TO
Filters: School Or College: "University of Utah" Research Institute: "Institute for Clean and Secure Energy (ICSE)" Collection: "ir_eua"
| Title | Date | Subject | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
 |
Phase 2: Clean and secure energy from coal: Quarterly progress report: October 1, 2010 to December 31, 2010 | 2011-01-31 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; stationary power generation; LES; DQMOM approach; oxy-coal flames; coal | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 152 |
 |
Phase 2: Clean and secure energy from coal: Quarterly progress report: July 1, 2010 to September 30, 2010 | 2010-10-01 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; stationary power generation; Oxycoal; OFC; coal | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 153 |
 |
Phase 2: Clean and secure energy from coal: Quarterly progress report: April 1, 2010 to June 30, 2010 | 2010-08-01 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; stationary power generation; DQMOM approach | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 154 |
 |
Phase 2: Clean and secure energy from coal: Quarterly progress report: January 1, 2010 to March 31, 2010 | 2009-01-30 | domestic coal resources; ICSE; capture CO2; stationary power generation; velocity model; bitumous coal; coal | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 155 |
 |
Phase 2: Clean and secure energy from coal: Quarterly progress report: October 1, 2009 to December 31, 2009 | 2010-01-30 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; stationary power generation; oxy-coal flames; coal gasification process | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 156 |
 |
Pore scale analysis of oil sand/oil shale pyrolysis by X-ray Micro CT and LB simulation | 2010-04-28 | unconventional fuels; characterization of the pore networks; oil sand/shale resources; LB simulation; pyrolysis reations; Multiscale X-ray Micro/Nano Tomography | The research objectives include (1) CT characterization of the pore network structure for selected oil sand/oil shale resources, (2) LB simulation of flow through pore network structures to predict transport properties, such as permeability, and (3) CT analysis of pore network structure during pyrol... |
| 157 |
 |
Pore scale analysis of oil shale/sands pyrolysis | 2011-03-31 | pore scale analysis; oil shale/sands pyrolysis; shale oil production; domestic oil shale deposits | There are important questions concerning the quality and volume of pore space that is created when oil shale is pyrolyzed for the purpose of producing shale oil. In this report, 1.9 cm diameter cores of Mahogany oil shale were pyrolyzed at different temperatures and heating rates. Detailed 3D imagin... |
| 158 |
 |
Policy analysis of water availability and use issues for domestic oil shale and oil sands development: Topical Report: October 1, 2009 to March 31, 2010 | 2010-03 | oil shale/sands resources; energy source; unconventional fuels; water demands; water availability; domestic oil shale/sands development; topical report | Oil shale and oil sands resources located within the intermountain west represent a vast, and as of yet, commercially untapped source of energy. Development will require water, and demand for scarce water resources stands at the front of a long list of barriers to commercialization. Water requiremen... |
| 159 |
 |
Policy analysis of produced water issues associated with in-situ thermal technologies: Topical report: October 1, 2009 to December 31, 2010 | 2011-01 | topical report; produced water issues; in situ thermal technologies; oil shale/sands; water rights; domestic energy source | Commercial scale oil shale and oil sands development will require water, the amount of which will depend on the technologies adopted and the scale of development that occurs. Water in oil shale and oil sands country is already in scarce supply, and because of the arid nature of the region and limita... |
| 160 |
 |
Pore scale analysis of oil sand/oil shale pyrolysis by X-ray Micro CT and LB simulation | 2010-03-03 | pore scale analysis; oil sand/shale pyrolysis; X-ray Micro CT and LB simulation; Lamellar Structure of Oil Shale | The research objectives include (1) CT characterization of the pore network structure for selected oil sand/oil shale resources, (2) LB simulation of flow through pore network structures to predict transport properties, such as permeability, and (3) CT analysis of pore network structure during pyrol... |
| 161 |
 |
Oxy-gas process heaters for efficient CO2 capture | 2010-04-28 | oil shale and oil sands technology; greenhouse gas emissions; GHG; large eddy simulation; LES; IFRF OXYFLAM | Implementation of oil shale/sands technologies in U.S. will require mitigation of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. |
| 162 |
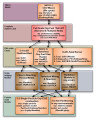 |
Oxy-fuel hierarchy | 2009-11-04 | oxy-fuel combustion; different fuel types; ICSE | Hierarchical chart for the oxy-fuel combustion research area showing connectivity between subtasks. This research area includes coal, gas, and oil oxy-burner technologies. This chart helps illustrate the integration and focus among the different fuel types and different scales represented in the hie... |
| 163 |
 |
Interaction between reactivity and flow in the in-situ production of oil from oil shale | 2009-10-23 | in situ; oil shale | In-situ Oil Shale Processing: 1) Underground resources are heated by some means to convert insoluable/ impermeable kerogen into oil and gas products. 2) The interlinked processes of heat transfer, kerogen conversion and flow are complex. 3) This paper is an attempt to understand these linkages. |
| 164 |
 |
Land and resource management issues relevant to deploying in-situ thermal technologies: Topical Report: October 1, 2009 to December 31, 2010 | 2011-01 | in-situ; oil shale; domestic energy source; oil sands | Utah is home to oil shale resources containing roughly 1.3 trillion barrels of oil equivalent and our nation's richest oil sands resources. If economically feasible and environmentally responsible means of tapping these resources can be developed, these resources could provide a safe and stable dome... |
| 165 |
 |
Ignition in 40kw co-axial turbulent diffusion oxy-coal jet flames | 2010-08-08 | 40kw co-axial turbulent diffusion; diffusion; oxy-coal; oxy-coal jet flames; partial pressure of O2; coal transport | Outline: 1) Introduction 2) Objectives 3) Experimental setup 4) Methodology to quantify flame stability 5) Results and discussion 6) Conclusions 7) Acknowledgements. The objective of this presentation is to better understand, the effects of partial pressure of O2 in a) the coal transport jet, and b)... |
| 166 |
 |
Investigation of coal char-slag transition during oxidation: Effect of temperature and residual carbon | 2009 | coal char; molten slag; bitumous coal; energy and fuels | The transition of coal char to molten slag at high conversion was studied for a bituminous coal using a laminar entrained-flow reactor under oxidizing conditions. Post-oxidized char particles were analyzed by various techniques including loss-on-ignition, gas adsorption analysis and scanning electro... |
| 167 |
 |
Lands with wilderness characteristics, Resource Management Plan constraints, and land exchanges: Cross-jurisdictional management and impacts on unconventional fuel development in Utah's Uinta Basin | 2012-03 | Utah oil shale; oil sands; unconventional fuel resources; land exchanges; land rights | Utah is rich in oil shale and oil sands resources. Chief among the challenges facing prospective unconventional fuel developers is the ability to access these resources. Access is heavily dependent upon land ownership and applicable management requirements. Understanding constraints on resource acce... |
| 168 |
 |
Gasification studies - Task 4 topical report, Utah Clean Coal Program, Reporting period October 2009 - July 2011 | 2011-10 | Gasification; pressurized entrained-flow coal gasifiers; coal | A key objective of the Task 4 activities has been to develop simulation tools to support development, troubleshooting and optimization of pressurized entrained-flow coal gasifiers. The overall gasifier models (Subtask 4.1) combine submodels for fluid flow (Subtask 4.2) and heat transfer (Subtask 4.3... |
| 169 |
 |
Evaluating opportunities for reducing life-cycle, well-to pump GHG emissions from conventional and unconventional fuels | 2010-04-28 | unconventional fuels; GHG emissions; conventional fuels; reducing life-cycle; oil shale; oil sands; coal | Resource extraction and upgrading. |
| 170 |
 |
Effect of pressure on copper/copper-oxide system functioning as an oxygen carrier in chemical looping combustion | 2010-06-10 | copper/copper-oxide system; chemical looping combustion; CLC; high pressure thermogravimetic analysis | Chemical Looping Combustion (CLC) is a promising technology that will utilize more efficient harvesting of energy along with decreased CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. In CLC system the emissions are composed of CO2 and H2O allowing the CO2 to be captured and disposed of in an environmentally more... |
| 171 |
 |
Digital library and interactive map projects at the Institute for Clean and Secure Energy, University of Utah | 2009-10-23 | ICSE; digital repository | The Instituteʼs repository is a not-for-profit service for researchers, and we are working to include a variety of documents, data, and maps relevant to unconventional fuels research and development. |
| 172 |
 |
Effects of oxygen concentration and coal composition on aerosol chemistry in oxy firing | 2010-11-12 | aerosol chemistry; oxy firing; ICSE; coal aerosols; coal composition | Outline: 1) Objectives 2) Coals examined 3) Furnace, sampling, and analysis 4) Results 5) Conclusions. The objectives of the presentation is to provide a comparison of three different coal aerosols under two different oxy fired scenarios for predicting effects of coal composition on oxy firing. Exam... |
| 173 |
 |
High performance computing (hpc) in unconventional fuel production | 2013-05-07 | ICSE; Unconventional fuels; High performance computing; unconventional fuel production | Presentation given at the University of Utah Unconventional Fuels Conference, Salt Lake City, Utah, May 7, 2013. |
| 174 |
 |
KTIA corporate introduction | 2009-02-27 | KTIA; KTI; mines | Overview of KTIA's continuing oil sands development activities in Utah, presented at the 2009 Western U.S. Oil Sands Conference by Soung-Joon Kim, Chief Operating Officer, Korea Technology Industry America, Inc. |
| 175 |
 |
A technical, economic, and legal assessment of North American heavy oil, oil sands, and oil shale resources: In response to Energy Policy Act of 2005 Section 369(p) | 2007-09 | Oil sands; Oil shale; Heavy oil; Energy Policy Act; 2005; Climate Change; Petroleum; Oil Cost; United States; North American heavy oil; Utah Heavy Oil Program; UHOP; World economic development; Energy; Canadian oil sands; Unconventional resources ;Technical; Economic; Legal assessment | Against the backdrop of world population growth, rapid economic expansion in the world's most populous countries, challenging political climates in many oil-producing nations, and the specter of climate change, worldwide energy consumption is projected to increase from the 2004 level of just over 40... |
