Collection of materials relating to neuro-ophthalmology as part of the Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
- NOVEL981
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_novel"
| Title | Creator | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
 |
1% Pilocarpine Testing | Karl C. Golnik, MD | A brief description of using Pilocarpine to test the pupils in patients with anisocoria. | Pharmacological Testing; Pilocarpine |
| 152 |
 |
Anatomic and Physiologic Basis for Gaze Stability | Ariel Winnick and Meagan Seay, DO | Diagram describing the anatomic and physiologic basis of gaze stability. | Gaze Stability |
| 153 |
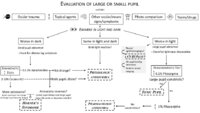 |
Pupil Evaluation Flowchart | Ariel Winnick; Eric Caskey, MD; Meagan Seay, DO | Flow chart outlining the evaluation of large or small pupils. | Pupil Evaluation |
| 154 |
 |
Pituitary Surgery | Jonathan Forbes | Operative video of endoscopic endonasal resection of pituitary macroadenoma. Describes intracapsular versus extracapsular techniques. | Pituitary Surgery |
| 155 |
 |
Large Vessel Occlusion | Justin Gibson, MD; Charles Prestigiacomo, MD | Example of a diagnostic cerebroangiogram performed on a patient undergoing a stroke. | Angiogram; Stroke |
| 156 |
 |
Cerebral Aneurysm | Justin Gibson, MD; Charles Prestigiacomo, MD | Cerebral angiogram of a patient with an arteriovenous malformation, or AVM. | Angiogram; Cerebral Aneurysm |
| 157 |
 |
Arteriovenous Malformation | Justin Gibson, MD; Charles Prestigiacomo, MD | A diagnostic cerebroangiogram performed on a patient who presented with worst headache of life, found to have a Fisher Grade 3 subarachnoid hemorrhage. | Angiogram; Arteriovenous Malformation; AVM |
| 158 |
 |
Normal Angiogram | Justin Gibson, MD; Charles Prestigiacomo, MD | Example of a normal diagnostic cerebroangiogram. | Angiogram |
| 159 |
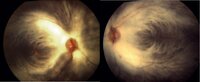 |
Myelinated Nerve Fibers | Carmen Chan,RN, PhD, FAAN | Fundus photos from a patient with extensive myelinated nerve fibers. The patient had normal visual functions. | Myelinated Nerve Fibers |
| 160 |
 |
Superior Segmental Optic Disc Hypoplasia (SSOH) "Topless Disc Syndrome" | Sparsh Jain, Medical Student; Ryan Walsh, MD | This is a case of superior segmental optic disc hypoplasia that was found incidentally after a screening visual field test revealed an asymptomatic inferior field defect in the left eye. The patient has a unilateral SSOH in the left eye. | Superior Segmental Optic Disc Hypoplasia (SSOH) |
| 161 |
 |
Heavy Eye Syndrome | Meagan D. Seay, DO; Bradley J. Katz, MD | A brief overview of heavy eye syndrome. | Heavy Eye Syndrome |
| 162 |
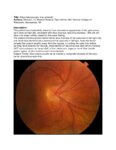 |
Situs Inversus Optic Disc Anomaly | Michael Hii, Medical Student; Ryan Walsh, MD | This patient was incidentally-noted to have anomalous appearance of the optic discs, right more so than left, consistent with situs inversus optic disc anomaly. She did not have any visual deficits related to this exam finding. ; The patient's fundus photos demonstrate situs inversus of the optic ... | Situs Inversus Optic Disc Anomaly |
| 163 |
 |
Suprasellar Meningioma | Sumayya Almarzouqi, MD | Description of a case of suprasellar or sellar mass causeing chiasmal compression. | Suprasellar Meningioma |
| 164 |
 |
Bergmeister Papilla | Sumayya Almarzouqi, MD | A brief overview of Bergmeister papilla, a rare congenital disc anomaly. It arises from the center of the optic disc consists of a small tuft of fibrous tissue and represents a remnant of the fetal hyaloid artery. | Bergmeister Papilla |
| 165 |
 |
Myelinated Nerve Fibers | John J. Chen, MD, PhD | Fundus photographs of a 19-year old female with prominent peripapillary myelinated nerve fibers in both eyes that was incidentally found on routine eye examination. | Myelinated Nerve Fibers |
| 166 |
 |
Brown Syndrome | Meagan Seay, DO | A brief overview of Brown Syndrome. | Brown Syndrome |
| 167 |
 |
Peripapillary Myelinated Nerve Fibers | John J. Chen, MD, PhD | Fundus photographs of a 19-year old female with prominent peripapillary myelinated nerve fibers in both eyes that was incidentally found on routine eye examination. | Myelinated Nerve Fibers |
| 168 |
 |
Myelinated Retinal Nerve Fibers | Scott N. Grossman, MD | A 33 year old man has noted chronically poor vision OS - left eye color noted to be 'orange' instead of red. fundus photos revealed myelinated retinal nerve fiber layer OU (OS>OD) with corresponding linear paracentral scotoma on Humphrey visual field 24-2 OS corresponding with greatest degree of my... | Myelinated Retinal Nerve Fibers |
| 169 |
 |
Modern Imaging of Optic Disc Drusen | Meagan Seay, DO | This is a short powerpoint describing imaging techniques (specifically OCT-EDI, fundus autofluorescence, and B-scan ultrasonography) for optic disc drusen. Examples of these techniques are included. | Optic Disc Drusen; Imaging; OCT-EDI; Fundus Autofluorescence; B-scan Ultrasonography |
| 170 |
 |
Myotonic Dystrophy | Brian Villafuerte, MD, Ezequiel Piccione, MD | Presentation covering an overview of myotonic dystrophy. | Myotonic Dystrophy |
| 171 |
 |
Congenital Hydrocephalus | Mays El-Dairi, MD | Presentation covering an overview of congenital hydrocephalus. | Congenital Hydrocephalus |
| 172 |
 |
Fibrous Dysplasia | Mays El-Dairi, MD | Presentation covering an overview of fibrous dysplasia. | Fibrous Dysplasia |
| 173 |
 |
Muscular Dystrophy Classification | Brian Villafuerte, MD, Ezequiel Piccione, MD | Presentation covering an overview of muscular dystrophy classification. | Muscular Dystrophy Classification |
| 174 |
 |
Tolosa Hunt Syndrome | Sahil Aggarwal, MD; Jason Liss, MD | Presentation covering an overview of Tolosa Hunt Syndrome. | Tolosa Hunt Syndrome |
| 175 |
 |
Temporal Artery Biopsy Procedure | Nooran Badeeb; Danah Albreiki | Temporal artery biopsy is a procedure that is done in a patient with suspicion of GCA (Giant cell Arteritis), and some of the clinical manifestations that prompts us to suspect the diagnosis in patients older than 50 years old are: 1. GCA symptoms e.g. new onset headache. 2 . Visual symptoms: - Visi... | Temporal Artery Biopsy; GCA; Temporal Arteritis |
