| Title |
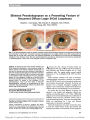
Positive apraclonidine test 36 hours after acute onset of horner syndrome in dorsolateral pontomedullary stroke. |
| Creator |
Lebas, Maud; Seror, Julien; Debroucker, Thomas |
| Affiliation |
Department of Ophthalmology, Hpital Delafontaine, Saint-Denis, France. |
| Abstract |
A 40-year-old man developed a Horner syndrome as part of a dorsolateral medullary brainstem infarction. Thirty-six hours after the onset of the stroke, topical instillation of 0.5% apraclonidine produced reversal of anisocoria. This is the first case in which apraclonidine testing has been applied to a patient with a Horner syndrome caused by a lesion in the first segment of the oculosympathetic pathway and the shortest reported interval between clinical manifestations of the lesion and apraclonidine-induced reversal of anisocoria. A review of all reported cases of apraclonidine testing in Horner syndrome suggests that this is a promising diagnostic adjunct that must be validated in larger studies. |
| Subject |
Adrenergic alpha-Agonists; Adult; Clonidine; Horner Syndrome; Humans; Magnetic Resonance Angiography; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Male; Pons; Stroke |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Publication Type |
Journal Article |
| Collection |
Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library: Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology Archives: https://novel.utah.edu/jno/ |
| Publisher |
Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins |
| Holding Institution |
Spencer S. Eccles Health Sciences Library, University of Utah |
| Rights Management |
© North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society |
| Setname |
ehsl_novel_jno |
| ID |
227017 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6m07bj2/227017 |