Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |
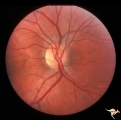 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Has no optic cup. Patient has pseudotumor cerebri. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache, transient visual obscurations. | Image |
| 202 |
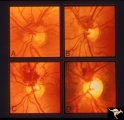 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Convolutions | Collection of prepapillary arterial congenital convolutions. Note: Typically involve the superior retinal arterioles. Purely arterial malformations (not arterial venous). Within the convolution in C, there are multiple tortuous loops. Not associated with cerebral vascular malformations and they do n... | Image |
| 203 |
 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Note ghost vessels, signs of involution within the malformation. Natural history is spontaneous involution of arterial loops within the malformation. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinal arteriovenous malf... | Image |
| 204 |
 |
Venous Anomalies - Exit Anomalies | Disc of inferior conus. Anomalous venous exits. Disc edge veins of Kraupa. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital anomaly, exit anomaly. Disease/Diagnosis: Exit anomaly, edge veins. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 205 |
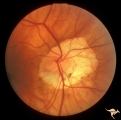 |
Venous Anomalies - Exit Anomalies | Choriovaginal vein. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital anomaly of choroidal venous drainage. Disease/Diagnosis: Choriovaginal vein. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 206 |
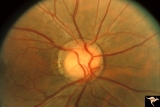 |
Venous Anomalies - Exit Anomalies | All venous systems drain through single vein. ""Where do they go?"" Disc edge veins of Kraupa. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital anomaly, exit anomaly. Disease/Diagnosis: Exit anomaly, edge veins. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 207 |
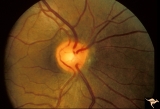 |
Venous Anomalies - Exit Anomalies | Inferior edge veins of Kraupa. Arterial branches appear to be cilioretinal. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital anomaly, exit anomaly. Disease/Diagnosis: Exit anomaly, edge veins. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 208 |
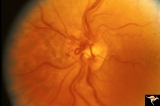 |
Venous Anomalies - Prepapillary Venous Convolutions (Acquired) | Prepapillary venous convolutions - acquired. Acquired after central retinal vein occlusion. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Prepapillary venous convolutions - acquired. Disease/Diagnosis: Prepapillary venous convolutions - acquired. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 209 |
 |
C31 Empty Disc | Right eye. Papillorenal Syndrome (PRS). Same patient as C_32. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 210 |
 |
C32 Empty Disc | Left eye. Papillorenal Syndrome (PRS). Same patient as C_31. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 211 |
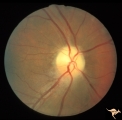 |
IB109 Post Ischemic (AION) Cupless Atrophy | Right eye, 1983 Top half of disc is pale. Striking focal arteriole narrowing. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 212 |
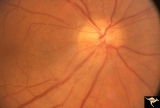 |
IB114a Post Ischemic (AION) Cupless Atrophy | 1991, acute AION in a disc with a cup, pair with IB1_14b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 213 |
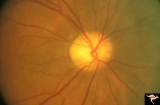 |
IB114b Post Ischemic (AION) Atrophy in a Disc with a Cup | 1996, same as IB1_14a five years later reveals pallor, arteriole narrowing and optic cup. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 214 |
 |
Retinocerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (Wyburn Mason Syndrome) | Retinocerebral arteriovenous malformation showing multiple arteriovenous shunts, both small and large. (Cross reference with V12-28 this section). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn Mason Syndrome. Clinical: Arteriovenous loop in the inferior temporal r... | Image |
| 215 |
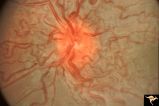 |
Retinocerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (Wyburn Mason Syndrome) | Florid arteriovenous malformation of the optic disc and surrounding retina, Caput medusa (Cross reference with V12-28 this section). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn Mason Syndrome. | Image |
| 216 |
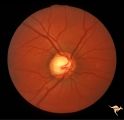 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis); Color of the retina is deep red (sometimes called tomato catsup) due to a four fold thickening of the choroidal vascular bed. Optic disc is cupped due to elevated intraocular pressure. (Secondary glaucoma) Patient had a major ""port wine"" m... | Image |
| 217 |
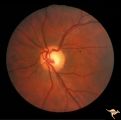 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Left eye is normal, without the deep red from thickened Choroid. Pair with R1_B1a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Diffuse choroidal hemangioma; Glaucoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Sturge Weber Syndrome. Clinical: Port wine hemangioma of the face. | Image |
| 218 |
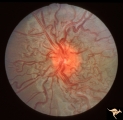 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. No corresponding malformation of brain. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 219 |
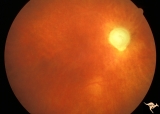 |
IC103c Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with Choroidal Arteriole Occlusion | 1988, Central retinal artery occlusion and choroidal vascular occlusion, 70 year old woman with history of central retinal artery occlusion 30 years prior. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Combined central retinal and choroidal arteriolar occlusion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Combined central retinal and ch... | Image |
| 220 |
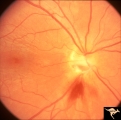 |
G103 Evulsion | Partial evulsion of the right optic nerve. Notice what is left of superior optic nerve. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic disc has been evulsed. Disease/ Diagnosis: Evulsion of the optic disc. | Image |
| 221 |
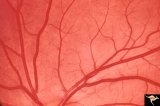 |
Ocular Hypertension | Chronic simple glaucoma. 1976. Magnified of IIB3_3a. Note slits in upper arcuate nerve fiber layer. Pair with IIB3_3a. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like defects in the arcuate nerve fiber bundles. Disease/Diagnosis: Elevated intraocular pressure. Clinical: Elevated intra... | Image |
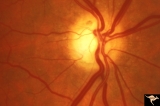
| 222 |
 |
Ocular Hypertension | Chronic simple glaucoma. 1976. Note slits in upper arcuate nerve fiber layer. Pair with IIB3_3b. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like defects in the arcuate nerve fiber bundles. Disease/Diagnosis: Elevated intraocular pressure. Clinical: Elevated intraocular pressure. | Image |
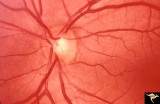
| 223 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy with ""Twin Peaks"" papilledema. Central band of the optic disc is completely atrophic and does not swell. ""Axons that are not there can not swell."" Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic tract injury. Disease/Diagnosis: Twin peaks papilledema. Clinical: Left homony... | Image |
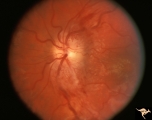
| 224 |
 |
Diffuse Atrophy | Bilateral primary or retrograde optic atrophy from bilateral optic nerve sheath meningiomas. Pair with IIA1_2a. Left eye. 1984. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Bilateral optic nerve sheath meningiomas. Disease/Diagnosis: Retrograde optic atrophy. Clinical: Bilateral visual loss. | Image |
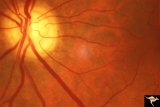
| 225 |
 |
IIA102a Diffuse Atrophy | Bilateral primary or retrograde optic atrophy from bilateral optic nerve sheath meningiomas. Pair with IIA1_2b. Right eye. 1984. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Bilateral optic nerve sheath meningiomas. Disease/ Diagnosis: Retrograde optic atrophy. Clinical: Bilateral visual loss. | Image |
