A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_novel_gold
| Title | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
Alternating Hypertropias - Bilateral 4th Nerve Palsies and Alternating Skew Deviation | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are two patients with alternating hypertropias. The first is a 70-year-old woman with a diagnosis of cerebellar ataxia, neuropathy, vestibular areflexia syndrome (CANVAS). In the video, both spontaneous downbeat... | Skew Deviation; Alignment; Fourth Nerve Palsy; Cerebellar Pathology; Jerk Nystagmus; Downbeat Nystagmus; Gaze Evoked Nystagmus |
| 2 |
 |
+ HIT, + Skew, Unidirectional Nystagmus: Central Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Wallenberg Syndrome | This is a 45-year-old woman who presented to the ED with acute prolonged vertigo and vertical diplopia. She was seen as an outpatient 1 month after her ED visit, and double vision and balance were improving by that time. Her HINTS testing showed the following (seen in the video): 1) Head Impulse - A... | VOR HIT Abnormal; Abnormal Alignment; Skew; Jerk Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular Nystagmus |
| 3 |
 |
Sequelae of Cerebellar Hemorrhage - Gaze-evoked Nystagmus, Alternating Skew Deviation and Palatal Tremor | This is a 75-yo-woman presenting with a gait disorder. Two years prior, she suffered a cerebellar hemorrhage. On examination, there were typical cerebellar ocular motor signs including gaze-evoked nystagmus, choppy smooth pursuit and VOR suppression, and saccadic dysmetria. There was also an alterna... | Assessing Abnormal Alignment; Jerk Nystagmus; Gaze Evoked Nystagmus; Oculopalatal Myoclonus |
| 4 |
 |
Vestibular Neuritis with a Peripheral Skew Deviation | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 55-year-old hypertensive man who developed acute onset continuous vertigo and presented to the Emergency Department (ED) after several hours of symptoms. He was noted to have spontaneous nystagmus and had a nor... | Abnormal VOR; Abnormal Alignment; Eighth Nerve; Skew Deviation; Lateropulsion; Jerk Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular Syndrome |
| 5 |
 |
Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Ocular Tilt Reaction Due to Bacterial Labyrinthitis | This is a patient who initially presented with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus) and right sided hearing loss, and was diagnosed with bacterial labyrinthritis. Her HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central etiolo... | VOR HIT; Alignment; Jerk Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular |
| 6 |
 |
Skew Deviation and Spontaneous Nystagmus Due to Posterior Fossa Lesions | This is a 50-year-old woman who reported the abrupt onset of imbalance, right upper extremity incoordination and binocular vertical diplopia several months prior to her presentation to our clinic. On examination, she had a left hypertropia that was fairly comitant (measuring 5 prism diopters) assoc... | Abnormal Alignment; Jerk Nystagmus; Upbeat Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus; Rotary Nystagmus; Skew Deviation |
| 7 |
 |
Skew Deviation and the Triad of the Ocular Tilt Reaction (OTR) | This is a patient who presented with vertical diplopia, who was found to have a complete ocular tilt reaction including the following features: (1) Skew deviation - right hypertropia that was about 30 prism diopters in all directions of gaze including right, left, up, down, as well as in right and ... | |
| 8 |
 |
Paroxysmal Ocular Tilt Reaction | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-year-old woman who 2 years prior experienced a left sided hypertensive hemorrhagic stroke, resulting in right hemiparesis, dysarthria and vertical diplopia. The initial vertical diplopia resolved completely a... | Midbrain OMS; Skew Deviation; Jerk Nystagmus; Abnormal Alignment |
| 9 |
 |
The Utriculo-Ocular Motor Pathways - Physiologic and Pathologic Ocular Tilt Reaction: OTR Diagram Pathologic EOMs Labelled (Figure 3) | A skew deviation is a non-paralytic vertical ocular misalignment that is due to imbalance in the utriculo-ocular motor pathways. While vestibular jerk nystagmus is a consequence of static semicircular canal pathway imbalance (e.g., left-beating nystagmus due to acute right vestibular hypofunction fr... | Skew Deviation |
| 10 |
 |
The Utriculo-Ocular Motor Pathways - Physiologic and Pathologic Ocular Tilt Reaction: Pathologic OTR (Figure 2) | A skew deviation is a non-paralytic vertical ocular misalignment that is due to imbalance in the utriculo-ocular motor pathways. While vestibular jerk nystagmus is a consequence of static semicircular canal pathway imbalance (e.g., left-beating nystagmus due to acute right vestibular hypofunction fr... | Skew Deviation |
| 11 |
 |
The Utriculo-Ocular Motor Pathways - Physiologic and Pathologic Ocular Tilt Reaction: Physiologic Ocular Tilt Reaction (OTR) (Figure 1) | A skew deviation is a non-paralytic vertical ocular misalignment that is due to imbalance in the utriculo-ocular motor pathways. While vestibular jerk nystagmus is a consequence of static semicircular canal pathway imbalance (e.g., left-beating nystagmus due to acute right vestibular hypofunction fr... | Skew Deviation |
| 12 |
 |
HINTS Exam and Saccadic Dysmetria in Lateral Medullary Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old who experienced the abrupt onset of prolonged vertigo following chiropractic therapy 2 months prior. Initial work-up included an MRI and MR angiogram - MR-diffusion weighted imaging showed an acute l... | Abnormal Saccades; Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Jerk Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus; Normal VOR; Skew Deviation; OMS Medulla |
| 13 |
 |
Central HINTS (With an Abnormal Head Impulse Sign) in the Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Lateral Pontine/Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Demyelination | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year-old man presenting with vertigo, diplopia and mild left facial weakness (not seen in the video). On exam, there was right-beating nystagmus (RBN) in primary gaze that increased in right gaze (in accordan... | Abnormal Alignment; Vestibulocochlear; OMS Pons; Rotary Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular Nystagmus; Jerk Nystagmus; VOR HIT Abnormal |
| 14 |
 |
Wallenberg Syndrome in MS | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: 30-yo-woman with MS presenting with acute vertigo and vertical diplopia. Examination demonstrated several aspects of the Wallenberg syndrome (her acute demyelinating lesion was in the left lateral medulla): ipsilesional (... | Vestibulo-ocular Reflex; Head Impulse Testing; Abnormal Alignment; Lateropulsion; Wallenberg Syndrome; Medulla; Vestibular Nystagmus; Skew Deviation |
| 15 |
 |
Test Your Knowledge - The Acute Vestibular Syndrome and Ptosis | What is the most likely localization in this patient presenting with vertical diplopia and acute onset prolonged vertigo? A. Right medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) B. Left medial longitudinal fasciculus C. Right medulla D. Left medulla E. Left midbrain A. Incorrect. A right MLF lesion (stroke, M... | Jerk Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Vestibular Nystagmus; Skew Deviation; Upbeat Nystagmus; Torsional Nystagmus; Rotary Nystagmus; Horner Syndrome |
| 16 |
 |
Ocular Alignment | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: These tests allow for detection of eso-, exo- or hyperdeviations (phorias (one eye viewing) or tropias (both eyes viewing) that can be seen with ocular motor palsy, skew deviation, or with cerebellar disease (commonly eso... | Alignment; Exam |
| 17 |
 |
The Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Skew Deviation, Gaze-evoked Nystagmus, and Bilaterally Abnormal Head Impulse Testing Due to AICA Stroke | This is a 60-year-old man with the acute onset of prolonged vertigo and nystagmus, consistent with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS). HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) exam demonstrated a central pattern: 1) Head impulse test (HIT) was abnormal to the right and to the left. An abnormal... | Abnormal VOR-HIT; Abnormal Alignment; Skew; Jerk Nystagmus; Gaze Evoked Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Seventh Nerve; OMS Pons; OMS Cerebellar |
| 18 |
 |
Acute Vestibular Syndrome With Skew Deviation and Positive Head Impulse Test Due to a Demyelinating Lesion | This is a patient who initially presented with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus). ; See https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=187730 for additional history. ; Her HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central e... | VOR HIT; Alignment; Acute Vestibular |
| 19 |
 |
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus Syndrome with Prominent Spontaneous Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-year-old man who experienced the abrupt onset of diplopia and imbalance. He had typical features of a left medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) syndrome including left internuclear ophthalmoplegia (INO) and l... | INO; Jerk Nystagmus; Upbeat Nystagmus; Rotary Nystagmus; Skew Deviation; OMS Pons; Abnormal Alignment; Abducting Nystagmus |
| 20 |
 |
Demonstration of HINTS Examination in a Normal Subject | In the acute vestibular syndrome - consisting of acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus, imbalance, nausea/vomiting, head motion intolerance which is typically due to vestibular neuritis or posterior fossa stroke - a 3 step test of ocular motor and vestibular function known as HINTS, has hig... | Acute Vestibular; Normal VOR; Vertigo; HINTS examination |
| 21 |
 |
How to Measure Ocular Alignment Virtually | Ocular alignment: the alternate cover test can be performed by instructing the patient to hold their head steady, fix their eyes on the camera (or a more distant target - the closer the fixation target, the more of an exodeviation the examiner will see), and use their cell phone (or a spoon) to occl... | Ocular Alignment |
| 22 |
 |
Vertical Gaze Palsy and Saccadic Intrusions Due to Anti-Ri from Head and Neck Carcinoma | A 55-yo- woman was admitted for imbalance and double vision. Three weeks prior to presentation she first noticed swelling on the right side of her face and neck. CT of the head and neck showed right-sided cervical adenopathy and enlarged left retropharyngeal node. Ultrasound- guided biopsy of the n... | OMS Mesencephalon; Square Wave Jerks; Upgaze Palsy; Downgaze Palsy; Abnormal Range; Skew; Vertical Gaze Palsy |
| 23 |
 |
Assessing Utricle Pathway Function and the Effects of Convergence on Nystagmus in Acute Vestibular Neuritis | A 35-year-old woman presented a few days after the onset of room-spinning vertigo. She denied diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia, dysphonia, incoordination, numbness, and weakness. On examination, she had subtle spontaneous right-beat nystagmus (RBN). This nystagmus increased in amplitude and frequency... | Vestibular Nystagmus; Jerk Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Eighth Nerve; Abnormal VHIT |
| 24 |
 |
The Most Common Vestibular Conditions Categorized by Timing and Triggers, with Specific Ocular Motor and Vestibular Features that Should be Sought for Each | HINTS+ = Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew, ‘Plus' bedside assessment of auditory function; HIT = head impulse test; NP = nerve palsy; BPPV = benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; SCDS = superior canal dehiscence syndrome; BVL = bilateral vestibular loss; PPPD = persistent postural perceptual ... | Vestibular Examination |
| 25 |
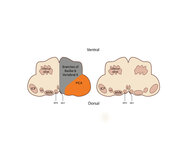 |
Figure 53: Vascular Distribution and Anatomy Relevant to the Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome | This axial section of the medulla highlights those structures that, when damaged, are responsible for the vestibular and ocular motor features of the Wallenberg syndrome. The nucleus prepositus hypoglossi (NPH) and medial vestibular nucleus (MVN) complex is important for horizontal gaze-holding (neu... |
