Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
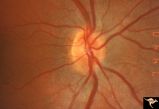 |
H62 Superior Segmental Optic Hypoplasia (SSOH) Topless Disc Syndrome | Right eye. Disc looks almost normal but superior nerve fiber layer is thinned and represents a mild form of SSOH. Same patient as H_61 and H_63. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Superior segmental optic hypoplasia (SSOH). Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 52 |
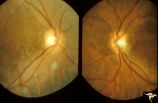 |
H80 Chiasmal Hemioptic Hypoplasia | Discs show striking nasal hypoplasia and band atrophy. DeMorsier synrome. Congenital bitemporal hemianopia with see-saw nystagmus. Note vertically oral shape of these hypoplastic nerves. The CT scan showed the median bar of the chiasm in this patient is totally hypoplastic. Anatomy: Optic disc. Path... | Image |
| 53 |
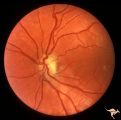 |
H85 Chiasmal Hemioptic Hypoplasia | Congenital bitemporal hemianopia with marked bi-nasal hypoplasia. Right eye. 17 year old male. Same patient as H_84. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal hemioptic hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly involving chiasm. | Image |
| 54 |
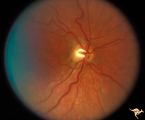 |
H86 Chiasmal Hemioptic Hypoplasia | Congenital bitemporal hemianopia with nasal hypoplasia. 24 year old man. Same patient as H_87. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal hemioptic hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly involving chiasm. | Image |
| 55 |
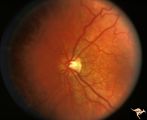 |
H87 Chiasmal Hemioptic Hypoplasia | Congenital bitemporal hemianopia with nasal hypoplasia. 24 year old man. Same patient as H_86. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal hemioptic hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly involving chiasm. | Image |
| 56 |
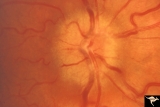 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema due to elevated intracranial pressure. Right eye. This eye has papilledema. Patient described transient monocular blindness with turning right eye. Asymmetric papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Iidiopathic intracranial hyper... | Image |
| 57 |
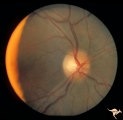 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Patient had tumor on right side. Right sided large meningioma. Disc edema due to tumor. 29 year old black woman. The right disc has mild temporal pallor. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Uninaleral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Meningioma of the brain. Clinical: Headache. | Image |
| 58 |
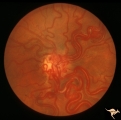 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations (Racemous angioma). Found in a 13 year old girl who had extension of this arteriovenous malformation up her right optic nerve into her thalamus and into her midbrain. Patient had large intra-cerebral AVM (Wyburn-Mason Syndrome). Patient died 10 years later of mass... | Image |
| 59 |
 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Two years later after interventional embolic obliteration of orbital AVM. Same patient as V_26. Ref: #73. Anatomy: Optic disc; Brain. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation of retina and brain. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn-Mason syndrome. Clinical: Blindness in the i... | Image |
| 60 |
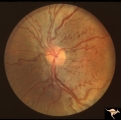 |
Venous Anomalies - Congenital Venous Tortuosity | Congenital venous tortuosity in a young girl with a cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM). Same eye as V_55. This does not represent a Wyburn-Mason Syndrome. It was a congenital retinal venous anomaly, not a retinal AVM. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital venous tortuosity. Disease/Diag... | Image |
| 61 |
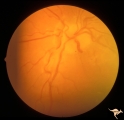 |
Venous Anomalies - Exit Anomalies | Disc edge veins of Kraupa in 14 year old boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital anomaly, exit anomaly. Disease/Diagnosis: Exit anomaly, edge veins. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 62 |
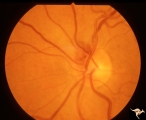 |
Venous Anomalies - Prepapillary Venous Convolutions (Congenital) | Sub-retinal and prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Edge vein. Large vein draining subretinally into the choroid. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Disease/Diagnosis: Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 63 |
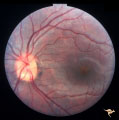 |
Visible Drusen with Visual Field Loss | Left eye.16 year old girl: PP26b: buried drusen at the lower pole of the disc; PP26a: Visible drusen with visual field loss. Notice the thinning of the nerve fibers in both the superior and inferior arcuate bundles. PP26c: Goldmann visual field. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic ... | Image |
| 64 |
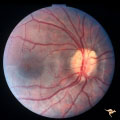 |
Visible Drusen with Visual Field Loss | Right eye.16 year old girl: PP26a: Visible drusen with visual field loss. Notice the thinning of the nerve fibers in both the superior and inferior arcuate bundles. PP26b: buried drusen; PP26c: Goldmann visual field. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Druse... | Image |
| 65 |
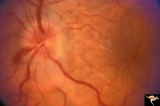 |
A101 Disc Swelling due to Intraocular Hypotension | Ocular hypotension following lens replacement surgery. Retinal/macular folds. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Disc edema. Disease/ Diagnosis: Intraocular hypotension. Clinical: Low intraocular pressure or intraocular hypotension. | Image |
| 66 |
 |
H06 Panhypoplasia | Bilateral hypoplasia. Top is Right eye - moderate. Bottom is Left eye - severe. Note venous tortuosity. Good example of double ring sign. De Morsier's syndrome.Septo-optic dysplasia. Same patient as H_7. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. ... | Image |
| 67 |
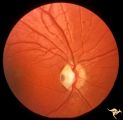 |
C06 Pits of the Optic Disc | Right eye. Temporal pit. 6 year old with see-saw nystagmus. Anatomy: Optic disc. Clinical: Six-year old with see-saw nystagmus. | Image |
| 68 |
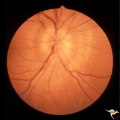 |
A201 Disc Swelling with Big Blind Spot Syndrome | Blind spot larger than could be explained by visible edema. Subretinal white dots probably indicate margin of blind spot. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Unknown. Disease/ Diagnosis: Big blind spot syndrome. Clinical: symptoms: photosias, blurred vision signs: Disc swelling; white spots in t... | Image |
| 69 |
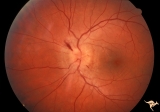 |
A202 Disc Swelling with Big Blind Spot Syndrome | Blind spot larger than could be explained by visible disc edema. Reference: Fletcher WA, Imes RK, Goodman D, Hoyt WF. Acute idiopathic blind spot enlargement. A big blind spot disc edema. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988 Jan;106(1):44-9. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Unknown. Disease/ Diagnosis: Big ... | Image |
| 70 |
 |
A203 Disc Swelling with Big Blind Spot Syndrome | Slight inferior swelling in patient with grossly enlarged blind spot. 66 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Unknown. Disease/ Diagnosis: Big blind spot syndrome. Clinical: symptoms: photopsias; blurred vision signs: disc swelling; white dots in the retina; enlarged blind spot on... | Image |
| 71 |
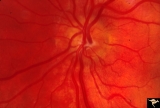 |
Crowded Disc (Family) | Anomalous vasculature with congenital disc margin blurring. Note optic cup is absent. Pair with brother in PP1a & b. Mother has drusen of the optic disc in PP11aa & b. Sister has drusen in PP11c. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variant. Cause of appearance is too many fibers entering into a s... | Image |
| 72 |
 |
PP8a Crowded Disc with Significant Nasal Disc Blurring | Congenital nasal disc blurring. Myopic eyes. Thai girl patient. One wonders about vitreal adherence to the disc. PP 8a right eye. Pair with left eye in PP8b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurre... | Image |
| 73 |
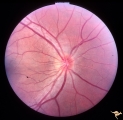 |
Congenitally Crowded Disc - Little Red Disc | Right eye: "little red disc". Congenitally blurred disc. 26 year old man. Anatomy: Optic disc Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc Disease/Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurred disc. Little red disc. | Image |
| 74 |
 |
Buried Drusen | 5 year old boy. Bilateral buried drusen. Notice the lumpy nasal disc elevation. This patient had a twin brother whose optic disc drusen were exposed. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical notes: Normally functioning eye with ... | Image |
| 75 |
 |
Buried Drusen | 5 year old boy. Bilateral buried drusen. Notice the lumpy nasal disc elevation. This patient had a twin brother whose optic disc drusen were exposed. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical notes: Normally functioning eye with ... | Image |
