Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
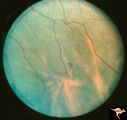 |
Von Hippel Lindau Disease | Von Hippel Lindau Disease with a mini retinal tumor. Pair with R1_C4b. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Hemangioblastoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Von Hippel Lindau disease. Clinical: No visual symptoms. Imaging: Flourescien angiogram in R1_C4b. | Image |
| 102 |
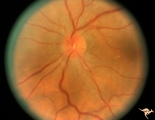 |
C105 Disc Edema with Systemic Lupus | Mild disc edema blurs the inferior disc margin. Flourescein angiogram in D1_06. Same patient as D1_06 an D1_07. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to vasculitis (Lupus). Disease/ Diagnosis: Lupus papillopathy. | Image |
| 103 |
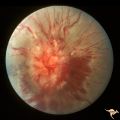 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis) with retinal evidence of central retinal vein occlusion. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Diffuse choroidal hemangioma; Glaucoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Sturge Weber Syndrome. Clinical: Port wine hemangioma of the face. | Image |
| 104 |
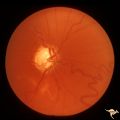 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis); Color of the retina is deep red (sometimes called tomato catsup) due to a four fold thickening of the choroidal vascular bed. Glaucomatous cupping of the optic nerve. Striking retinal venous vascular anomalies on the disc and in the retina. ... | Image |
| 105 |
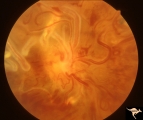 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Wyburn-Mason Syndrome in man with orbital cranial component. After embolization of the orbital and cranial component, the retinal malformation involuted further. Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Post-treatment. Close up view of the disc. October 21, 1992. Same patient as V_23 and V_25. Anatomy: ... | Image |
| 106 |
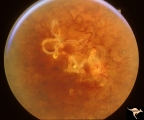 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Wyburn-Mason Syndrome in man with orbital cranial component. After embolization of the orbital and cranial component, the retinal malformation involuted further. Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Post-treatment. Wide angle view of slide V_24. October 21, 1992. Same patient as V_23 and V_24. Anat... | Image |
| 107 |
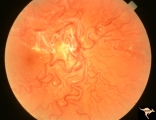 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Wyburn-Mason Syndrome in man with orbital cranial component. Pre-treatment. Retinal arteriovenous malformations, pre-involution. April 27, 1992. Same patient as V_24 and V_25. Anatomy: Optic disc; Brain. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation of retina and brain. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn-Mason syndr... | Image |
| 108 |
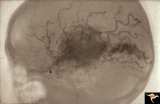 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Wyburn-Mason Syndrome. Angiogram showing extension of vascular malformation up the right optic nerve (arrow) through the thalamus and into the right visual cortex. References #3 and #73. Anatomy: Brain. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wy... | Image |
| 109 |
 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Partially involved. Same patient as V_27. Anatomy: Optic disc; Brain. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation of retina and brain. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn-Mason syndrome. Clinical: Blindness in the involved eye, proptosis. | Image |
| 110 |
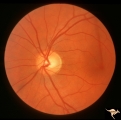 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy in an eye with temporal hemianopia. Wyburn-Mason Syndrome extending to the chiasm. Left eye 1975. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right sided chiasmal AVM. Disease/Diagnosis: Band atrophy due to chiasmal AVM and Wyburn-Mason Syndrome. Clinical: Blind right eye, temp... | Image |
| 111 |
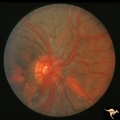 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn-Mason syndrome. Clinical: Cerebral symptoms, questionable seizures. | Image |
| 112 |
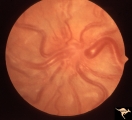 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Clinical: Reduced vision. | Image |
| 113 |
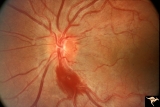 |
IE02b Acute Leber Optic Neuropathy | Acute Leber Optic Neuropathy. Formation of hemorrhage one year after IE_02a. At this time, he was beginning to lose central vision. .Note thinning of the nerve fiber layer temporally, 3:00 - 4:00 Pair with IE_02a. March 26, 1980. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic neuropathy. Disease/ Diagnosis: ... | Image |
| 114 |
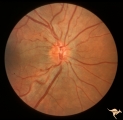 |
IE01 Acute Leber Optic Neuropathy | Pseudo edema with peripapillary microangiopathy in a brother of boy with Leber Optic Neuropathy. Not pale nerve yet. Right eye. Same patient as IE_02a and IE_02b. August 7, 1979. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic neuropathy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Optic neuropathy. Clinical: Asymptomatic | Image |
| 115 |
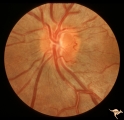 |
IE02a Acute Leber Optic Neuropathy | Acute Leber Optic Neuropathy, Left eye. Same patient as IE_01 and IE_02b. August 7, 1979. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic neuropathy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Leber's optic neuropathy. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 116 |
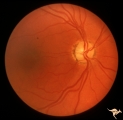 |
IF201a Temporal Cupping with Dominant Hereditary Optic Atrophy | 1969. Dominant hereditary optic atrophy (Kjer) Pair with IF2_1b. Right eye. Boy with reduced central acuity since childhood. Discs are pale temporally and the temporal nerve fiber layer is thin. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Dominant hereditary optic atrophy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Dominant hereditar... | Image |
| 117 |
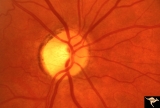 |
IF205a Temporal Cupping with Dominant Hereditary Optic Atrophy | 1970. Right eye. Pair with IF2_5b. 55 year old woman with deficient vision all her life. Typical pattern of dominant hereditary atrophy. Temporal pallor and shallow cupping. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Dominant hereditary optic atrophy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Dominant hereditary optic atrophy. Cli... | Image |
| 118 |
 |
IF205b Temporal Cupping with Dominant Hereditary Optic Atrophy | 1970. Left eye. Pair with IF2_5a. 55 year old woman with deficient vision all her life. Typical pattern of dominant hereditary atrophy. Temporal pallor and shallow cupping. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Dominant hereditary optic atrophy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Dominant hereditary optic atrophy. Clin... | Image |
| 119 |
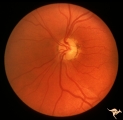 |
IF201b Temporal Cupping with Dominant Hereditary Optic Atrophy | 1969. Dominant hereditary optic atrophy (Kjer) Pair with IF2_1a. Left eye. Boy with reduced central acuity since childhood. and the temporal nerve fiber layer is thin. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Dominant hereditary optic atrophy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Dominant hereditary optic atrophy. Clinical: ... | Image |
| 120 |
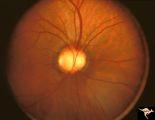 |
C23 Empty Disc | Father of patient in C_21 and C_22. Father has central retinal artery, multiple cilioretinal arteries and had previously unsuspected renal failure. Papillorenal Syndrome (PRS). Reference: Parsa,CF et al. Ophthalmology. 2001. 108(4): 738-49Barroso LH, Hoyt WF, Narahara M. Can the arterial supply of ... | Image |
| 121 |
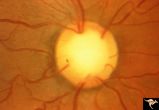 |
C21 Empty Disc | Right eye. All cilioretinal fundus. No central retinal artery. Handmann anomaly. Frequently associated with renal dysplasia. Pair with C_22 an C_23. Reference: Barroso LH, Hoyt WF, Narahara M. Can the arterial supply of the retina in man be exclusively cilioretinal? J Neuroophthalmol. 1994 Jun;14(2... | Image |
| 122 |
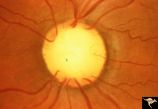 |
C22 Empty Disc | Left eye. All cilioretinal fundus. No central retinal artery. Handmann anomaly. Frequently associated with renal dysplasia. Pair with C_21 an C_23. Reference: Barroso LH, Hoyt WF, Narahara M. Can the arterial supply of the retina in man be exclusively cilioretinal? J Neuroophthalmol. 1994 Jun;14(2)... | Image |
| 123 |
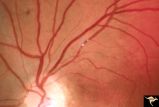 |
Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy (Susac Syndrome) | Two plaques which have been called Psuedo-emboli. This plaque is not the result of embolism, but is the result of the microangioplastic process underlying the syndrome. (NANOS 2001 by Egan, RA). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Microangiopathy involving brain, auditory nerve and retina. Disease/Diagnosi... | Image |
| 124 |
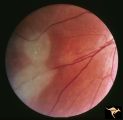 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Has two astrocytic hamartomas. Lower shows a few specs of calcification. Note how the tumor obscures the underlying retinal vessels. Left eye. Pair with R1_D4a. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 125 |
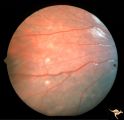 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Two very small tuberous sclerosis lesions. Group with R1_D7a, b, d. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
