A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_gold"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
 |
Pinched Nose Valsalva | Valsalva (closed glottis or pinched nose): instruct the patient to take a deep breath and ‘bear down' (closed glottis) or take a deep breath and ‘try to pop their ears' (pinched nose). Assess for nystagmus. In superior canal dehiscence, pressure changes may be transmitted to the superior canal, ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 102 |
 |
Vibration | Vibration: instruct the patient to self-administer this test with an electric toothbrush or vibrator/massager, if available. Vibration of the mastoids and vertex will induce an ipsilesional slow phase with unilateral vestibular loss (https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=1427582). | Image/MovingImage |
| 103 |
 |
Eye Handbook App for OKN | Optokinetic nystagmus (OKN): one way this can be examined virtually is using a smartphone application (e.g. Eye Handbook © app used in this video) or optokinetic tape/flag/drum held in front of the examiner's camera. The optokinetic stimulus should occupy the full screen of the patient's device (ea... | Image/MovingImage |
| 104 |
 |
Dix-Hallpike | The safety of the patient should be prioritized when completing this test virtually, and the examiner should avoid putting the patient in a position where a fall may occur. Floor (or bed) Dix-Hallpike: this test can be used for patients who are fully mobile and able to get down to the floor and up a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 105 |
 |
Modified (Chair) Dix-Hallpike | The safety of the patient should be prioritized when completing this test virtually, and the examiner should avoid putting the patient in a position where a fall may occur. Modified (chair) Dix-Hallpike:(1) this test can be used for patients who may not be able to safely undertake the traditional Di... | Image/MovingImage |
| 106 |
 |
Saccades | Saccades: instruct the patient to make rapid movements of their eyes in each gaze direction, noting the speed, conjugacy, latency, and accuracy. First have the patient look between an eccentric target and the camera horizontally and vertically, making assessment of accuracy easier - e.g., overshooti... | Image/MovingImage |
| 107 |
 |
VOR Suppression | VOR suppression (VORS): instruct the patient to fix on the camera which they should hold in front of their eyes, while turning their torso slowly in the horizontal plane. The vertical plane can then be assessed by instructing the patient to flex and extend the neck under the same conditions. A demon... | Image/MovingImage |
| 108 |
 |
Active Head Impulse Test | Active head impulse test (HIT): instruct the patient to fix their eyes on the camera and turn their head 20o to the right/left, and then make a rapid movement toward the midline to align their head with the camera again, keeping their eyes fixed on the camera throughout. A simple instruction is to a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 109 |
 |
Convergence | Convergence: instruct the patient to focus on their thumb held at arm's length, and slowly move their thumb towards their nose. This may bring out or cause reversal of vertical nystagmus (e.g., transition from upbeat to downbeat nystagmus in Wernicke's encephalopathy [see example of transition from ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 110 |
 |
Head-Shaking (2-3 Hz) | Head-shaking: instruct the patient to close their eyes and perform active rapid head-shaking at 2-3 Hz for ~15 secs. If a unilateral vestibulopathy is present, head-shaking-induced (contralesional) nystagmus is often provoked, with the slow phase toward the affected ear. With central lesions, the ny... | Image/MovingImage |
| 111 |
 |
Range of Motion (Ductions) | Range of motion (ductions): check the range of each individual eye (ductions) if there is diplopia or if a motility deficit is suspected. Instructing the patient to hold their head 20o to the right or to the left may provide a better view of the range of horizontal gaze, if there is diplopia or if a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 112 |
 |
Smooth Pursuit | Smooth pursuit: instruct the patient to hold their head steady, fix their eyes on the camera and slowly move the camera in the horizontal and vertical planes. Or, have the patient focus on their outstretched thumbnail (or other small fixation target), while following the slowly moving object horizon... | Image/MovingImage |
| 113 |
 |
Supine Roll Test | Supine roll test: used to test for horizontal canal (HC) BPPV. While horizontal nystagmus due to HC-BPPV is often seen with DH, the roll test will usually maximize nystagmus and vertigo with the HC variant. The patient can be guided through a self-administered supine roll test while lying on the flo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 114 |
 |
Dynamic Visual Acuity | Dynamic Visual Acuity: the examiner can use screen-sharing to provide a visual acuity chart. Instruct the patient to sit at the appropriate distance from their screen at which the lowest line on the visual acuity chart is just readable. Have the patient move their head (horizontally to evaluate the ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 115 |
 |
Fixation and Gaze Holding | Fixation and gaze-holding: assess for nystagmus or saccadic intrusions by observing the eyes in primary position. Then instruct the patient to look in each position of gaze, and to hold that position to assess for gaze-evoked nystagmus. In doing so, motility can also be evaluated with both eyes view... | Image/MovingImage |
| 116 |
 |
How to Measure Ocular Alignment Virtually | Ocular alignment: the alternate cover test can be performed by instructing the patient to hold their head steady, fix their eyes on the camera (or a more distant target - the closer the fixation target, the more of an exodeviation the examiner will see), and use their cell phone (or a spoon) to occl... | Image/MovingImage |
| 117 |
 |
Hyperventilation | Hyperventilation: instruct the patient to breathe rapidly in and out of their mouth for 40-60 seconds. Alkalosis and changes in ionized calcium may improve conduction through an affected segment of 8th cranial nerve due to vestibular schwannoma (https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=1213447) o... | Image/MovingImage |
| 118 |
 |
Penlight Cover Test (Partial Removal of Fixation) | Penlight cover test (partial removal of fixation): during in-person clinical encounters, the maneuvers below are best tested with complete (or near complete) removal of fixation (e.g., Frenzel or video Frenzel goggles). Removal of fixation is more challenging during virtual evaluations but can be ap... | Image/MovingImage |
| 119 |
 |
Valsalva (Closed Glottis) | Valsalva (closed glottis or pinched nose): instruct the patient to take a deep breath and ‘bear down' (closed glottis) or take a deep breath and ‘try to pop their ears' (pinched nose). Assess for nystagmus. In superior canal dehiscence, pressure changes may be transmitted to the superior canal, ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 120 |
 |
Eyelid Nystagmus | Lid nystagmus is a rhythmic eyelid movement commonly seen as an epiphenomenon of vertical nystagmus (typically upbeating, as in this case) due to a shared central pathway controlling elevation of the lid and supraduction. There can be isolated lid nystagmus if there is accompanying impairment of su... | Image/MovingImage |
| 121 |
 |
Abnormal Visually-enhanced Vestibulo-ocular Reflex (vVOR) in Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome (CANVAS) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This patient complained of chronic (unexplained cough), progressive numbness in the legs and feet, gait instability, and oscillopsia when walking or with head movements. Examination showed excessive square-wave jerks, bil... | Image/MovingImage |
| 122 |
 |
Expanded Nystagmus & Saccadic Intrusions/Oscillations Differential | Expanded nystagmus & saccadic intrusions/ oscillations differential | Text |
| 123 |
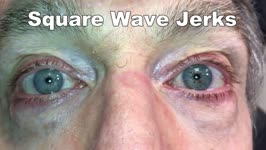 |
Saccadic Intrusions (Square Wave Jerks, SWJ) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are SWJ, which is the most common example of a saccadic intrusion. Here the patient is fixating on the camera, and all of the sudden a saccade takes the eyes off the fixation target, there's a brief intersaccadi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 124 |
 |
An Optokinetic Stimulation Home Exercise Program | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A plainly written program of optokinetic exercise intended for patient use at home. 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿𝗼-𝗼𝗽𝗵𝘁𝗵𝗮𝗹𝗺𝗼𝗹𝗼𝗴𝘆 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿𝗼-𝗼𝘁𝗼𝗹𝗼𝗴𝘆 ... | Text |
| 125 |
 |
Expanded Acute Onset Persistent Vision Loss Differential | Text |
