| Title |
Acute Ophthalmoplegia and Nystagmus in Infants Fed a Thiamine-Deficient Formula |
| Creator |
Kesler, A; Stolovitch, C; Hoffmann, C; Avni, I; Morad, Y |
| Affiliation |
Neuro-ophthalmology Unit (AK) and the Department of Ophthalmology (AK,CS), Tel Aviv Medical Center, and the Sackler School of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel. kesler@netvision.net.il |
| Abstract |
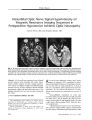
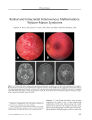
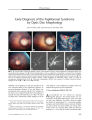
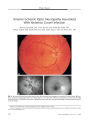
In 2003, an epidemic of Wernicke encephalopathy (WE) developed in Israeli infants fed a thiamine-deficient soy-based formula. Approximately 20 infants were affected out of an estimated 3500 fed the vitamin-deficient formula. The finding of gaze abnormalities in a single infant by neuro-ophthalmologists led to the unraveling of the epidemic. In this report, the findings in three infants are described. Early diagnosis and treatment with parenteral thiamine led to complete neurologic recovery in two infants; in the third infant, delayed diagnosis may have been responsible for severe lingering deficits. This is the first reported epidemic of WE secondary to thiamine-deficient infant formula. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to avoid persistent neurologic impairment. |
| Subject |
Acute Disease; Female; Humans; Infant; Infant Formula, administration & dosage; Israel, epidemiology; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Male; Nystagmus, Pathologic, diagnosis; Nystagmus, Pathologic, etiology; Ophthalmoplegia, diagnosis; Ophthalmoplegia, etiology; Periaqueductal Gray, pathology; Soy Foods, adverse effects; Thiamine, administration & dosage; Thiamine Deficiency, complications; Wernicke Encephalopathy, diagnosis; Wernicke Encephalopathy, epidemiology; Wernicke Encephalopathy, etiology |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Publication Type |
Journal Article |
| Collection |
Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library: Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology Archives: https://novel.utah.edu/jno/ |
| Publisher |
Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins |
| Holding Institution |
Spencer S. Eccles Health Sciences Library, University of Utah |
| Rights Management |
© North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society |
| Setname |
ehsl_novel_jno |
| ID |
225429 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s69058t8/225429 |