TO
| Title | Date | Subject | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 |
 |
Sedimentology of oil-impregnated, lacustrine and fluvial sandstone, P.R. Spring area, southeast Uinta Basin, Utah | 1970-08 | sedimentology; lacustrine and fluvial sandstone; P. R. Spring area; Oil-impregnated lacustrine and fluvial sandstone | Oil-impregnated intervals, up to 75 feet thick within a stratigraphic interval of about 250 feet in the Garden Gulch and Parachute Creek Members of the Green River Formation (Eocene), are exposed in beds that dip gently northward in the P. R. Spring area. Reserve estimates indicate that there may be... |
| 77 |
 |
Recovery of oil from Utah's tar sands | 1983-03-31 | Utah tar sands; bitumen cleaning; PRS-R tar sands; fluidized bed thermal recovery | This report covers the work accomplished at the University of Utah on Utah's tar sands during the period: October 1, 1979 to March 31, 1983. The work reported is a continuation of the program carried out over a period of years at the University. The primary effort of the work covered in this report ... |
| 78 |
 |
Recovery of bitumen from oil-impregnated sandstone deposits of Utah | 1975-11 | potential oil; bitumen; oil-impregnated sandstone (tar sand) deposits; tar sands; bitumen recovery | Utah contains at least 26 billion barrels of potential oil as bitumen in oil-impregnated sandstone (tar sand) deposits. As shown in this paper, these tar sands are significantly different in physical and chemical properties from commercially developed Canadian tar sands. These differences prevent di... |
| 79 |
 |
Recovery of oil from Utah's tar sands | 1979-11-30 | oil recovery; Utah tar sands; hot water recovery; thermal processing; synthetic fuel | This project is designed to develop necessary engineering data and technology for recovery of oil from Utah's tar sands. Progress reports for four major aspects of this project, namely Hot Water Recovery, Energy Recovery in Thermal Processing, Effect of Variables in Thermal Processing and Bitumen Pr... |
| 80 |
 |
Geologic characterization of Utah oil shale deposits | 2010-04-28 | oil shale development; geologic framework; lake evolution; oil shale; stratigraphic correlation | Why Geology? Economic prospectivity of oil shale development in the Uinta Basin relies heavily on establishing a solid geologic framework. Understanding lake evolution matters. |
| 81 |
 |
Quarterly Progress Report Phase 3: Clean and Secure Energy from Coal - October 1, 2011 to December 31, 2011 | 2012-02-16 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; Oxy-Coal | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 82 |
 |
Quarterly Progress Report Phase 3: Clean and Secure Energy from Coal - July 1, 2011 to September 30, 2011 | 2011-09 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; OFC | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 83 |
 |
Quarterly Progress Report Phase 3: Clean and Secure Energy from Coal - April 1, 2012 to June 30, 2012 | 2012-07-01 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; stationary power generation; oxyfuel combustor (OFC) | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 84 |
 |
Quarterly Progress Report Phase 3: Clean and Secure Energy from Coal - October 1, 2012 to December 31, 2012 | 2013-01-01 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; Oxy-Coal; Gasification | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 85 |
 |
Quarterly Progress Report Phase 3: Clean and Secure Energy from Coal - January 1, 2012 to March 30, 2012 | 2010-05-01 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; OFC simulation | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 86 |
 |
Phase II: Clean and Secure Energy from Coal: Quarterly Progress Report: January 1, 2011 to March 30, 2011 | 2011-05-01 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; coal; Oxycoal simulation team; coal sequestration | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 87 |
 |
Phase 2: Clean and secure energy from coal: Quarterly progress report: October 1, 2010 to December 31, 2010 | 2011-01-31 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; stationary power generation; LES; DQMOM approach; oxy-coal flames; coal | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 88 |
 |
Phase 2: Clean and secure energy from coal: Quarterly progress report: July 1, 2010 to September 30, 2010 | 2010-10-01 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; stationary power generation; Oxycoal; OFC; coal | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 89 |
 |
Phase 2: Clean and secure energy from coal: Quarterly progress report: April 1, 2010 to June 30, 2010 | 2010-08-01 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; stationary power generation; DQMOM approach | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 90 |
 |
Phase 2: Clean and secure energy from coal: Quarterly progress report: January 1, 2010 to March 31, 2010 | 2009-01-30 | domestic coal resources; ICSE; capture CO2; stationary power generation; velocity model; bitumous coal; coal | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 91 |
 |
Phase 2: Clean and secure energy from coal: Quarterly progress report: October 1, 2009 to December 31, 2009 | 2010-01-30 | domestic coal resources; CO2 capture; stationary power generation; oxy-coal flames; coal gasification process | The University of Utah is pursuing research to utilize the vast energy stored in our domestic coal resources and to do so in a manner that will capture CO2 from combustion from stationary power generation. The research is organized around the theme of validation and uncertainty quantification throug... |
| 92 |
 |
Pore scale analysis of oil sand/oil shale pyrolysis by X-ray Micro CT and LB simulation | 2010-04-28 | unconventional fuels; characterization of the pore networks; oil sand/shale resources; LB simulation; pyrolysis reations; Multiscale X-ray Micro/Nano Tomography | The research objectives include (1) CT characterization of the pore network structure for selected oil sand/oil shale resources, (2) LB simulation of flow through pore network structures to predict transport properties, such as permeability, and (3) CT analysis of pore network structure during pyrol... |
| 93 |
 |
Pore scale analysis of oil shale/sands pyrolysis | 2011-03-31 | pore scale analysis; oil shale/sands pyrolysis; shale oil production; domestic oil shale deposits | There are important questions concerning the quality and volume of pore space that is created when oil shale is pyrolyzed for the purpose of producing shale oil. In this report, 1.9 cm diameter cores of Mahogany oil shale were pyrolyzed at different temperatures and heating rates. Detailed 3D imagin... |
| 94 |
 |
Policy analysis of water availability and use issues for domestic oil shale and oil sands development: Topical Report: October 1, 2009 to March 31, 2010 | 2010-03 | oil shale/sands resources; energy source; unconventional fuels; water demands; water availability; domestic oil shale/sands development; topical report | Oil shale and oil sands resources located within the intermountain west represent a vast, and as of yet, commercially untapped source of energy. Development will require water, and demand for scarce water resources stands at the front of a long list of barriers to commercialization. Water requiremen... |
| 95 |
 |
Policy analysis of produced water issues associated with in-situ thermal technologies: Topical report: October 1, 2009 to December 31, 2010 | 2011-01 | topical report; produced water issues; in situ thermal technologies; oil shale/sands; water rights; domestic energy source | Commercial scale oil shale and oil sands development will require water, the amount of which will depend on the technologies adopted and the scale of development that occurs. Water in oil shale and oil sands country is already in scarce supply, and because of the arid nature of the region and limita... |
| 96 |
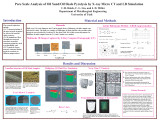 |
Pore scale analysis of oil sand/oil shale pyrolysis by X-ray Micro CT and LB simulation | 2010-03-03 | pore scale analysis; oil sand/shale pyrolysis; X-ray Micro CT and LB simulation; Lamellar Structure of Oil Shale | The research objectives include (1) CT characterization of the pore network structure for selected oil sand/oil shale resources, (2) LB simulation of flow through pore network structures to predict transport properties, such as permeability, and (3) CT analysis of pore network structure during pyrol... |
| 97 |
 |
Oxy-gas process heaters for efficient CO2 capture | 2010-04-28 | oil shale and oil sands technology; greenhouse gas emissions; GHG; large eddy simulation; LES; IFRF OXYFLAM | Implementation of oil shale/sands technologies in U.S. will require mitigation of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. |
| 98 |
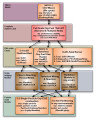 |
Oxy-fuel hierarchy | 2009-11-04 | oxy-fuel combustion; different fuel types; ICSE | Hierarchical chart for the oxy-fuel combustion research area showing connectivity between subtasks. This research area includes coal, gas, and oil oxy-burner technologies. This chart helps illustrate the integration and focus among the different fuel types and different scales represented in the hie... |
| 99 |
 |
P. R. spring oil-impregnated sandstone deposit Uintah and Grand Counties, Utah | 1970-02 | oil-impregnated sandstone beds; oil impregnation; oil shale; lenticular sandstones; siltstones | Oil-impregnated sandstone beds underlie at least 214 square miles in the southeastern Uinta Basin and may extend northward beneath cover. One to as many as five principal saturated zones, 3 to 75 feet thick, occur in a 250-foot interval that dips gently northward. The northernmost outcrops are overl... |
| 100 |
 |
Interaction between reactivity and flow in the in-situ production of oil from oil shale | 2009-10-23 | in situ; oil shale | In-situ Oil Shale Processing: 1) Underground resources are heated by some means to convert insoluable/ impermeable kerogen into oil and gas products. 2) The interlinked processes of heat transfer, kerogen conversion and flow are complex. 3) This paper is an attempt to understand these linkages. |
