| Title |
The Prediction of No Emissions from an Industrial Burner |
| Creator |
Missaghi, M.; Pourkashanian, M.; Williams, A.; Yap, L. |
| Publisher |
University of Utah |
| Date |
1990 |
| Spatial Coverage |
presented at San Francisco, California |
| Abstract |
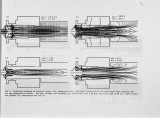
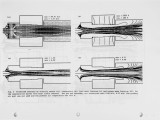
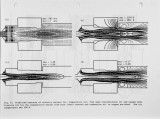
A recently developed 3-D post-processing package was linked to the output from commercial combustion computer code to predict the NOx emission in a regenerative burner used in the steel industry. To evaluate the effect of turbulence/chemistry interaction on the rate of formation of thermal and prompt-NO two essential physical phenomena, not properly described in previous models, were included in the post-processing code. First, the influence of turbulent fluctuations in temperature on NO formation rate is evaluated using a two-variable formalism for the treatment of chemical reactions leading to NO emissions and, second, the effects of radical superequilibrirum formed in turbulent flames on thermal NO formation is quantified. In addition, the influence of oxygen enrichment in the primary or secondary air on combustion performance especially on the level of NO emission was examined. The validity of the post-processing code was compared with measured values of NOx obtained at industrial laboratories. The predictions showed that NO emissions are in good qualitative agreement with experimentally observed values when the effects of superequilibrium radical formation and turbulence/chemistry interaction are considered. Virtually all the prompt-NO in the flame occurred in the mixing area of primary air and fuel, and the rate of formation of thermal NO reaches its maximum value far downstream of the burner just after secondary air injection. By adding oxygen (in the range of 2-8%) to the primary air, the temperature distribution was more uniform with maximum temperatures not exceeding the preheated air/fuel case. Here the NO emissions did not change significantly. In conclusion our findings indicate that the postprocessing package described here could provide detailed and accurate information on the NO emission in all types of industrial burners. |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights |
This material may be protected by copyright. Permission required for use in any form. For further information please contact the American Flame Research Committee. |
| Conversion Specifications |
Original scanned with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. |
| Scanning Technician |
Cliodhna Davis |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s65141sn |
| Setname |
uu_afrc |
| ID |
6091 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s65141sn |