Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
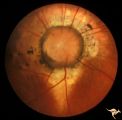 |
C13 Morning Glory Disc | "Morning Glory" disc with peripapillary choroidal defect extending inferiorly. Patient has transphenoidal encephalocele. Note tapering edge like an arrow pointing to patient's basal encephalocele and cleft palate. Reference: Brodsky MC, Hoyt WF, Hoyt CS, Miller NR, Lam BL. Atypical retinochoroidal ... | Image |
| 27 |
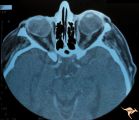 |
H41 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal, Tilted (Dysverted) Disc | CT scan of patient in H_40 showing marked nasal ectasia of the eyeballs. CT scan shows obliquely inserted optic nerves and marked nasal dysplasia of the eyeballs. Anatomy: Optic disc; retina. Pathology: Hypoplasia secondary to retinal lesion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Segmental optic disc hypoplasia. Imag... | Image |
| 28 |
 |
H39 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal, Tilted (Dysverted) Disc | Visual field of patient in H_38 showing upper temporal field depression caused by inferior nasal hypoplasia. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Hypoplasia secondary to retinal lesion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Segmental optic disc hypoplasia. Clinical: Man with bitemporal visual field defects. | Image |
| 29 |
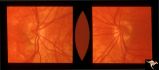 |
H37 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal, Tilted (Dysverted) Disc | Tilted (dysverted) disc in patient with high myopia. Note inferior nasal crescents with accompanying segmental hypoplasia. Man with bitemporal visual field defect. Anatomy: Optic disc, retina. Pathology: Hypoplasia secondary to retinal lesion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Segmental optic disc hypoplasia. Cli... | Image |
| 30 |
 |
H40 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal, Tilted (Dysverted) Disc | 60 year old woman with incidental bitemporal visual field depression. Extreme tilting of optic disc with inferior nasal segmental hypoplasia. Nasal retinal ectasia. Same patient as H_41. Anatomy: Optic disc; retina. Pathology: Hypoplasia secondary to retinal lesion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Segmental opt... | Image |
| 31 |
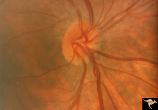 |
H38 Segmental Hypoplasia; Retinal; Tilted (Dysverted) Disc | Right eye. Man with tilted (dysverted) disc with inferior nasal crescent and high myopia. Same patient as H_39. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Hypoplasia secondary to retinal lesion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Segmental optic disc hypoplasia. Clinical: Man with bitemporal visual field defects. | Image |
| 32 |
 |
Post Papilledema, Secondary Optic Atrophy | Right eye. Post papilledema with chronic gliosis. arterial narrowing. ""high-water"" marks. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with optic atrophy. | Image |
| 33 |
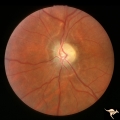 |
Post Papilledema, Secondary Optic Atrophy | Left eye. Post papilledema with chronic gliosis. arterial narrowing. "high-water" marks. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with optic atrophy. | Image |
| 34 |
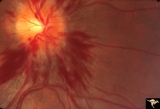 |
Bilateral Hemorrhagic Papilledema from Saggital Sinus Thrombosis | Left eye. 20 year old woman on oral contraceptives. Bilateral hemorrhagic Papilledema from sagittal sinus thrombosis. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema; hemorrhagic papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Superior saggital sinus thrombosis due to BCP use. Clinical notes: Chronic headache. | Image |
| 35 |
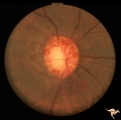 |
IC102c Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with Cilioretinal Collaterals | Right eye, 1982, Central retinal artery occlusion with cilioretinal collateral occlusions due to calcific embolic occlusion behind the lamina cribrosa due to calcific valvular heart disease. Collaterals have been called "Nettleship Collaterals", recognizing the British physician who first described ... | Image |
| 36 |
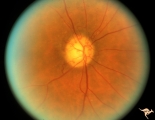 |
IC102b Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with Cilioretinal Collaterals | Right eye, 1991, Central retinal artery occlusion with cilioretinal collateral occlusions due to calcific embolic occlusion behind the lamina cribrosa due to calcific valvular heart disease. Collaterals have been called "Nettleship Collaterals", recognizing the British physician who first described ... | Image |
| 37 |
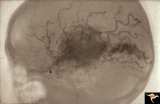 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Wyburn-Mason Syndrome. Angiogram showing extension of vascular malformation up the right optic nerve (arrow) through the thalamus and into the right visual cortex. References #3 and #73. Anatomy: Brain. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wy... | Image |
| 38 |
 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Partially involved. Same patient as V_27. Anatomy: Optic disc; Brain. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation of retina and brain. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn-Mason syndrome. Clinical: Blindness in the involved eye, proptosis. | Image |
| 39 |
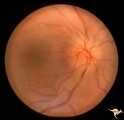 |
Bilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Bilateral Papilledema with hypoparathyroidism. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema with hypoparathyroidism. | Image |
| 40 |
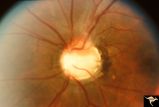 |
C08 Pits of the Optic Disc | Left eye. Large cavitary anomaly (pit). Man. 20/100 visual acuity. Superior nasal visual field defect. May not have a central retinal artery. Anatomy: Optic disc. Clinical: Man. 20/100 visual acuity. Superior nasal visual field defect. | Image |
| 41 |
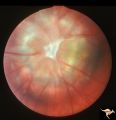 |
C17 Morning Glory Disc | "Morning Glory" disc. CT normal. Anatomy: Optic disc. Clinical: CT normal. | Image |
| 42 |
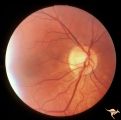 |
C38 Anomalous Pale Disc | Megalopapilla in -8 myopic eye. Right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Clinical: High myope. | Image |
| 43 |
 |
Cyanotic Heart Disease with Clubbing of Fingernails | Note the cyanotic nail beds and clubbing. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Pseudotumor due to cyanotic heart disease. Clinical: Young boy with clubbing. | Image |
| 44 |
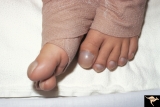 |
Cyanotic Heart Disease with Clubbing of Toes | Bilateral Papilledema with cyanotic heart disease. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Pseudotumor due to cyanotic heart disease. Clinical: Young boy with clubbing. | Image |
| 45 |
 |
Familial Drusen | Right eye: Mother with obvious optic nerve drusen. Note the blurred temporal margin where buried drusen can not be seen.; PP_11b: mother visible drusen; Buried drusen; lumpy disc. Combine with PP_1a & b and PP_2 (sons) and PP_11c (daughter). Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic dis... | Image |
| 46 |
 |
Familial Drusen | Left eye. PP_11b: Mother visible drusen; buried drusen; lumpy disc. PP_11a: Mother with obvious optic nerve drusen; Combine with PP_1a & b and PP_2 (sons) and PP_11c (daughter). Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Congen... | Image |
| 47 |
 |
H05 Panhypoplasia | Right eye. Distinctive septo-optic dysplasia.Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Left eye normal. Amblyopic right eye. 24 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 48 |
 |
H19 Panhypoplasia | Mild hypoplasia with dysplasia in right eye. Right eye. Normal left eye. Same patient as H_20. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 49 |
 |
H20 Panhypoplasia | Mild hypoplasia with dysplasia in right eye. Left eye. Same patient as H_19. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 50 |
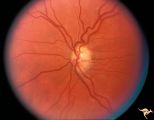 |
H52 Superior Segmental Optic Hypoplasia (SSOH) Topless Disc Syndrome | High exit point of central retinal vessels. Superior choroidal crescent. Complete loss of nerve fiber layer entering disc from above. Inferior altitudinal field defect. Type 1 diabetic mother. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Superior segmental optic hypoplasia (SSOH). Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital ... | Image |
