Collection of materials relating to neuro-ophthalmology as part of the Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
- NOVEL230
| Title | Creator | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |
 |
The Visual Pathway: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD | A brief review of the anatomy of the eye and the photic stimulation of the receptors is followed by a gross exploration of the visual pathway from the optic nerve, chiasm, and tract to the thalamus stressing how the left part of the visual world reaches the right hemisphere. Visual fields are relate... | Visual Pathway; Brain; Dissections |
| 202 |
 |
The Normal Unfixed Brain: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD | The consistency and vulnerability of the brain is demonstrated along with the clear and glistening pia and arachnoid and the tough dura. The cushioning function of the CSF is stressed and the features are pointed out on the ventral surface. The uncus and temporal lobes are normal with arteries free ... | Brain; Dissections |
| 203 |
 |
Cortical Localization: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD | The lobes of the brain are defined together with their major functions. The visual field representation in the occipital lobe is explained with a diagram. Speech areas and the major types of aphasia are discussed in the dominant hemisphere and parietal lesions of neglect and spatial orientation are ... | Cortical Localization; Brain; Dissections |
| 204 |
 |
Introduction: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD | The regions and lobes of the brain are identified along with some of the nerves and vessels. The basic functions of the cortex of each lobe are introduced along with principal sulci and gyri. The importance of the left hemisphere for language and the temporal lobe in memory are mentioned along with ... | Brain; Dissections |
| 205 |
 |
Brain Stem & Reflexes: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD | The cranial nerves are reviewed again on a specimen with vessels. Next, landmarks on gross brain stem sections are shown. Stressed are the three reflexes associated with each of the three levels: pupillary, corneal and gag reflexes and their associated cranial nerves. Finally cross sections of myeli... | Brain Stem; Reflexes |
| 206 |
 |
Cerebral Circulation: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD | The major vessels of the anterior and posterior circulation are demonstrated along with the Circle of Willis on both a model and in an animation. The distribution of the three major cerebral arteries is demonstrated along with the concept of a watershed zone. A gross specimen with good vessels is al... | Cerebral Circulation; Brain; Dissections |
| 207 |
 |
Sensation from the Face: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD | Sensation from the face travels in one of two pathways both of which eventually converge to form the trigeminothalamic tract that reaches the thalamus. The tract that carries pain and temperature is confusing because it first descends before crossing while the equivalent of Dorsal Column-Medical Lem... | Brain; Dissections |
| 208 |
 |
The Ventricles: Neuroanatomy Video Lab - Brain Dissections | Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD | The ventricles are demonstrated and named on a model cast as well as in rotating 3D reconstructions. The production, function, circulation and removal of CSF produced by the choroid plexus is discussed using a diagram and then reviewed on frontal, axial and sagittal brain specimens and corresponding... | Ventricles; Brain; Dissection |
| 209 |
 |
Cogan's Lid Twitch Sign | Raed Behbehani, MD | Cogan's lid twitch sign is a twitch sign of he upper lid upon looking straight from a sustained downgaze position. It is associated with Ocular Myasthenia Gavis. | Myasthenia; Ptosis; Lid Twitch |
| 210 |
 |
Upbeat Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD, | A patient with a brain stem syndrome due to demyelination and upbeat nystagmus. | Upbeat Nystagmus |
| 211 |
 |
Parinaud Syndrome | Raed Behbehani, MD | Parinaud syndrome, as called dorsal midbrain syndrome, is due to dorsal midbrain lesions from compression (e.g., a tumor), demyelination, or ischemia. The syndrome is characterized by limitation of upward gaze, convergence retraction nystagmus, light near dissociation, and lid retraction (Collier's ... | Dorsal Mibrain Syndrome; Parinaud's Syndrome |
| 212 |
 |
Square Wave Jerks with Contrapulsion | Raed Behbehani, MD | A patient with history of brain stem stroke 2 months ago (right hemifacial anesthesia , left sided weakness and bulbar symptoms dysphagia) comes complaining of oscillipsia , binocular vertical diplopia). On exam he had a vertical tropia of 3-4 PD (Skew deviation), dissociated nystagmus , and saccadi... | Square Wave Jerks; Contrapulsion |
| 213 |
 |
Oculopalatal Tremor | Raed Behbehani, MD | This is a usually vertical, pendular nystagmus associated with synchronous rhythmic movement of the palate, developing months after a severe brain stem stroke. The stroke involves the dentato-rubro-olivary tract (Mollaret's triangle). MRI can show hypertrophy of the inferior olivary nucleus in the m... | Oculopalatal Tremor |
| 214 |
 |
Optic Nerve Sheath Fenestration | Raed Behbehani, MD | Optic nerve sheath fenestration is performed to manage papilledema causing progressive loss of vision , due to raised intracranial pressure from Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension or Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis. The procedure is usually performed in cases of severe visual field loss or when m... | Optic Nerve Sheath Fenestration |
| 215 |
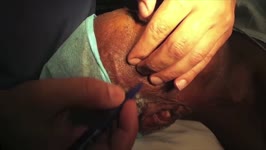 |
Temporal Artery Biopsy | Raed Behbehani, MD | This is a video of Superficial Temporal Artery Biopsy done under local anaesthesia for a patient who was suspected to have Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA. GCA is vasculitis of the medium sized vessels than can lead to permanent visual loss by causing Arteritis Ischemic Optic Neuropathy. The diagnosis of ... | Temporal Artery Biopsy; Giant Cell Arteritis |
| 216 |
 |
Pulsating Exophthalmos | Raed Behbehani, MD | This patient had brain surgery with bone removal resulted in transmission of CSF pulsation into the orbit and pulsating exophthalmos. This sign can also be seen in patient with neurofibromatosis with hypoplasia of the sphenoid wing bone. | Pulsating Exophthalmos; Neurofibromatosis |
| 217 |
 |
Congenital Oculomotor Apraxia | Raed Behbehani, MD | Congenital Ocular Motor Apraxia is an uncommon condition that causes children to have difficulty moving their eyes horizontally or from side to side. They are usually unable to quickly move their eyes from side to side and often have to turn their head (head jerking) and not just their eyes to track... | Oculomotor Apraxia |
| 218 |
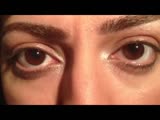 |
Downbeat Nystagmus Anti-GAD Cerebellar Syndrome | Raed Behbehani, MD | A patient with Anti-GAD positive Cerebellar syndrome with ataxia and opsoclonus due to downbeat nystagmus , treated with Baclofen with some improvement. | Downbeat Nystagmus |
| 219 |
 |
See-Saw Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD | This nystagmus localizes to lesions supra/parasellar region (Large sellar and hypothalamic lesion) and is characterized by a see saw movement of elevation/intorsion of one eye and depression/extorsion of the other eye in a pendular fashion. This patient had a large pituitary macro-adenoma with supra... | See-Saw Nystagmus |
| 220 |
 |
Ocular Neuromyotonia | Raed Behbehani, MD | Ocular Neuromytonia is a characterised by by paroxysmal tonic contraction of the extraocular muscles supplied by the oculomotor nerve. It is has been reported after cranial radiation therapy, especially to the sellar-parasellar region and from compressive lesions such tumours or aneurysms. The patho... | Ocular Neuromyotania |
| 221 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD | PAN is a nystagamus characterized by a cycle of uniderectional jerk nystagamus for 60-90 sec , a pause for 10-20 sec and a a cycle of a jerk nystagmus in the opposite direction for 60-90 sec. It is found in brain stem and cerebellar conditions as well as ocular albinism ( as in this patient). | Periodic Alternating Nystagmus |
| 222 |
 |
See-Saw Nystagmus | Raed Behbehani, MD | See-saw nystagmus is a localizing nystagmus to lesions of the sellar and parasellar region. "It's characterized by synchronous elevation and intorsion of one eye and depression and extorsion of the contra lateral eye . This patent has a craniopharyngioma, which was operated twice, optic atrophy and ... | See-Saw Nystagmus |
| 223 |
 |
Marcus Gunn Jaw Winking | Raed Behbehani, MD | Marcus Gunn Jaw Wink causes congenital ptosis and eyelid retraction associated with jaw movement or sucking. It's due to "miswiring" between 3rd and 5th cranial nerves. The treatment of ptosis in children is surgery to prevent amblyopia . | Jaw Winking; Marcus Gunn |
| 224 |
 |
Apraxia of Eyelid Opening | Raed Behbehani, MD | Patient has Parkinson disease and has developed this condition following deep brain stimulation. | Apraxia; Eyelid Opening |
| 225 |
 |
Pertinent Pupillary Problems | Karl C. Golnik, MD | Pupil Exam is a narrated PowerPoint that covers the basic of examining pupils. | Pupil Exam; Pupil |
