A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_novel_gold
| Title | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 301 |
 |
Vertical Vergence and Fusional Amplitude | Essential information on vertical fusional vergences. | Normal Alignment; Abnormal Alignment; Fourth Nerve Palsy; Vergence; Fusional Amplitudes |
| 302 |
 |
Vestibular Neuritis with + Head Impulse Test and Unidirectional Nystagmus | Vestibular neuritis is the most common cause of the acute vestibular syndrome, which is characterized by continuous vertigo and spontaneous nystagmus lasting days. It may be mimicked by central causes, including stroke, but in the hands of subspecialists, the HINTS+ (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test o... | Jerk Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular; Vestibular Nystagmus |
| 303 |
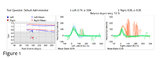 |
Vestibular Neuritis with + Head Impulse Test and Unidirectional Nystagmus (Figure 1) | Vestibular neuritis is the most common cause of the acute vestibular syndrome, which is characterized by continuous vertigo and spontaneous nystagmus lasting days. It may be mimicked by central causes, including stroke, but in the hands of subspecialists, the HINTS+ (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of... | Jerk Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular; Vestibular Nystagmus |
| 304 |
 |
Vibration | Vibration: instruct the patient to self-administer this test with an electric toothbrush or vibrator/massager, if available. Vibration of the mastoids and vertex will induce an ipsilesional slow phase with unilateral vestibular loss (https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=1427582). | Vibration |
| 305 |
 |
Video Head Impulse Testing | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: The video head impulse test (vHIT) is a clinical assessment technique used to assess the function of the semicircular canals-the angular acceleration detectors-which initiate the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). The HIT and... | Normal VOR; Abnormal VOR; Vestibular Lab Testing; Video Head Impulse Testing |
| 306 |
 |
The Virtual (Telemedicine) Ocular Motor Examination | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This document is based on Approach to the Ocular Motor & Vestibular History and Examination: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s64x9bq1, but adapted and edited for the telemedicine exam. Virtual Ocular Motor Ex... | Saccades; Ocular Stability; Vestibular Examination |
| 307 |
 |
The Virtual (Telemedicine) Vestibular Examination | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This document is based on Approach to the Ocular Motor & Vestibular History and Examination: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s64x9bq1, but adapted and edited for the telemedicine exam. Virtual vestibular ex... | Saccades; Ocular Stability; Vestibular Examination |
| 308 |
 |
VOR Suppression | VOR suppression (VORS): instruct the patient to fix on the camera which they should hold in front of their eyes, while turning their torso slowly in the horizontal plane. The vertical plane can then be assessed by instructing the patient to flex and extend the neck under the same conditions. A demon... | VOR Suppression |
| 309 |
 |
A flowchart approach to nystagmus/intrusions | In tandem with the flowchart, the following added clues should be used to help with etiology: i) vector [horizontal, vertical, torsional]; ii) binocular or monocular; iii) spontaneous or provoked [e.g., BPPV]; iv) change with monocular viewing or gaze direction; v) rest of history, neurologic, and o... | Primary subjects of the item, or main keywords: Nystagmus, saccadic intrusions, abnormal eye movements, neuro-otology, neuro-ophthalmology |
| 310 |
 |
Central HINTS (With an Abnormal Head Impulse Sign) in the Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Lateral Pontine/Middle Cerebellar Peduncle Demyelination | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year-old man presenting with vertigo, diplopia and mild left facial weakness (not seen in the video). On exam, there was right-beating nystagmus (RBN) in primary gaze that increased in right gaze (in accordan... | Abnormal Alignment; Vestibulocochlear; OMS Pons; Rotary Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular Nystagmus; Jerk Nystagmus; VOR HIT Abnormal |
| 311 |
 |
Central Positional Vertigo and Nystagmus in a Posterior Fossa Tumor | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 30-year old woman who presented with positional vertigo and vomiting following a concussion related to a car accident 3 months prior. She was initially diagnosed with posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal posit... | Vestibular Nystagmus; Jerk Nystagmus; Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus; Central Positional Nystagmus; Cerebellar OMS; Downbeat Nystagmus; Upbeat Nystagmus |
| 312 |
 |
Convergence | Can bring out or change the direction of vertical nystagmus in Wernicke's, or cerebellar disease; may be impaired in Parkinson's disease, head trauma, elderly patients; may overcome an adduction deficit with an INO. Instructional ocular motor examination procedures. | Convergence; Exam; Abnormal Saccades |
| 313 |
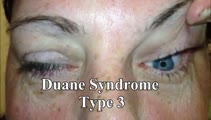 |
Duane's Syndrome Type III | This is a 40-yo-woman seen in neurology clinic for a complaint unrelated to her eyes. On exam, there was impaired adduction and abduction OS. In adduction, there was narrowing of the palpebral fissure OS, a result of her globe retraction due to co-contraction of the medial and lateral rectus muscles... | Duane's Syndrome; Type 3 |
| 314 |
 |
Head-Shaking Nystagmus | Head-shaking nystagmus: With a peripheral lesion, similar to vibration, transiently accentuates vestibular asymmetry when baseline VOR function is asymmetric, central patterns are well described and have localizing value (e.g., causing vertical nystagmus after horizontal head-shaking, horizontal nys... | Nystagmus; Head-shaking Nystagmus; Exam |
| 315 |
 |
HINTS Exam and Saccadic Dysmetria in Lateral Medullary Stroke | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old who experienced the abrupt onset of prolonged vertigo following chiropractic therapy 2 months prior. Initial work-up included an MRI and MR angiogram - MR-diffusion weighted imaging showed an acute l... | Abnormal Saccades; Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Jerk Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus; Normal VOR; Skew Deviation; OMS Medulla |
| 316 |
 |
Lateral Pontine Stroke Involving the Superior Vestibular Nucleus Causing Spontaneous Upbeat-torsional Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A 65-year-old man presented to the emergency department with spontaneous vertigo and unsteadiness, and had was noted to have spontaneous upbeat nystagmus (UBN), also with a torsional component (top poles beating toward th... | Jerk Nystagmus; Upbeat Nystagmus; Torsional Nystagmus; Pons; Acute Vestibular Syndrome |
| 317 |
 |
Ocular Alignment | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: These tests allow for detection of eso-, exo- or hyperdeviations (phorias (one eye viewing) or tropias (both eyes viewing) that can be seen with ocular motor palsy, skew deviation, or with cerebellar disease (commonly eso... | Alignment; Exam |
| 318 |
 |
Range of Eye Movements and Evaluation for Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Range: Assesses for motility deficit due to an ocular motor palsy, particularly if a posterior fossa localization is being considered; Nystagmus: Spontaneous nystagmus may or may not be noted and gaze-evoked nystagmus is ... | Exam; Nystagmus; Range of Eye Movements |
| 319 |
 |
Saccades | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: The examiner should note: conjugacy (a lag of the adducting eye may be seen with an INO); accuracy (posterior fossa lesions commonly produce dysmetria (overshooting or undershooting); velocity (if slow, may suggest a lesi... | Saccades; Exam; Conjugacy; Abnormal Saccades |
| 320 |
 |
Smooth Pursuit | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A pursuit deficit in one direction suggests an ipsilesional localization, but beware of a superimposed spontaneous nystagmus; a pursuit deficit in all directions is commonly seen with cerebellar lesions. 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿�... | Pursuit; Exam |
| 321 |
 |
Test Your Knowledge - The Acute Vestibular Syndrome and Ptosis | What is the most likely localization in this patient presenting with vertical diplopia and acute onset prolonged vertigo? A. Right medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) B. Left medial longitudinal fasciculus C. Right medulla D. Left medulla E. Left midbrain A. Incorrect. A right MLF lesion (stroke, M... | Jerk Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Vestibular Nystagmus; Skew Deviation; Upbeat Nystagmus; Torsional Nystagmus; Rotary Nystagmus; Horner Syndrome |
| 322 |
 |
Test Your Knowledge - Vertical-Torsional Nystagmus | Question #1: Watch the first portion of the video until you are told to stop. Is this vestibular nystagmus more likely to be peripheral or central? A. Peripheral B. Central Answer for #1: A. Incorrect. While the patient has upbeat-torsional (top poles beating toward the right ear) nystagmus which is... | Jerk Nystagmus; Rotary Nystagmus; Upbeat Nystagmus; INO; Skew; Abnormal Alignment; Abnormal Saccades; Vestibular Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular Syndrome |
| 323 |
 |
VOR (Slow and Fast) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Slow vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR): Since smooth pursuit and VOR systems are both active, if eye movements are choppy with this maneuver this implies deficits in both pursuit and the vestibular system as in CANVAS; Fast (... | Vestibulo-ocular Reflex (VOR); Exam |
| 324 |
 |
VOR (Suppression) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Deficits in pursuit and vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR)S usually go together, except when the VOR is absent or markedly diminished in which case there is no VOR to suppress, so that VORS seems better than pursuit. This is a... | Vestibulo-ocular Reflex (VOR) Supression; Exam |
| 325 |
 |
Assessing Utricle Pathway Function and the Effects of Convergence on Nystagmus in Acute Vestibular Neuritis | A 35-year-old woman presented a few days after the onset of room-spinning vertigo. She denied diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia, dysphonia, incoordination, numbness, and weakness. On examination, she had subtle spontaneous right-beat nystagmus (RBN). This nystagmus increased in amplitude and frequency... | Vestibular Nystagmus; Jerk Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Eighth Nerve; Abnormal VHIT |
