Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 476 |
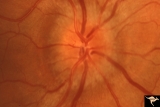 |
D103 Disc Edema with Systemic Lupus | 28 year old woman with systemic Lupus erythematosus. Vision 20/20 but blind spot enlarged. Same patient as D1_02. Magnified. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to vasculitis (Lupus). Disease/ Diagnosis: Lupus papillopathy. Clinical: Normal vision with enlarged blind spot on visual... | Image |
| 477 |
 |
Early Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Resolving | Left eye. Same eye as P_34a. One month post op, papilledema resolving. Boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema from posterior fossa hemangioblastoma. | Image |
| 478 |
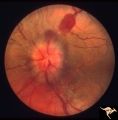 |
Early Papilledema due to Tumor | Left eye. Asymmetric Papilledema with posterior fossa hemangioblastoma. Left - moderate papilledema. Blurring of disc. Young man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema from posterior fossa hemangioblastoma. | Image |
| 479 |
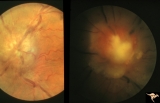 |
F2b09 Optic Disc Swelling from Malignant Optic Nerve Glioma | Malignant optic nerve glioma of adulthood with blindness and optic disc edema. Right image shows white material extruded from the swollen optic disc. This material is myelin being squeezed into the eye from the nerve infarction. Autopsy specimen of this eye shown in F2b_10. Reference: Hoyt WF, Meshe... | Image |
| 480 |
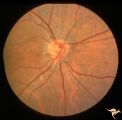 |
H77 Inferior Segmental Optic Hypoplasia (ISOH) | ISOH. Superior visual field defect. Inferior choroidal crescent. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Inferior segmental optic hypoplasia (ISOH). Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 481 |
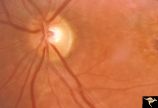 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 482 |
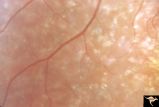 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 483 |
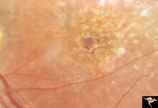 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 484 |
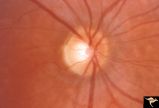 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 485 |
 |
PP7a Crowded disc | PP7a: right eye crowded disc with blurred margin. Note anomalous vascular pattern and glial tissue on the disc; PP7b- left disc is cupless disc and normal. 10 year old girl with gonadal dysgenesis and growth retardation. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Di... | Image |
| 486 |
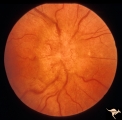 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye.Chronic Papilledema in right eye. Woman. Pseudo Foster Kennedy due to asymmetric papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri) causing pseudo Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: ... | Image |
| 487 |
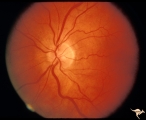 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Flat cupless disc. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri) causing pseudo Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: Visual loss in atrophic eye; obese. | Image |
| 488 |
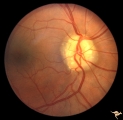 |
Vascular Complications of Drusen: Drusen Causing Loss of Superior Retinal Arterial Supply | PP32a: right; PP32b: left eye. Right eye is an obvious drusen disc. Patient had marked field defects. Left eye has occlusion of superior branch of the central retinal artery at 11:30 with the inferior retinal artery supplying collateral to the superior retina. Notice the branch of the inferior ret... | Image |
| 489 |
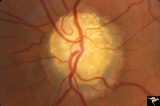 |
Vascular Complications of Drusen: Drusen Causing Loss of Superior Retinal Arterial Supply | PP32a: right; PP32b: left eye. Left eye has occlusion of superior branch of the central retinal artery at 11:30 with the inferior retinal artery supplying collateral to the superior retina. Notice the branch of the inferior retinal artery moves superiorly heading toward the upper retina. Drusen w... | Image |
| 490 |
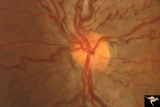 |
Venous Anomalies - Congenital Venous Tortuosity | Congenital venous tortuosity. Magnified slide. Same eye as V_53. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital venous tortuosity. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital venous tortuosity. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 491 |
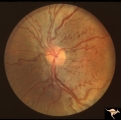 |
Venous Anomalies - Congenital Venous Tortuosity | Congenital venous tortuosity in a young girl with a cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM). Same eye as V_55. This does not represent a Wyburn-Mason Syndrome. It was a congenital retinal venous anomaly, not a retinal AVM. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital venous tortuosity. Disease/Diag... | Image |
| 492 |
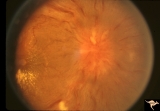 |
F205 Optic Nerve Sheath Meningioma | Optic nerve meningioma of right optic nerve. Progressive visual field loss. Notice macular star and "cotton wool" spots. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic optic disc swelling caused by optic nerve sheath meningioma. Disease/ Diagnosis: Chronic optic disc swelling caused by optic nerve sheath m... | Image |
| 493 |
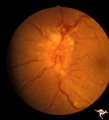 |
F206 Intracavernous Meningioma Extending Into the Orbit | Intracavernous meningioma extending into the orbit. Female patient. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Intracavernous meningioma. Disease/ Diagnosis: Neoplastic papillopathy. | Image |
| 494 |
 |
Medullated Nerve Fibers with Papilledema | Left eye. papilledema only. Man with metastatic gastric carcinoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema plus medullated nerve fibers. | Image |
| 495 |
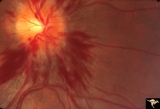 |
Bilateral Hemorrhagic Papilledema from Saggital Sinus Thrombosis | Left eye. 20 year old woman on oral contraceptives. Bilateral hemorrhagic Papilledema from sagittal sinus thrombosis. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema; hemorrhagic papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Superior saggital sinus thrombosis due to BCP use. Clinical notes: Chronic headache. | Image |
| 496 |
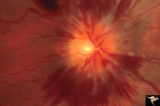 |
Bilateral Hemorrhagic Papilledema from Saggital Sinus Thrombosis | Right eye. 20 year old woman on oral contraceptives. Bilateral hemorrhagic Papilledema from sagittal sinus thrombosis. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema; hemorrhagic papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Superior sagittal sinus thrombosis due to BCP use. Clinical notes: Chronic headache. | Image |
| 497 |
 |
Medullated Nerve Fibers with Papilledema | Right eye. Papilledema superimposed upon medullated nerve fibers. Man with metastatic gastric carcinoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema plus medullated nerve fibers. | Image |
| 498 |
 |
C33 Anomalous Pale Disc | Woman. Multiple cilioretinal arteries. Veins all empty into eye. Anomalous venous exit from nasal edge of optic disc. Visual function normal. Pair with C_36. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 499 |
 |
C36 Anomalous Pale Disc | Multiple cilioretinal arteries. Pale appearance. Normal optic nerve function. Good example of "empty disc". Pair with C_33. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 500 |
 |
Bilateral Papilledema from Pseudotumor | Right eye. Pseudotumor syndrome. Multiple endocrine adenomas. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Bilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Pseudotumor associated with multiple endocrine adenomas. Clinical notes: Headache; Obesity. | Image |
