Collection of materials relating to neuro-ophthalmology as part of the Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
- NOVEL226
| Title | Creator | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |
 |
Patient Portal: Giant Cell Arteritis | Anne S. Abel, MD | Giant cell arteritis is an inflammatory condition that can cause vision loss, double vision, fever, new persistent headaches, scalp tenderness, and jaw pain with chewing. GCA is caused by inflammation of blood vessels, primarily in the head and neck. Sometimes called "temporal arteritis," GCA frequ... | Giant cell arteritis |
| 202 |
 |
Patient Portal: Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) | Devin D. Mackay, MD | Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also called pseudotumor cerebri, is a condition in which there is high pressure in the fluid surrounding your brain, spinal cord and optic nerves. This can cause headaches and problems with vision. Although the cause(s) of the condition is not fully unders... | Idiopathic intracranial hypertension; Pseudotumor cerebri |
| 203 |
 |
Patient Portal: Homonymous Hemianopsia | James C. O'Brien, MD | Homonymous hemianopia refers to an absence of vision towards one side of the visual world in each eye. The damage that caused this problem is in the brain and not in the eyes. | Homonymous hemianopia; Visual pathway |
| 204 |
 |
Patient Portal: Optic Neuritis | Anthony Brune, DO | Optic neuritis is inflammation of the optic nerve. In optic neuritis, the covering around the fibers of the optic nerve (myelin) is damaged by inflammation (demyelination), which typically results in blurred or dark vision. | Optic neuritis; Myelin; Demyelination |
| 205 |
 |
Patient Portal: Transient Vision Loss | Anthony Brune, DO | Transient visual loss is the term used to describe loss of part or all of the vision in one or both eyes temporarily. Some people do not experience a complete loss of the affected vision and instead describe the abnormality as "blurring" or like "looking through a veil." The vision typically returns... | Transient visual loss |
| 206 |
 |
Patient Portal: Anisocoria | Nagham Al-Zubidi, MD | Anisocoria is a medical term for unequal pupil size. Normally our pupils are relatively the same size. While small differences in pupil size are normal and can even come and go (physiologic anisocoria), constant and significant differences in pupil sizes may be a sign of damage to the brain or the n... | Anisocoria; Horner Syndrome; 3rd Cranial Nerve Palsy; Adie Tonic Pupil |
| 207 |
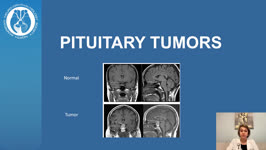 |
Patient Portal: Pituitary Adenoma | Nagham Al-Zubidi, MD | The pituitary gland is a pea-sized gland that sits underneath the base of the brain. It produces and releases many hormones. These hormones control your metabolism, stress level, growth, ovulation and menstruation in women, sperm and testosterone production in men, milk production, and urine product... | Pituitary Adenoma; Pituitary Tumor |
| 208 |
 |
One and a Half Syndrome Following Resection of a Posterior Fossa Epidermoid Cyst | Christine Xu; Claire Basco, MS, NP-C; Kiarash Shahlaie; Yin Allison Liu | This is a case of One and a Half Syndrome following resection of a posterior fossa epidermoid cyst. A 31-year-old male initially presented with left facial droop and bilateral ptosis, and a "down and out" gaze of the left eye. He underwent imaging and was diagnosed with an epidermoid cyst located in... | Abducens Nucleus; Epidermoid Cyst; Extraocular Movements; Gaze Palsy; Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia; Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus; Neurosurgery; One and a Half Syndrome |
| 209 |
 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Complications of Chemotherapy | Nagham Al-Zubidi; May Ameri | This lecture covers the effect of antineoplastic chemotherapy, which can cause damage to the optic nerve and the ocular motor nerves. | Antineoplastic Chemotherapy; Ocular Motor Nerve Damage; Optic Atrophy; Optic Nerve Damage; Optic Nerve Edema; Optic Neuritis |
| 210 |
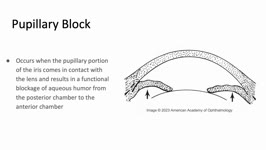 |
Pupillary Block | Sujata Dalal; James Brian Davis; Amanda Dean Henderson | Pupillary block occurs when the pupillary margin of the iris contacts the anterior surface of the lens. This creates a barrier for the outflow of aqueous humor from the posterior chamber to the anterior chamber and resultant increased pressure in the posterior chamber. This pressure can cause the ir... | Angle-Closure Glaucoma; Iris Bombe; Narrow Angle; Pupillary Block |
| 211 |
 |
Behind the Mask | Pame Dávila; Nagham Al-Zubidi | Case report describing temporal artery amyloidosis masquerading as giant cell arteritis. | Giant cell arteritis; Temporal arteritis; Temporal artery amyloidosis |
| 212 |
 |
Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome (RCVS) | Felix Yang; Sean Gratton | This is a narrated powerpoint that reviews Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction syndrome. It discusses the diagnostic basics and evaluation and management. It compares RCVS to Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES). | Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System; Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome; Subarachnoid Hemorrhage; Thunderclap Headache |
| 213 |
 |
Glaucoma: Evaluation and Principles of Management | Anand Haran; Sean Gratton | This is a narrated powerpoint that reviews the basics of glaucoma. It covers Primary Open Angle Glaucoma and Angle Closure Glaucoma, and includes reviews of the pathophysiology, evaluation, and management | Angle Closure Glaucoma; Glaucoma; Primary Open Angle Glaucoma |
| 214 |
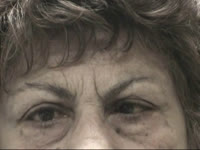 |
Sixth nerve palsy or not? (Video) | Vivian Paraskevi Douglas; Konstantinos Douglas; Nurhan Torun | Here in we present a case of a 72-yearold Caucasian female with remote history of breast cancer who presented with diplopia in the right gaze over the past several months. There had been no improvement after a 5-day course of steroids by an outside ophthalmologist. On neuro-ophthalmic examination, t... | Abduction deficit; Diplopia; Orbital imaging |
| 215 |
 |
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Stroke: Cerebral Hypoxia | Danny Alevy; James Brian Davis; Amanda Dean Henderson | Neurons are particularly vulnerable to oxygen deprivation. Cerebral hypoxia can be caused by arterial thrombosis, embolism, hypoperfusion, cervical artery dissection, or cryptogenic causes. About 1/3 of ischemic strokes are from cryptogenic causes. Embolic strokes are the next most common (20-30%), ... | Atherosclerosis; Cerebral Hypoxia; Cervical Artery Dissection; Cryptogenic Ischemia; Embolism; Hypoperfusion; Ischemia; Stroke; Thrombosis |
| 216 |
 |
Idocyanine Green Angiography | Tanner Nordseth; Evan Wotipka; Talhah Zubair; Anne Abel; Hossein Nazari | This narrated PowerPoint presentation gives an overview of idocyanine green angiography. Historical significance, diagnostic utility, and comparison to fluorescein angiography are discussed. | Angiography; Choroidal imaging; Idocyanine green |
| 217 |
 |
Financial Social Legal Implications of Genetic Testing | Jonathan Thomas; James Brian Davis | Genetic testing looks for mutations in DNA and can give insight into genetic diseases. Costs associated with genetic testing are the testing itself, as well as genetic counseling. Test results may lead to further considerations, which may impact finances. Genetic test results can have a social impac... | Financial; Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act of 2008; Genetic Testing; Legal; Social |
| 218 |
 |
Injury Prevention in the Visually Impaired | Jonathan Thomas; James Brian Davis; Amanda Dean Henderson | With an aging population in the US, the number of those with visual impairments is also rising. Visual impairments increase the risk of falls, injuries, and other deficiencies, but there are several potential strategies to prevent these injuries. Members of the healthcare team can help visually impa... | Fall; Injury Prevention; Low Vision Specialist; Visually Impaired |
| 219 |
 |
Headache Associated With Low or High Intracranial Pressure | Yu Hsin Chen; Amanda Dean Henderson; James Brian Davis | When intracranial pressure changes, the most common symptom is headache, which often has a positional component. We introduce various etiologies of headaches attributed to increased or low intracranial pressure, with idiopathic intracranial hypertension (or primary pseudotumor cerebri), post-dural p... | CSF Leak; Headache; Intracranial Hypertension; Intracranial Hypotension; Papilledema; Pseudotumor Cerebri |
| 220 |
 |
Worth 4-Dot Test | Angela Cao; Anne Abel | This presentation describes the Worth 4-Dot test, demonstrates how to perform the test, and interpret results. | Amblyopia; Diplopia; Worth 4-dot Test |
| 221 |
 |
NANOS Illustrated Curriculum Section D Introduction | Meagan D. Seay, DO; Victoria S. Pelak, MD | Introduction video to the resources available in Section D of the NANOS Illustrated Curriculum. | Lesions, Afferent Visual Pathway; Disorders, Afferent Visual Pathway; Pupillary Anatomy; Disorders, Pupillary Function; Lesions, Efferent Visual Pathway; Ocular Motility; Abnormal Eye Movements; Eyelids; Abnormal Facial Movements |
| 222 |
 |
NANOS Illustrated Curriculum Section G Introduction | Meagan D. Seay, DO | Introduction video to the resources available in Section G of the NANOS Illustrated Curriculum. | Obesity, Management; Low Vision, Management; Genetic Diseases, Management; Patient Counseling |
| 223 |
 |
Overview of Medical Malpractice, Torts, and Tort Reform | Sarah Jacober; Sean Gratton | This is a brief narrated powerpoint, which serves as an introduction to the basics of medical malpractice. The definition and history of medical malpractice are explored. The relationship between medical malpractice and tort law are explained, and tort reform is introduced. | Lawsuit; Malpractice; Medical Malpractice; Medicolegal; Tort Reform; Torts |
| 224 |
 |
Generative Adversarial Networks in Ophthalmology | Babajide Olubusayo Owosela; Anjolaoluwa Popoola; Sachin Kedar | In this video we will describe Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) models and its applications and limitations in Ophthalmology. GAN, a technique within machine learning, enables computers to utilize real data to generate valuable synthetic data, artificially produced information that mimics the s... | Artificial Intelligence; Generative Adversarial Networks; Machine Learning; Synthetic Data |
| 225 |
 |
Age Related Macular Degeneration | Riya H. Patel; James Brian Davis; Amanda Dean Henderson | Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a degenerative disease of the retina that causes central vision loss, and it is the leading cause of blindness in the developed world. Age is a strong nonmodifiable risk factor for AMD. Patients may have genetic susceptibility to AMD from mutations in genes ... | AMD; AREDS2; Exudative; Geographic Atrophy; Macular Degeneration; Nonexudative |
