AAO-NANOS Neuro-Ophthalmology Clinical Collection: Derived from the AAO-NANOS Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology collection produced on CD. The images are of selected cases from the NANOS teaching slide exchange, and the CD was produced under the direction of Larry Frohman, MD and Andrew Lee, MD.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO); The North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Association (NANOS).
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Creator | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 276 |
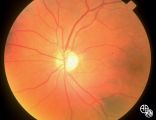 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Roger Turbin, MD | Shown are the fundi of a - year old child with dominant optic atrophy, 20/200 OU. Pair with 1996_59. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital optic atrophy. |
| 277 |
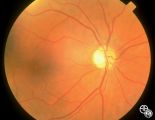 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Roger Turbin, MD | Shown are the fundi of a - year old child with dominant optic atrophy, 20/200 OU. Pair with 1996_60. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital optic atrophy. |
| 278 |
 |
Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Disorders | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Myasthenia gravis should be considered in any patient with painless, pupil-spared, nonapoptotic ophthalmoplegia. It may mimic any ophthalmoparesis. Involvement of the medical rectus may result in a pseudointernuclear ophthalmoplegia. Pair with 96_24 and 96_25. |
| 279 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Traumatic damage to the third cranial nerve may result in aberrant regeneration of fibers that innervate the eyelid, pupil, or extraocular muscles. For instance, there may be lid retraction in attempted downgaze. Any combination of aberrant activation of third nerve-innervated structures may occur, ... |
| 280 |
 |
Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Disorders | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Myasthenia gravis should be considered in any patient with painless, pupil-spared, nonapoptotic ophthalmoplegia. It may mimic any ophthalmoparesis. Involvement of the medical rectus may result in a pseudointernuclear ophthalmoplegia. Pair with 96_23 and 96_25. |
| 281 |
 |
Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Disorders | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Myasthenia gravis should be considered in any patient with painless, pupil-spared, nonapoptotic ophthalmoplegia. It may mimic any ophthalmoparesis. Involvement of the medical rectus may result in a pseudointernuclear ophthalmoplegia. Pair with 96_23 and 96_24. |
| 282 |
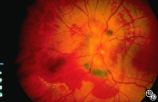 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Papilledema may produce visual loss due to chronic atrophic papilledema, secondary macular hemorrhage, exudate or edema, secondary ischemic optic neuropathy, or secondary subretinal neovascular membrane formation. |
| 283 |
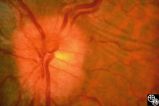 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Papilledema in pseudotumor cerebri may result in adjacent choroidal or retinal folds. |
| 284 |
 |
Isolated Congenital Optic Disc Anomalies | Rosa A. Tang, MD | This patient has optic disc drusen and evidence of a superimposed optic neuropathy, including loss of visual field, an ipsilateral afferent pupillary defect, and optic atrophy. Although optic disc drusen typically causes visual field loss without visual acuity loss superimposed, ischemic optic neuro... |
| 285 |
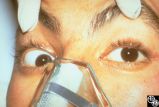 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Skew deviation is a vertical deviation that is not localized to any one muscle or muscle group. The deviation may be comitant or not, and intermittent or constant. Skew deviation is often defined by the company it keeps, that is, skew usually occurs in association with other brain-stem signs, and is... |
| 286 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Skew deviation is a vertical deviation that is not localized to any one muscle or muscle group. The deviation may be comitant or not, and intermittent or constant. Skew deviation is often defined by the company it keeps, that is, skew usually occurs in association with other brain-stem signs, and is... |
| 287 |
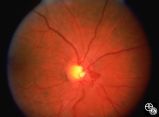 |
Acquired Disc Changes | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Although optociliary shunt vessels are venous collaterals that typically form in response to chronic venous obstruction, they may occur on a congenital basis as seen here. |
| 288 |
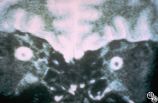 |
Isolated Optic Neuritis/Neuropathy | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Papilledema is a term reserved for optic disc edema related to increased intracranial pressure. Fluid within the optic nerve sheath or elevation of the intraocular optic nerve head may be visible on magnetic resonance imaging studies of the head and orbit. |
| 289 |
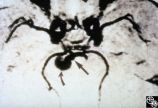 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Imaging-MRI | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Aneurisms may result in neuro-ophthalmologic sign and symptoms by direct compression of the afferent or efferent systems or by the secondary effects of hemorrhage. Basilar aneurisms may result in ocular motor deficits such as a unilateral or bilateral third nerve palsy. |
| 290 |
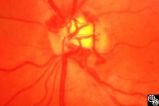 |
Acquired Disc Changes | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Optociliary shunt vessels are venous collaterals that form in response to chronic venous obstruction. They may occur in patients following central retinal vein occlusion. |
| 291 |
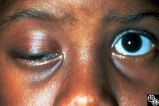 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Cyclical oculomotor paresis may occur in patients as an intermittent phenomenon, with a paretic phase and diplopia and intervals that are nonparetic. The history and examination are classic for the disorder. Pair with Images 95_19 and 95_20. |
| 292 |
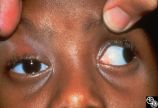 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Cyclical oculomotor paresis may occur in patients as an intermittent phenomenon, with a paretic phase and diplopia and intervals that are nonparetic. The history and examination are classic for the disorder. Pair with Images 95_18 and 95_19. |
| 293 |
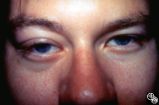 |
Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Disorders | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Systemic lymphoma may occur in the orbit and may involve the lacrimal gland. Patients usually present with a painless, progressive proptosis or a mass. CT scan usually demonstrates an irregularly shaped lesion conforming to the globe or lacrimal fossa, and bone erosion is not usually found. Pair wit... |
| 294 |
 |
Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Disorders | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Systemic lymphoma may occur in the orbit and may involve the lacrimal gland. Patients usually present with a painless, progressive proptosis or a mass. CT scan usually demonstrates an irregularly shaped lesion conforming to the globe or lacrimal fossa, and bone erosion is not usually found. Pair wit... |
| 295 |
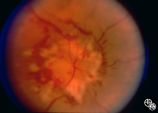 |
Systemic Disorders With Optic Nerve and Retinal Findings | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Neoplasms may result in an optic neuropathy by direct metastatic involvement. In this patient, a lung adenocarcinoma was metastatic to the optic nerve.This is a fundus photo. |
| 296 |
 |
Motility Disturbances | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Cyclical oculomotor paresis may occur in patients as an intermittent phenomenon, with a paretic phase and diplopia and intervals that are nonparetic. The history and examination are classic for the disorder. Pair with Images 95_18 and 95_20. |
| 297 |
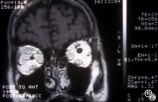 |
Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Disorders | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Thyroid eye disease may cause proptosis and extraocular muscle enlargement that may be seen on orbital imaging studies. In general, coronal images allow the best visualization of the extraocular muscle enlargement. Pair with 94_44 and 94_46. |
| 298 |
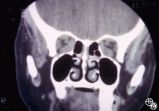 |
Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Disorders | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Thyroid eye disease may cause proptosis and extraocular muscle enlargement that may be seen on orbital imaging studies. In general, coronal images allow the best visualization of the extraocular muscle enlargement. Pair with 94_44 and 94_45. |
| 299 |
 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Imaging-MRI | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Aneurisms may result in neuro-ophthalmologic sign and symptoms by direct compression of the afferent or efferent systems or by the secondary effects of hemorrhage. Basilar aneurisms may result in ocular motor deficits such as a unilateral or bilateral third nerve palsy. |
| 300 |
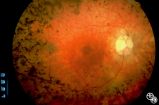 |
Optic Neuropathies | Rosa A. Tang, MD | Optic atrophy might be a false-localizing sign of optic nerve disease, as retinal disease may secondarily produce optic atrophy. In retinitis pigmentosa, for example, patients may exhibit a waxy disc palor. Fundus imaging. Anatomy: Retina. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa; Optic atrophy. |
