A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
The Canalith Repositioning Maneuver/Epley Maneuver for Right Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo | Posterior canal (PC) accounts for 70-90% cases of BPPV [1-3] and resolves with canalith repositioning maneuvers 90% of the time [4-20]. The Epley maneuver is considered a gold-standard treatment, with class 1 evidence for use. | Text |
| 27 |
 |
The Gans Maneuver for Right Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo | This maneuver is recommended for individuals with cervical restrictions or precautions, as the maneuver avoids cervical hyperextension and may reduce cervical pain associated with repositioning maneuvers. The Epley maneuver has higher subjective and objective success rates compared to the Gans maneu... | Text |
| 28 |
 |
Gufoni Maneuver for Right Horizontal Canal-Cupulolithiasis (Apgeotropic Nystagmus) | The Gufoni Maneuver can be used to treat horizontal canal cupulolithaisis. 1. The patient starts in a seated position. 2. The patient transitions quickly to lying on their affected side. 3. The patient lies on their affected side for two minutes with the head in a neutral position. 4. The patient's ... | Text |
| 29 |
 |
Kim Maneuver for Anterior Canal BPPV | The Kim Maneuver for Anterior Canal can be used to treat individuals with anterior canal BPPV. 1. The patient's head is turned 45 degrees towards the unaffected side. 2. The patient transitions into a supine position with the head hanging 30 degrees below the horizon. 3. After two minutes, the head ... | Text |
| 30 |
 |
The Kim Maneuver for Right Horizontal Cupulolithiasis | The Kim Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal cupulolithiasis cases where the otoconia may be located on either side of the cupula. 1. The patient begins in a supine position. 2. The patient's head is turned 135 degrees towards the affected side and oscillation is applied to the affected side f... | Text |
| 31 |
 |
Modified Zuma for Right Horizontal Canal Canalithiasis (Geotropic Nystagmus) | The Modified Zuma maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal canalithiasis (geotropic nystagmus. 1. Patient begins in a seated position. 2. The patient's head is rotated 45 degrees towards the unaffected side. 3. The patient transitions to lying on their affected side and maintains this position for... | Text |
| 32 |
 |
Right Dix Hallpike Test | The Dix-Hallpike tests for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). A test is positive when a patient reports vertigo, dizziness, or sensation of movement or falling with nystagmus present. When the head is in this position, it allows the posterior canal to be aligned with the gravitational vect... | Text |
| 33 |
 |
Right Half Hallpike Test | The Half Hallpike Test compliments the Dix Hallpike Test and is traditionally used to assist with the diagnosis of posterior canal-benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BC-BPPV), cupulolithiasis, as it may produce a greater degree of deflection under the action of gravity without latency when the ot... | Text |
| 34 |
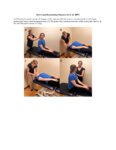 |
Short Canal Repositioning Maneuver for Anterior Canal BPPV | The Short Canal Repositioning Maneuver is used to treat anterior canal BPPV. 1. The patient's head is rotated 45-degrees towards the affected side. 2. The patient's maintains head in a 45-degree position and enters a head hanging position (40 degrees below the horizontal). 3. The patient then mainta... | Text |
| 35 |
 |
Side-lying Test for Right BPPV | The side-lying test is an alternative for the Dix Hallpike Test as it reduces the need for cervical extension. The interpretation of a positive test is the same as the Dix Hallpike Test. | Text |
| 36 |
 |
Square Wave Maneuver for Apogeotropic Horizontal Canal BPPV | The square wave maneuver is designed to treat individuals with horizontal canal cupulolithaisis and is commonly used when individuals have cervical restrictions and the affected side is not well identified at baseline. 1. The patient begins in the supine position with the head 20 to 30 degrees above... | Text |
| 37 |
 |
Supine Head-Hanging Test | The supine head-hanging test is more sensitive for AC-BPPV, but it does not differentiate laterality, as both canals are stimulated at the same time [1-3]. When the individual returns to a seated position, the otoconia should hypothetically move closer to the utricle, which continues their ampullofu... | Text |
| 38 |
 |
Supine Roll Test/Pagnini-McClure Test | The supine roll test or the Pagnini-McClure Test is used to assess for horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. A test is positive when a patient reports vertigo, dizziness, or sensation of movement or falling with nystagmus present. Apogetropic nystagmus is indicative of cupulolithias... | Text |
| 39 |
 |
Test of Latency | The Test of Latency is used to identify which side is involved for patients with horizontal canal BPPV and is used in conjunction with the Supine Roll Test. For canalithiasis, lateralization is considered the side with a shorter latency time. For cupulolithasis, lateralization is considered the side... | Text |
| 40 |
 |
Yacovino Maneuver or the Deep Head Hanging Maneuver for Anterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo | The Yacovino maneuver is used to treat anterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (AC-BPPV) and does not require the clinician to distinguish which side is involved. Additionally, when the patient completes cervical flexion, the motion may cause otoconial debris to enter the posterior semi... | Text |
| 41 |
 |
Zuma Maneuver for Right Horizontal Canal Cupulolithiasis (Apogeotropic Nystagmus) | The Zuma Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal cupulolithiasis (apogeotropic nystagmus). 1. The patient begins in a seated position. 2. The patient transitions quickly to lying position on their affected side, with their head in neutral, and maintains this position for three minutes. 3. The pat... | Text |
| 42 |
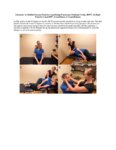 |
Liberatory or Modified Semont, Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) for Right Posterior Canal BPPV (Canalithiasis or Cupulolithiasis) | Posterior canal (PC) accounts for 70-90% cases of BPPV [1-3] and resolves with canalith repositioning maneuvers 90% of the time [4-13]. The Semont/Liberatory maneuver is considered a gold-standard treatment, with class 1 evidence for use and success rates close to 90% [4-13].The Liberatory maneuver ... | Text |
| 43 |
 |
Li Maneuver for Geotropic Right HC-BPPV, Canalithiasis | The Li maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal, canalithiasis. When compared to the Gufoni maneuver, the Li maneuver was as effective to treat HC-BPPV and there was no significant difference between the maneuvers; however, the Li Maneuver may take less time to complete. 1. The patient starts in a... | Text |
| 44 |
 |
Gufoni Maneuver for Left Horizontal Canal BPPV, Canalithiasis (Geotropic Nystagmus) | The Gufoni maneuver may be preferable to the BBQ roll, as the Gufoni maneuver does not require the individual to roll or be in a prone position, making the maneuver more feasible to complete for individuals who are elderly, obese and/or experience immobility. Antecedently, some clinicians remember t... | Text |
| 45 |
 |
Brandt-Daroff Exercises | Brandt-Daroff exercises are less effective than the Epley and the Semont maneuvers and are not shown to prevent recurrence [1-3]. Brandt-Daroff exercises may still be beneficial for habituation exercises and to reduce phobic responses to lying supine or side-lying after the resolution of BPPV. This ... | Text |
| 46 |
 |
BBQ Roll for Right Horizontal Canal BPPV, Canalithiasis (Geotropic Nystagmus) | The BBQ Roll/Lampert Maneuver has been shown to be an effective treatment and is supported by a level I classification study. 1. The patient starts in a supine position with the head positioned 30 degrees above the horizon. 2. While maintaining head elevation, the patient's head (or whole body) is r... | Text |
