A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |
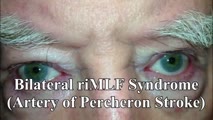 |
riMLF Syndrome from Artery of Percheron Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-yo-man who suffered the abrupt onset of loss of consciousness followed by difficulty looking down. MRI showed bilateral rostral midbrain strokes in the distribution of the artery of Percheron. He could not in... | Image/MovingImage |
| 202 |
 |
Unilateral 3rd, 4th, and 6th Nerve Palsies Due to Cavernous Sinus Meningioma | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman presenting with a partial 3rd nerve palsy (mild pupil involvement), partial 6th nerve palsy, and no clear incyclotorsion with downgaze, suggestive of additional 4th nerve palsy, all on the left... | Image/MovingImage |
| 203 |
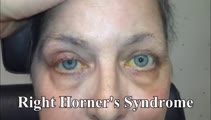 |
Central 4th Nerve Palsy with Contralateral Horner's Syndrome | This is a 60-yo-woman who presented with a complaint of diplopia. Examination demonstrated a left hypertropia that worsened in right and down gaze as well as in left head tilt, and a left 4th nerve palsy was diagnosed. There was also evidence of a mild motility deficit in down/medial gaze OS, consis... | Image/MovingImage |
| 204 |
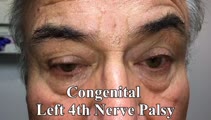 |
Inferior Oblique Overaction in a Congenital 4th Nerve Palsy | 60-yo-man complaining of intermittent oblique diplopia. There was a left hypertropia that worsened in down gaze, right gaze and in left head tilt. There was a large vertical fusional amplitude in addition to a longstanding rightward head tilt, and on examination there was left inferior oblique overa... | Image/MovingImage |
| 205 |
 |
Complete Microvascular 6th Nerve Palsy with Slow Abducting Saccade | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 90-year-man with HTN, HLD, DM who woke up with horizontal diplopia. Two years prior, he was diagnosed with a microvascular right 6th nerve palsy that resolved over several months. There was little concern for gi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 206 |
 |
One-and-a-Half Syndrome Due to Pontine Hemorrhage | This is a 50-year-old woman who, while exercising in the gym, suddenly experienced vertigo, nausea, vomiting, tingling in the left arm, and diplopia. MRI demonstrated a brainstem hemorrhage that involved the right greater than left pons. Examination demonstrated a right horizontal gaze palsy due to ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 207 |
 |
Leukemic Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis Causing 4th and 6th Nerve Palsies | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 55-yo-man with CML that recurred as AML. Diagonal diplopia developed, and on examination he was found to have a partial right 6th nerve palsy, in addition to a left hypertropia that increased in right gaze, down... | Image/MovingImage |
| 208 |
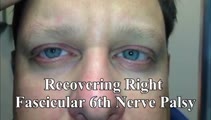 |
Slow Abducting Saccade in 6th Nerve Palsy | 40-yo-man with a right fascicular 6th nerve palsy due to stroke. There was improvement and only a minimal residual right abduction paresis OD by this visit, but still a relatively slow right abducting saccade seen in the video, especially apparent in the slow motion segment. Video shows slow abduct... | Image/MovingImage |
| 209 |
 |
Horner's Syndrome with Anhidrosis | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with the onset of ptosis OD years prior, with clear evidence of a Horner's syndrome. Imaging of the oculosympathetic tract was unrevealing. The patient also mentioned that with exercise, the left side of... | Image/MovingImage |
| 210 |
 |
Apraclonidine Testing in Horner's syndrome | This patient experienced relatively abrupt ptosis and was seen and diagnosed with a Horner's syndrome within a few days of the onset. There were no other exam findings and history did not offer clues as to the etiology. Neuroimaging of the oculosympathetic tract was unrevealing. Apraclonidine testin... | Image/MovingImage |
| 211 |
 |
Skew Deviation and the Triad of the Ocular Tilt Reaction (OTR) | This is a patient who presented with vertical diplopia, who was found to have a complete ocular tilt reaction including the following features: (1) Skew deviation - right hypertropia that was about 30 prism diopters in all directions of gaze including right, left, up, down, as well as in right and ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 212 |
 |
Mesodiencephalic Stroke Causing Unilateral riMLF and INC Ocular Motor Syndromes | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-year-old man who experienced the sudden onset of diplopia (with horizontal and vertical components), dysarthria and imbalance. An MRI performed the following day showed a left mesodiencephalic stroke. The pat... | Image/MovingImage |
| 213 |
 |
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus Syndrome with Prominent Spontaneous Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-year-old man who experienced the abrupt onset of diplopia and imbalance. He had typical features of a left medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) syndrome including left internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) and l... | Image/MovingImage |
| 214 |
 |
Paroxysmal Ocular Tilt Reaction | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-year-old woman who 2 years prior experienced a left sided hypertensive hemorrhagic stroke, resulting in right hemiparesis, dysarthria and vertical diplopia. The initial vertical diplopia resolved completely a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 215 |
 |
Alternating Hypertropias - Bilateral 4th Nerve Palsies and Alternating Skew Deviation | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are two patients with alternating hypertropias. The first is a 70-year-old woman with a diagnosis of cerebellar ataxia, neuropathy, vestibular areflexia syndrome (CANVAS). In the video, both spontaneous downbeat... | Image/MovingImage |
| 216 |
 |
Isolated Central 4th Nerve Palsy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-year-old man with a right hypertropia that worsened in left and down gaze in addition to right head tilt, and improved in left head tilt. There was subjective excyclotorsion OD with double Maddox rod testing.... | Image/MovingImage |
| 217 |
 |
Eye Signs in Infantile Esotropia - Latent Nystagmus and Inferior Oblique Overaction | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 25-yo-man with a history of amblyopia and intermittent eye crossing. On exam, he had a comitant 25 prism diopter esotropia, and other features of infantile (or congenital) esotropia including: latent nystagmus (... | Image/MovingImage |
| 218 |
 |
PSP with Complete Ophthalmoplegia and Inability to Suppress the VOR | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-year-old woman presenting with visual complaints in the setting of advanced progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). She had complete vertical and horizontal ophthalmoplegia, although the vestibulo-ocular reflex... | Image/MovingImage |
| 219 |
 |
Saccadic Smooth Pursuit and Vestibulo-ocular Reflex Suppression (VORS) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 20-yo-man who suffered a left MCA stroke years prior. Upon evaluation of his eye movements, saccades and all classes of eye movements were normal, although his smooth pursuit and VORS were choppy to the left (ip... | Image/MovingImage |
| 220 |
 |
Head-Shaking (2-3 Hz) | Head-shaking: instruct the patient to close their eyes and perform active rapid head-shaking at 2-3 Hz for ~15 secs. If a unilateral vestibulopathy is present, head-shaking-induced (contralesional) nystagmus is often provoked, with the slow phase toward the affected ear. With central lesions, the ny... | Image/MovingImage |
| 221 |
 |
Typical Features of Duane Syndrome Type 1 | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient seen for vestibular complaints, who on exam, was found to have (unrelated to her vestibular symptoms) impaired abduction OS. In adduction, there was narrowing of the palpebral fissure OS, a result of glo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 222 |
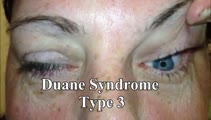 |
Duane's Syndrome Type III | This is a 40-yo-woman seen in neurology clinic for a complaint unrelated to her eyes. On exam, there was impaired adduction and abduction OS. In adduction, there was narrowing of the palpebral fissure OS, a result of her globe retraction due to co-contraction of the medial and lateral rectus muscles... | Image/MovingImage |
| 223 |
 |
Convergence | Can bring out or change the direction of vertical nystagmus in Wernicke's, or cerebellar disease; may be impaired in Parkinson's disease, head trauma, elderly patients; may overcome an adduction deficit with an INO. Instructional ocular motor examination procedures. | Image/MovingImage |
| 224 |
 |
Gaze-Evoked and Centripetal Nystagmus in Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease | This is a 65-year-old woman who experienced a progressive cerebellopathy over several months. Initially, she presented with mild gait imbalance and positional vertigo, and there was only apogeotropic positional nystagmus (more pronounced in supine roll test compared to Dix-Hallpike) with a very slig... | Image/MovingImage |
| 225 |
 |
Test Your Knowledge: The Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus and Bilaterally Abnormal Head Impulse Testing Due to Middle Cerebellar Peduncle and Flocculus Hemorrhage | This is a 70-year-old woman with a history of atrial fibrillation on warfarin presenting with acute prolonged vertigo and imbalance. In addition to the findings demonstrated in the first part of the video, what else should be seen to reassure the examiner that the etiology of her vertigo is benign? ... | Image/MovingImage |
