A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_novel_gold
1 - 25 of 23
| Title | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
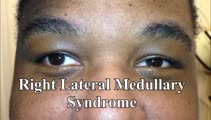 |
Saccadic Dysmetria and Ocular Lateropulsion in Lateral Medullary Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-yo-man who suffered a right lateral medullary stroke. Examination showed saccadic hypermetria to the right (ipsilesional), hypometria to the left (contralesional)and rightward ocular lateropulsion (ipsilesion... | Lateral Medullary Syndrome; Wallenberg Syndrome; Saccadic Dysmetria; Ocular Lateropulsion; Saccades |
| 2 |
 |
Cerebellar Eye Signs in SCA8 | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-yo-man with a diagnosis of SCA 8 who had appendicular and gait ataxia in addition to choppy smooth pursuit and VORS, downbeat nystagmus, saccadic hypermetria, and gaze-evoked nystagmus with rebound nystagmus.... | Saccadic Dysmetria; Downbeat Nystagmus; Gaze-evoked Nystagmus; Vestibulo-ocular Reflex (VOR) Supression; Saccades |
| 3 |
 |
Saccades | Saccades: instruct the patient to make rapid movements of their eyes in each gaze direction, noting the speed, conjugacy, latency, and accuracy. First have the patient look between an eccentric target and the camera horizontally and vertically, making assessment of accuracy easier - e.g., overshooti... | Saccades |
| 4 |
 |
HINTS Exam and Saccadic Dysmetria in Lateral Medullary Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old who experienced the abrupt onset of prolonged vertigo following chiropractic therapy 2 months prior. Initial work-up included an MRI and MR angiogram - MR-diffusion weighted imaging showed an acute l... | Abnormal Saccades; Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Jerk Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus; Normal VOR; Skew Deviation; OMS Medulla |
| 5 |
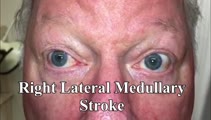 |
Unidirectional Nystagmus in Lateral Medullary Syndrome | This is a 70-yo-man who presented with acute vertigo. Examination demonstrated very mild spontaneous torsional nystagmus (towards the right ear) in primary (not seen well in this video), with robust downbeat-torsional (towards right ear) nystagmus in right gaze and (less robust) almost pure torsiona... | Medula; Rotary Nystagmus; Jerk Nystagmus; Acute Vestibula; Vestibular Nystagmus; Abnormal Saccades |
| 6 |
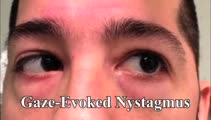 |
Gaze-evoked and Rebound Nystagmus in a Cerebellar Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: 30-yo-man with the subacute onset of a cerebellar syndrome. After extensive evaluation and progression, it was thought that this represented an autoimmune process and there was some improvement with immunosuppression. He ... | Jerk Nystagmus; End-gaze Nystagmus; Gaze-evoked Nystagmus; Rebound Nystagmus; Cerebellar Pathology |
| 7 |
 |
Saccadic Pathways in the Brainstem and Cerebellum & Mechanism for Saccadic Dysmetria in Wallenberg Syndrome - Abnormal Function of the Brainstem/Cerebellar Saccadic Pathways with a Left Wallenberg Syndrome | The end result of a lesion involving the climbing fibers within the left lateral medulla is deficient rightward saccades (contralesional hypometric saccades), and over-active leftward saccades (ipsilesional hypermetric saccades), and ipsilesional ocular lateropulsion given this baseline imbalance. M... | Medulla OMS; Normal Saccades; Abnormal Saccades; Figures |
| 8 |
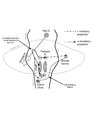 |
Saccadic Pathways in the Brainstem and Cerebellum & Mechanism for Saccadic Dysmetria in Wallenberg Syndrome - Normal Function of the Brainstem/Cerebellar Saccadic Pathways | The inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) carries climbing fibers to the dorsal vermis, and these fibers have an inhibitory influence over the Purkinje cells. These Purkinje cells normally inhibit the ipsilateral fastigial nucleus, and the fastigial nucleus projects to the contralateral inhibitory burs... | Medulla OMS; Normal Saccades; Abnormal Saccades; Figures |
| 9 |
 |
Paraflocculus (Tonsillar) Ocular Motor Syndrome and Dysmetria in a Chiari Malformation - Pre and Post-Operative Exams | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 25-year-old woman presenting with 6 months or progressive imbalance, binocular vertical diplopia, and occipital headaches, which were brought on or aggravated by coughing or sneezing. Examination demonstrated hy... | Saccades; Skew Diviation; VOR Supression; Pursuit; Medulla |
| 10 |
 |
Smooth Pursuit | Smooth pursuit: instruct the patient to hold their head steady, fix their eyes on the camera and slowly move the camera in the horizontal and vertical planes. Or, have the patient focus on their outstretched thumbnail (or other small fixation target), while following the slowly moving object horizon... | Smooth Pursuit |
| 11 |
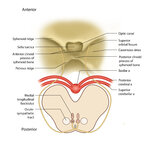 |
Figure 51: Lateral Medullary Lesion Causing Saccadic Dysmetria (Supplement) | ||
| 12 |
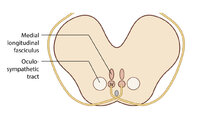 |
Figure 51: Lateral Medullary Lesion Causing Saccadic Dysmetria (Supplement) | ||
| 13 |
 |
Saccades | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: The examiner should note: conjugacy (a lag of the adducting eye may be seen with an INO); accuracy (posterior fossa lesions commonly produce dysmetria (overshooting or undershooting); velocity (if slow, may suggest a lesi... | Saccades; Exam; Conjugacy; Abnormal Saccades |
| 14 |
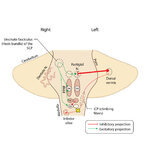 |
Figure 51: Lateral Medullary Lesion Causing Saccadic Dysmetria | A lesion of the left lateral medulla and inferior cerebellar peduncle (ICP) will cause decreased climbing fiber inhibition of the left dorsal vermis causing simple-spike (inhibitory) discharge of Purkinje cells to increase. Increased Purkinje cell firing leads to increased inhibition of the ipsilate... | |
| 15 |
 |
Saccadic Hypermetria and Ipsipulsion (Behind Closed Eyelids and with Vertical Saccades) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-year-old woman who experienced oscillopsia and vertical diplopia, due to spontaneous torsional nystagmus and a skew deviation (right hypotropia), respectively. The symptom onset was 7 months prior to these vi... | Jerk Nystagmus; Torsional Nystagmus; Saccades; Lateropulsion; Medulla |
| 16 |
 |
Paraneoplastic Downbeat Nystagmus and Cerebellar Ataxia Due to Small Cell Lung Carcinoma | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 61-year-old woman (non-smoker) who developed a gait disorder, dizziness and oscillopsia that was progressive over 2 months. Exam demonstrated spontaneous downbeat nystagmus with side pocket nystagmus in lateral ... | Jerk Nystagmus; Downbeat Nystagmus; Cerebellar Ataxia; Carcinoma |
| 17 |
 |
The Virtual (Telemedicine) Ocular Motor Examination | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This document is based on Approach to the Ocular Motor & Vestibular History and Examination: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s64x9bq1, but adapted and edited for the telemedicine exam. Virtual Ocular Motor Ex... | Saccades; Ocular Stability; Vestibular Examination |
| 18 |
 |
Sequelae of Cerebellar Hemorrhage - Gaze-evoked Nystagmus, Alternating Skew Deviation and Palatal Tremor | This is a 75-yo-woman presenting with a gait disorder. Two years prior, she suffered a cerebellar hemorrhage. On examination, there were typical cerebellar ocular motor signs including gaze-evoked nystagmus, choppy smooth pursuit and VOR suppression, and saccadic dysmetria. There was also an alterna... | Assessing Abnormal Alignment; Jerk Nystagmus; Gaze Evoked Nystagmus; Oculopalatal Myoclonus |
| 19 |
 |
The Most Common Vestibular Conditions Categorized by Timing and Triggers, with Specific Ocular Motor and Vestibular Features that Should be Sought for Each | HINTS+ = Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew, ‘Plus' bedside assessment of auditory function; HIT = head impulse test; NP = nerve palsy; BPPV = benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; SCDS = superior canal dehiscence syndrome; BVL = bilateral vestibular loss; PPPD = persistent postural perceptual ... | Vestibular Examination |
| 20 |
 |
The Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Dysarthria, Dysphagia, Dysphonia, Hemi-ataxia, and Saccadic Dysmetria Due to the Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman with the acute onset of vertigo, dysarthria, dysphagia and dysphonia/hoarseness (nucleus ambiguus), ptosis and imbalance. Her examination localized to a left lateral medullary (Wallenberg) synd... | Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Ninth Nerve; OMS Medulla; Abnormal Saccades; Tenth Nerve; Lateropulsion; Horner Syndrome |
| 21 |
 |
Test Your Knowledge - The Acute Vestibular Syndrome and Ptosis | What is the most likely localization in this patient presenting with vertical diplopia and acute onset prolonged vertigo? A. Right medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) B. Left medial longitudinal fasciculus C. Right medulla D. Left medulla E. Left midbrain A. Incorrect. A right MLF lesion (stroke, M... | Jerk Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Vestibular Nystagmus; Skew Deviation; Upbeat Nystagmus; Torsional Nystagmus; Rotary Nystagmus; Horner Syndrome |
| 22 |
 |
Approach to the Ocular Motor and Vestibular History and Examination | History and examination of ocular motor and vestibular. | Saccades; Ocular Stability; Vestibular Examination |
| 23 |
 |
Central Positional Vertigo and Nystagmus in a Posterior Fossa Tumor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year old woman who presented with positional vertigo and vomiting following a concussion related to a car accident 3 months prior. She was initially diagnosed with posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal posit... | Vestibular Nystagmus; Jerk Nystagmus; Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus; Central Positional Nystagmus; Cerebellar OMS; Downbeat Nystagmus; Upbeat Nystagmus |
1 - 25 of 23
