| Title |
Peripapillary nerve fiber layer thickening, telangiectasia, and retinal hemorrhages in wernicke encephalopathy. |
| Creator |
Bohnsack, Brenda L; Patel, Shreya S |
| Affiliation |
Kellogg Eye Center and Department of Ophthalmology and Vision Sciences, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48105, USA. |
| Abstract |
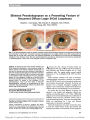
A young woman who underwent gastric bypass surgery for morbid obesity had intractable nausea and vomiting for several weeks postoperatively, leading to poor intake and excessive weight loss. In the ninth postoperative week, she became confused and off balance and reported blurred and double vision. Examination disclosed slow saccades, nystagmus, and impaired abduction of both eyes as well as memory loss and ataxia. Visual acuity was slightly subnormal, and ophthalmoscopy disclosed a thickened and telangiectatic peripapillary nerve fiber layer with retinal hemorrhages. MRI showed high T2 and FLAIR signal in the dorsomedial thalamus and mamillary bodies bilaterally, substantiating a clinical diagnosis of Wernicke encephalopathy (WE). After thiamine treatment, visual acuity returned to normal and eye movements and alignment almost completely normalized. Fundus abnormalities eventually regressed. Although the ocular motor findings of WE have been well documented, the ophthalmoscopic findings have not. Resembling the findings in Leber hereditary and toxic optic neuropathies, they may represent manifestations of impaired mitochondrial function in retinal ganglion cells and capillaries. Recognition that these ophthalmoscopic findings may occur in WE is important to avoid procedures such as lumbar puncture that may delay urgent treatment with thiamine. |
| Subject |
Female; Humans; Magnetic Resonance Imaging; Nerve Fibers; Peripheral Nerves; Retinal Hemorrhage; Telangiectasis; Tomography, Optical Coherence; Wernicke Encephalopathy; Young Adult |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Publication Type |
Journal Article |
| Collection |
Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library: Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology Archives: https://novel.utah.edu/jno/ |
| Publisher |
Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins |
| Holding Institution |
Spencer S. Eccles Health Sciences Library, University of Utah |
| Rights Management |
© North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society |
| Setname |
ehsl_novel_jno |
| ID |
227026 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6m07bj2/227026 |