John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_novel_jmec
| Identifier | Title | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
 |
Nutritional amblyopia.pdf | Nutritional Amblyopia | Example of patient with amblyopia with nutritional causes. | Nutritional Optic Atrophy; Wernicke's Encephalopathy |
| 152 |
 |
2-17 | Ocular Flutter | Two examples of patients, the first with rotary, flutter-like movements, but not ocular flutter, and the second with genuine ocular flutter. Discussion of difference between ocular flutter and nystagmus, and how to elicit ocular flutter. | Ocular Flutter |
| 153 |
 |
1-9 | Ocular Lateropulsion (Wallenberg's Syndrome) | Example of patient with ocular lateropulsion. Patient also has central Horner syndrome and nystagmus in right gaze. When shifting gaze back to forward, eyes overshoot their mark. Eyes laterally deviate to the right upon opening. | Ocular Lateropulsion; Wallenberg's Syndrome; Lateropulsion; Lateral Medullary Syndrome; Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery; Wallenberg Syndrome |
| 154 |
 |
1-23 | Ocular Myasthenia | Example of patient with myasthenia gravis. Demonstration of tensilon test. Patient shown to have bilateral ptosis, bilateral duction deficits, and left hypertropia. Discussion of techniques to observe subtle changes, such as bringing in a neutral observer or taking still photographs. Shows split-scr... | Ocular Myasthenia; Myasthenia Gravis; Ptosis, Myasthenic; Tensilon Test |
| 155 |
 |
NOVEL_Moran_2-29 | Ocular Myotonia | Example of patient with ocular myotonia. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze and opening and closing of eyes. Right eye is shown to be stuck in position after held gaze to the left and right, with very slow relaxation back into forward gaze. | Ocular Myotonia; Ocular Neuromyotonia; Dystrophies |
| 156 |
 |
Oculopalatal-Myoclonus-Williams | Oculopalatal Myoclonus | Oculopalatal myoclonus (OPM) Rhythmic oscillations of eyes and palate. Occurred after specific brainstem injury from stroke, following stenting. Related PowerPoint Presentation: http://content.lib.utah.edu/u?/EHSL-Moran-Neuro-opth,129 Disease/Diagnosis: Oculopalatal myoclonus. | Oculopalatal Myoclonus |
| 157 |
 |
Oculopalatal_Myoclonus_LWilliams.pdf | Oculopalatal Myoclonus (PPT) | Oculopalatal myoclonus (OPM) Rhythmic oscillations of eyes and palate. Occurred after specific brainstem injury from stroke, following stenting. Related Video: http://content.lib.utah.edu/u?/EHSL-Moran-Neuro-opth,128 Disease/Diagnosis: Oculopalatal myoclonus | Oculopalatal Myoclonus |
| 158 |
 |
1-15b | Opsoclonus | Example of patients with opsoclonus, a saccadic abnormality. | Opsoclonus |
| 159 |
 |
1-15 | Opsoclonus | Example of patients with opsoclonus, a saccadic abnormality. Discussion of characteristics of opsoclonus, such as involuntary, rapid, brief, random, conjugate saccades. Discussion of possible causes, including brain stem encephalitis (as in first patient), a paraneoplastic effect, tumors, and drug t... | Opsoclonus |
| 160 |
 |
Optic Disc pallor pseudo and real.pdf | Optic Disc Pallor Pseudo and Real | Discussion of the causes of optic disc pallor. | Optic Disc; Optic Atrophy; Pallor |
| 161 |
 |
Optic disc anat variants ophthres 2012.pdf | Optic Disc: Anatomy, Variants, Unusual discs | Discussion of viewing the optic disc. Includes development of direct ophthalmoscope. Covers normal optic disc and nerve fiber; nerve fiber loss and defects; cilioretinal arteries; venous anomolies; papilledema; pseudopapilledema; myopic disc; hyperoptic disc; little red discs; megallopapilla; myelin... | Optic Disc; Anomolies; Anatomy |
| 162 |
 |
Optic nerve tumors benign and malignant.pdf | Optic Nerve Tumors Benign and Malignant | Discussion of optic nerve tumors including meningioma and glioma. | Optic Nerve Tumors |
| 163 |
 |
OV_Tom_Oberg_Orbital_Exam | The Orbital Exam | Comprehensive demonstration of the entire orbital examination. | Orbital Examination |
| 164 |
 |
Papilledema 2013.pdf | Papilledema 2013 | Discussion of papilledema, the swelling due to increased pressure. | Papilledema |
| 165 |
 |
1-4 | Paradoxical Constriction of Pupils to Darkness (Flynn Phenomenon) | Example of patients both with and without paradoxical constriction of pupils. Observed in many congenital retinal disorders, such as achromatopsia, congenital stationary night-blindness, and Leber's congenital amaurosis. Sometimes seen in optic nerve disorders, such as dominant optic atrophy. | Pupil; Flynn Phenomenon |
| 166 |
 |
1-16 | Parinaud's Syndrome | Two examples of patients with Parinaud's syndrome, a dorsal midbrain syndrome. Discussion of hallmarks of this syndrome, including convergence retraction nystagmus, vertical gaze palsies, light-near dissociation, and Collier's Sign. Discussion of age-dependent disorders associated with this syndrome... | Parinaud's Syndrome; Dorsal Midbrain Syndrome |
| 167 |
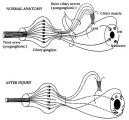 |
Figure-16 | Pathophysiology of Signs Associated with a Tonic Pupil | Pathophysiology of signs associated with a tonic pupil. Normally, all parasympathetic fibers of the third cranial nerve synapse in the ciliary ganglion (top). Most postganglionic fibers innervate the ciliary muscle (dashed lines). After injury to the ciliary ganglion, the pupil becomes denervated an... | Adie's Tonic Pupil; Pupil Disorders; Physiopathology, Iris; Pupil |
| 168 |
 |
2-12 | Periodic Alternating Nystagmus | Example of a patient with periodic alternating nystagmus, showing an alternation between left-beats and right-beats as the patient maintains forward gaze. Nystagmus maintain horizontal direction regardless of position of gaze. | Periodic Alternating Nystagmus |
| 169 |
 |
2-16 | Physiologic (End-Gaze) Nystagmus | Demonstration of physiological nystagmus, where oscillations do not represent pathology, but occur when the patient's gaze is drawn too far laterally. | End-Gaze Nystagmus; Physiologic Nystagmus |
| 170 |
 |
NOVEL_Moran_1-8 | Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | Progressive Supranuclear Palsy |
| 171 |
 |
1-14 | Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | Example of patient with progressive supranuclear palsy. Discussion of difference between saccadic movement in supranuclear palsy and nystagmus. Shows saccadic intrusions in forward gaze, pursuit, saccades, and doll's head maneuver. | Progressive Supranuclear Palsy |
| 172 |
 |
1-22 | Pulsating Exophthalmos | Example of a patient with neurofibromatosis with an absent sphenoid wing. Shows left eye pulsating back and forth with the pulse from front and side views. | Pulsating Exophthalmus |
| 173 |
 |
Pupil_Exam | Pupil Exam | Demonstration of pupil examination. | Examination, Ocular; Pupil Exam |
| 174 |
 |
Figure-17 | Pupil Signs in a 32-year-old Woman with Right-sided Adie's Pupil | Pupil signs in a 32-year-old woman with right-sided Adie's pupil. The right pupil is larger than the left pupil (top), reacts poorly to direct light stimulation (second panel), and better in response to near stimulation (third panel). The right pupil also shows a supersensitive response 30 minutes a... | Adie's Tonic Pupil; Innervation, Pupil; Drug Effects, Pupil; Physiology, Pupil |
| 175 |
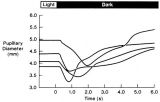 |
Figure-27 | Pupillogram Demonstrating Paradoxical Pupillary Constriction to Darkness | Pupillogram demonstrating paradoxical pupillary constriction to darkness in four patients with congenital achromatopsia. Note that the pupils initially constrict when the light is extinguished. (Price MJ, Thompson HS, Judisch GF et al: Pupillary constriction to darkness. Br J Ophthalmol 1981;69:205-... | Congenital, Color Vision Defects; Physiopathology, Color Vision Defects; Dark Adaptation; Flynn Phenomenon; Humans; Diagnostic Use, Infrared Rays; Congenital, Night Blindness; Physiopathology, Night Blindness; Physiopathology, Optic Nerve Diseases; Physiopathology, Pupil; Congenital, Retinal Disease... |
