A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_gold"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
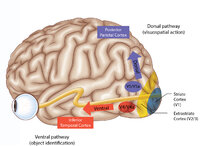 |
Figure 43: How the Brain Makes Sense of What It Sees - The Dorsal and Ventral Visual Pathways, and a 3 Tiered Approach to Vision | 1) Ventral ("what") stream - this begins with the ‘P' retinal ganglion cells à parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN, 3-6) à V1/striate cortex (in blue) à V4/V4a (fusiform and lingual gyri) à occipitotemporal regions. 2) Dorsal ("where") stream - this begins with the ‘M... | Image |
| 27 |
 |
Five Common Ocular Motor Signs in Cerebellar Disorders - Saccadic Hypermetria, Saccadic Pursuit & VOR Suppression, Gaze-evoked & Rebound Nystagmus | (1) Saccadic hypermetria - an overshoot of the visual target (2) Saccadic smooth pursuit - due to impaired pursuit and low gain, saccades are needed to keep up with the visual target. This gives it a ‘choppy' appearance. (3) Saccadic vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) suppression - another... | Image/MovingImage |
| 28 |
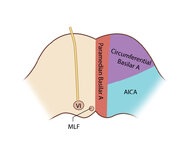 |
Figure 61: Vascular Distribution and Anatomy (Including 6th, 7th, 8th Nerves, MLF) of the Pons (Supplement) | Image | |
| 29 |
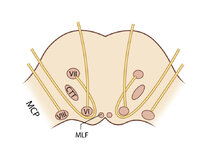 |
Figure 61: Vascular Distribution and Anatomy (Including 6th, 7th, 8th Nerves, MLF) of the Pons (Supplement) | Image | |
| 30 |
 |
CANVAS (Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, and Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome) Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) Figure | CANVAS (Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, and Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome) is a genetic condition consisting of slowly progressive late-onset ataxia, bilateral vestibulopathy, sensory neuropathy, chronic cough, and autonomic dysfunction. While the term vestibular areflexia typically implies bilateral... | Image |
| 31 |
 |
Abnormal Visually-enhanced Vestibulo-ocular Reflex (vVOR) in Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome (CANVAS) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This patient complained of chronic (unexplained cough), progressive numbness in the legs and feet, gait instability, and oscillopsia when walking or with head movements. Examination showed excessive square-wave jerks, bil... | Image/MovingImage |
| 32 |
 |
Assessing Utricle Pathway Function and the Effects of Convergence on Nystagmus in Acute Vestibular Neuritis | A 35-year-old woman presented a few days after the onset of room-spinning vertigo. She denied diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia, dysphonia, incoordination, numbness, and weakness. On examination, she had subtle spontaneous right-beat nystagmus (RBN). This nystagmus increased in amplitude and frequency... | Image/MovingImage |
| 33 |
 |
Upbeat Transitioning to Downbeat Nystagmus in Wernicke's Encephalopathy | This is a 30-year-old man with a history of alcohol abuse who presented to the hospital with inability to walk after several weeks of heavy drinking and malnutrition. While in the hospital, he noted that when he would look straight ahead, everything he saw would appear to be bouncing up and down - a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 34 |
 |
ENG, VNG, & VOG | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Electronystagmography (ENG), and videonystagmography (VNG) or videooculography (VOG) are a collection of tests of eye movements that are performed either using surface electrodes around the eye (ENG) or with video goggles... | Text |
| 35 |
 |
Provocative Maneuvers (Removal of Fixation, Vibration, Head-Shaking) to Accentuate Peripheral Vestibular Nystagmus) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: With an acute destructive process like vestibular neuritis that causes significant unilateral vestibular loss, spontaneous nystagmus is always present. However, over days to months, spontaneous nystagmus should resolve co... | Image/MovingImage |
| 36 |
 |
PSP with Vertical Gaze Palsy, Abnormal Optokinetic Nystagmus and Inability to Suppress Blinking to Light | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 75-year-old woman with a diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Examination demonstrated vertical supranuclear gaze palsy (i.e., it could be overcome by the vertical vestibulo-ocular reflex [VOR]), s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 37 |
 |
Slow Volitional Saccades and Poor Fast Phases to an Optokinetic Stimulus, with Preserved Head Impulse Testing | This is a 67-year-old woman presenting with imbalance and binocular horizontal diplopia at near. On examination there were frequent square wave jerks, limited supraduction OU and convergence insufficiency, which explained her diplopia. Pursuit and suppression of the vestibulo-ocular reflex were sa... | Image/MovingImage |
| 38 |
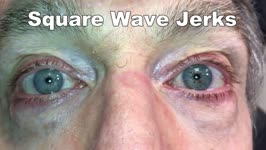 |
Saccadic Intrusions (Square Wave Jerks, SWJ) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are SWJ, which is the most common example of a saccadic intrusion. Here the patient is fixating on the camera, and all of the sudden a saccade takes the eyes off the fixation target, there's a brief intersaccadi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 39 |
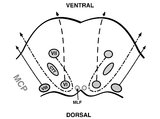 |
Pons: 6th, 7th, 8th, and Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Anatomy | From this cross-section of the pons, the proximity of the 7th and 8th fascicles can be appreciated, and a lateral inferior pontine syndrome (anterior inferior cerebellar artery territory), which could involve both of these fascicles, could cause acute prolonged vertigo accompanied by a + ipsilateral... | Image |
| 40 |
 |
The Most Common Audiovestibular Laboratory Tests, and the Specific Conditions in Which They May Assist in Making or Supporting the Diagnosis | VN = vestibular neuritis; VM = vestibular migraine; VP = vestibular paroxysmia; vHIT = video head impulse test; VNG = video-nystagmography; ENG = electronystagmography; VOG = video-oculography; VEMPs = vestibular evoked myogenic potentials; SCDS = superior canal dehiscence syndrome; BPPV = benign pa... | Text |
| 41 |
 |
The Most Common Vestibular Conditions Categorized by Timing and Triggers, with Specific Ocular Motor and Vestibular Features that Should be Sought for Each | HINTS+ = Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew, ‘Plus' bedside assessment of auditory function; HIT = head impulse test; NP = nerve palsy; BPPV = benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; SCDS = superior canal dehiscence syndrome; BVL = bilateral vestibular loss; PPPD = persistent postural perceptual ... | Text |
| 42 |
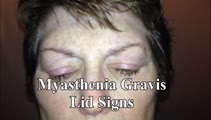 |
Typical Lid Signs (Cogan's Lid Twitch, Lid Hopping, Enhanced Ptosis) in Myasthenia Gravis | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-yo-woman with MG who displays typical eyelid signs including Cogan's lid twitch, lid hopping (appreciated during horizontal smooth pursuit in this patient), and enhanced ptosis in accordance with Hering's law... | Image/MovingImage |
| 43 |
 |
Anterior Canal BPPV | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Although the anterior canal (AC) variant of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is rare, mainly owing to its orientation relative to gravity (which makes otoconial debris much less likely to enter it), it can occu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 44 |
 |
Posterior Canal BPPV Treated with Semont Maneuver | This is a patient with left posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), and upbeat-torsional (towards the left ear) nystagmus was provoked by left Dix-Hallpike maneuver and left side-lying maneuver. This video demonstrates treatment of her left PC BPPV with the Semont maneuver.... | Image/MovingImage |
| 45 |
 |
Test Your Knowledge - Oscillopsia | This 65-year-old man with multiple sclerosis described that objects in front of him appear to spontaneously jump or move horizontally for the last few months. He reported that his symptoms occur independent of head movements and head impulse testing was normal. After viewing the video, what is the m... | Image/MovingImage |
| 46 |
 |
Vertical Vergence and Fusional Amplitude | Essential information on vertical fusional vergences. | Text |
| 47 |
 |
Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials (VEMPs) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials (VEMP) are electromyographic potential reflex tests that reflect the function of the saccule in cervical VEMP and the utricle in ocular VEMP.1 In the cervical VEMP an inhibitory refle... | Text |
| 48 |
 |
Pseudonystagmus Due to Bilateral Vestibular Loss and Head Tremor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 65-yo-woman with complaints of imbalance, dizziness, and horizontal oscillopsia. On exam, she had a high frequency, low amplitude (mainly horizontal) head tremor, and with ophthalmoscopy, the optic nerve was cle... | Image/MovingImage |
| 49 |
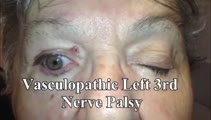 |
3rd Nerve Palsy With Preserved 4th Nerve Function | 80-yo-woman with a left vasculopathic 3rd nerve palsy (minimal pupil involvement of about 1 mm relative mydriasis OS - other etiologies ruled out and resolved as expected over months). Although the inferior rectus is paretic, intact superior oblique muscle function can be demonstrated by asking the ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 50 |
 |
6th Nerve Palsy as Initial Presentation of Metastatic Lung Cancer | A video describing 6th nerve palsy as initial presentation of metastatic lung cancer. | Image/MovingImage |
