| Title |
Low-Temperature Combustion Kinetics of Western Kentucky No 9 Coal |
| Creator |
Daw, C. S.; Krishnan, R. P. |
| Publisher |
University of Utah |
| Date |
1983 |
| Spatial Coverage |
Akron, Ohio |
| Abstract |
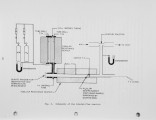
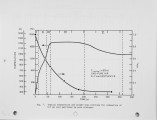
The combustion kinetics of Western Kentucky No. 9 coal were measured in a tubular-flow reactor. The primary objective was to develop a kinetic expression suitable for calculating the combustion rate of devolatilized char in an atmospheric fluidized bed combustor. Coal particles ranging from about 0.64 to 0.033 cm (0.25 to 0.013 in.) diameter were devolatilized and burned in air/nitrogen mixtures at reactor temperatures between 866 and 1090K (1100 and 1500°F) and at oxygen partial pressures between 0 and 0.21 atmospheres. Experiments with subliming naphthalene provided data for correlating the mass transfer between particles suspended in the reactor and the bulk gas stream. This correlation was then combined with the combustion data to separate the two primary rate components: external oxygen diffusion and intra-particle diffusion/reaction. The experimental results demonstrate that combustion of particles of about 0.64 cm (0.25 in.) diameter is almost completely dominated by external diffusion. As particle size is reduced, intra-particle processes rapidly become more important. At sizes less than 0.1 cm (0.04 in.), intra-particle diffusion/reaction is clearly the rate determining step. The intrinsic diffusion/reaction rate (based on external surface area) was found to have an apparent order of 0.6 in oxygen and an effective activation energy of 11.5 kcal/g-mole. It is hypothesized that the unusually low activation energy results from the effect of heating rate on internal surface area and/or catalysis due to inorganic impurities In the char. There is also evidence that the intra-particle resistance to diffusion is very low, requiring a diameter dependent term in the intrinsic reaction rate expression. |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights |
This material may be protected by copyright. Permission required for use in any form. For further information please contact the American Flame Research Committee. |
| Conversion Specifications |
Original scanned with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. |
| Scanning Technician |
Cliodhna Davis |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s6765hv2 |
| Setname |
uu_afrc |
| ID |
576 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6765hv2 |