher |
University of Utah |
| Date |
1990 |
| Spatial Coverage |
presented at San Francisco, California |
| Abstract |
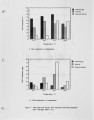
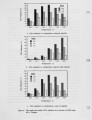
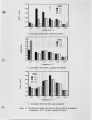
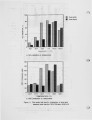
NOx control techniques currently under development Include combustion modification and post-combustion techniques. As these technologies are developed and implemented, it is important to ensure that NOx reductions are not achieved at the expense of producing other undesirable species. One possible concern Is the production of N2O from the NOx reduction process. The current work addressed the potential N2O production from selective non-catalytic NOx reduction (SNCR processes using ammonia, urea, and cyanuric acid injection). Previous work with SNCR processes has shown that ammonia injection produces minimal N2O emissions, while cyanuric acid Injection has, under certain conditions, almost quantitatively converted NOx to N2O. It has been suggested that urea might behave as a hybrid between ammonia and cyanuric acid. In the work described here, pilot scale testing and chemical kinetic modeling were used to characterize the N2O production from these processes over a range of process parameters. The data show that SNCR processes were all found to produce some N2O as a by-product. Ammonia Injection produced the lowest levels of N2O with N2O levels less than 4% of the NOx reduced. Cyanuric acid produced the highest levels ranging from 12-40% of the NOx reduced. The conversion of NOx to N2O with the urea injection ranged from 7-25%. |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights |
This material may be protected by copyright. Permission required for use in any form. For further information please contact the American Flame Research Committee. |
| Conversion Specifications |
Original scanned with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. |
| Scanning Technician |
Cliodhna Davis |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s68s4sfs |
| Setname |
uu_afrc |
| ID |
6066 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s68s4sfs |