Collection of materials relating to neuro-ophthalmology as part of the Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
- NOVEL224
| Title | Creator | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
 |
1% Pilocarpine Testing | Karl C. Golnik, MD | A brief description of using Pilocarpine to test the pupils in patients with anisocoria. | Pharmacological Testing; Pilocarpine |
| 52 |
 |
Introduction to NANOS NOTE | Karl C. Golnik, MD | Introduction to NANOS NOTE, a resource for non-neuro-ophthalmologists describing common examination techniques. | Neuro-Ophthalmology Examination Techniques |
| 53 |
 |
Refraction | Sean Gratton, MD | An introduction to refraction. | Refraction |
| 54 |
 |
Red Color Desaturation | Sean Gratton, MD | Exploring red color desaturation. | Red Color Desaturation |
| 55 |
 |
Limb-Kinetic Apraxia | James R. Bateman, MD, MPH; Victoria S. Pelak, MD | Introduction to the limb kinetic apraxia exam as part of the larger mental status examination. Video accompanies the The Mental Status Examination lecture at https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s64b7716 and Cognitive Assessment at: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6qc49rx | Mental Status |
| 56 |
 |
Introduction to the Evaluation of Visual Function | Sean Gratton, MD | An introduction to evaluating a patient's visual function. | Visual Function |
| 57 |
 |
Introduction to Funduscopic Examination | Valérie Biousse, MD | Introduction to the funduscopic examination section of the NExT curriculum. | Exams; Funduscopy |
| 58 |
 |
Patient Portal: Optic Disc Drusen | Cristiano Oliveira, MD | Optic disc drusen (ODD) are abnormal deposits of benign, usually calcified material within the optic disc, which is the front part of the optic nerve that connects each eye to the brain. We do not know the exact cause of optic disc drusen. They are present in 0.3-2% of people as an isolated case or ... | Optic disc drusen; Papilledema; Pseudopapilledema |
| 59 |
 |
Patient Portal: Microvascular Cranial Nerve Palsy | Meagan Seay, DO | A nerve palsy is an impairment in the function of a nerve, which results in a decrease in function of the corresponding muscles controlled by that nerve. In microvascular cranial nerve palsy, something affects the blood supply to one of the cranial nerves, causing it not to work. This is usually the... | Nerve palsy; Microvascular cranial nerve palsy; Cranial nerve 3; CN3; Oculomotor nerve; Cranial nerve 4; CN4; Trochlear nerve; Cranial nerve 6; CN6; Abducens nerve |
| 60 |
 |
Patient Portal: Non-Arteritic-Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (NAION) | Arun Sundaram, MD | Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION or NA-AION) is caused by decreased blood flow to the front part of the optic nerve (optic disc). It causes optic nerve swelling and sudden vision loss. NAION typically affects one eye, although the other eye sometimes suffers similar loss month... | Non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy; NAION; NA-AION; Optic nerve; Optic disc; Ophthalmic artery |
| 61 |
 |
Patient Portal: Myasthenia Gravis | Aroucha Vickers, DO | Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system creates antibodies (proteins that normally protect us) that may attack receptors on your muscles. This results in muscle weakness because the muscles do not receive the signals to contract (tighten). Muscles anywhere w... | Myasthenia gravis; Ptosis; Double vision |
| 62 |
 |
Patient Portal: Giant Cell Arteritis | Anne S. Abel, MD | Giant cell arteritis is an inflammatory condition that can cause vision loss, double vision, fever, new persistent headaches, scalp tenderness, and jaw pain with chewing. GCA is caused by inflammation of blood vessels, primarily in the head and neck. Sometimes called "temporal arteritis," GCA frequ... | Giant cell arteritis |
| 63 |
 |
Patient Portal: Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) | Devin D. Mackay, MD | Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), also called pseudotumor cerebri, is a condition in which there is high pressure in the fluid surrounding your brain, spinal cord and optic nerves. This can cause headaches and problems with vision. Although the cause(s) of the condition is not fully unders... | Idiopathic intracranial hypertension; Pseudotumor cerebri |
| 64 |
 |
Patient Portal: Homonymous Hemianopsia | James C. O'Brien, MD | Homonymous hemianopia refers to an absence of vision towards one side of the visual world in each eye. The damage that caused this problem is in the brain and not in the eyes. | Homonymous hemianopia; Visual pathway |
| 65 |
 |
Patient Portal: Optic Neuritis | Anthony Brune, DO | Optic neuritis is inflammation of the optic nerve. In optic neuritis, the covering around the fibers of the optic nerve (myelin) is damaged by inflammation (demyelination), which typically results in blurred or dark vision. | Optic neuritis; Myelin; Demyelination |
| 66 |
 |
Patient Portal: Transient Vision Loss | Anthony Brune, DO | Transient visual loss is the term used to describe loss of part or all of the vision in one or both eyes temporarily. Some people do not experience a complete loss of the affected vision and instead describe the abnormality as "blurring" or like "looking through a veil." The vision typically returns... | Transient visual loss |
| 67 |
 |
Introduction to the Slit Lamp and the Slit Lamp Examination | Chris Bair, MD and Tyler Quist, MD | This brief video from fourth-year medical students Chris Bair and Tyler Quist discusses the details of your ophthalmology rotation at the Moran Eye Center, as well as providing a primer on how to use the slit lamp and perform a basic eye exam. | Medical Student; Exam; Education |
| 68 |
 |
Headaches Related to Eye Disorders | Nikki Gill, MSIII; Sean Gratton, MD | Headache attributed to disorders of the eye: Angle closure glaucoma, Ocular inflammation, Refractive error, Trochlear headache, Ocular surface disorder | Eye Disorders; Headache; Angle Closure Glaucoma; Ocular Inflammation; Refractive Error; Trochlear Headache; Ocular Surface Disorder |
| 69 |
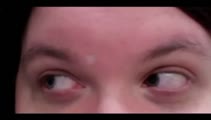 |
Bilateral Acquired Brown's Syndrome | Ryan D. Walsh, MD; Collin McClelland, MD | A 27 year old female with a history of Sjogren's syndrome reported a 2 year history of a vertical binocular diplopia with looking up-and-to-the right. She has also noticed an audible "click" when positioning her eyes in this direction. As depicted in the video, when attempting to look up-and-to-the... | Brown's syndrome; Brown syndrome; hypertropia; diplopia; disorder of ocular motility; Sjogren's syndrome |
| 70 |
 |
Basic Eyelid Measurements | John D. Ng, MD, MS, FACS | Demonstration of basic eyelid measurements. | Eyelid |
| 71 |
 |
Examination of Lymph Nodes | John D. Ng, MD, MS, FACS | Demonstration of lymph node examination. | Exam; Lymph Nodes |
| 72 |
 |
Ice Test in Myasthenic Ptosis | Julie Falardeau, MD | Demonstration of ice test. | Ice Test; Myasthenic Ptosis |
| 73 |
 |
Visual Fields Part 1: Performing The Tests | Jonathan Trobe, MD | Discussion and demonstration of visual field testing. | Visual Fields |
| 74 |
 |
Introduction to Evaluation in Special Situations in NANOS NOTE | John Pula, MD | An introduction to NOTE sections on Examination of the Comatose Patient and Examination of the Pediatric Patient. | Patient Examination; Pediatric Patient; Examination |
| 75 |
 |
Introduction to the NANOS Neuro-Ophthalmology Techniques of Examination (NOTE) | Karl C. Golnik, MD | An introduction to the NANOS Neuro-Ophthalmology Techniques of Examination (NOTE) | Examination; Eye Exam |
