A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_novel_gold Type: "Image"
| Title | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
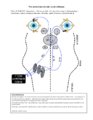 |
Vertical Semicircular Canal Pathways | Anterior Canal Pathway Afferents that originate in the anterior canals (AC) of the peripheral labyrinth first synapse in the ipsilateral vestibular nucleus. Three pathways exist: 1) medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) - right AC afferents to right medial vestibular nucleus (MVN), decussate and asc... | Anterior Canal Pathway; Posterior Canal Pathway |
| 52 |
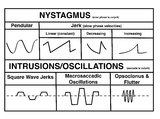 |
A Comparison of Nystagmus and Saccadic Intrusions/Oscillations | Nystagmus can be classified into pendular and jerk waveforms, where both are generated by a slow, pathologic phase. Corrective phase (the position reset mechanism) differs. In pendular nystagmus, the eyes move back and forth with about the same velocity and amplitude, similar to that of a pendulum... | Jerk Nystagmus; Flutter; Pendular Nystagmus; Square Wave Jerks; Opsoclonus |
| 53 |
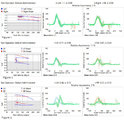 |
Ocular Motor & Vestibular Features of the MLF Syndrome (Figures 1, 2, and 3) | This 61-year-old woman with HTN and DM presented for evaluation of acute onset diagonal diplopia. Adduction OS was about 60% of normal while medialization OS improved with convergence. In right gaze, dissociated abducting nystagmus was present OD, and there was a clear adduction lag when asking he... | INO; Jerk Nystagmus; Torsional Nystagmus; Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus |
| 54 |
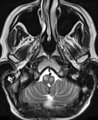 |
Oculopalatal Tremor with Prominent Nystagmus, Bilateral Horizontal Gaze Palsy, and Bilateral Facial Palsies (Figure 1) | Figure 1, MRI T2 sequence demonstrating hyperintensities involving bilateral inferior olives of the medulla. This is a 50-year-old woman who experienced the acute onset of right sixth and seventh nerve palsies and left hemiparesis. Two cavernomas within the right pons (one in the region of the facia... | Abnormal Range; Sixth Nerve Palsy; Facial Nerve; Horizontal Gaze Palsy; OMS Pons; Pendular Nystagmus; Oculopalatal |
| 55 |
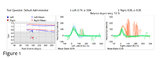 |
Vestibular Neuritis with + Head Impulse Test and Unidirectional Nystagmus (Figure 1) | Vestibular neuritis is the most common cause of the acute vestibular syndrome, which is characterized by continuous vertigo and spontaneous nystagmus lasting days. It may be mimicked by central causes, including stroke, but in the hands of subspecialists, the HINTS+ (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of... | Jerk Nystagmus; Acute Vestibular; Vestibular Nystagmus |
| 56 |
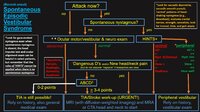 |
An Approach to the Patient with (Recent Onset) Spontaneous Episodic Vestibular Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A vascular etiology should always be on the differential diagnosis of the recent onset of the spontaneous (unprovoked) episodic vestibular syndrome (EVS), especially in the older population and when vascular risk factors ... | |
| 57 |
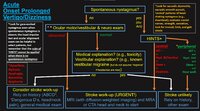 |
An Approach to the Patient with Acute Onset Prolonged Vertigo | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A vascular etiology should always be on the differential diagnosis of the acute onset prolonged vertigo, especially in the older population and when vascular risk factors are present. However, young patients can suffer fr... | |
| 58 |
 |
CANVAS (Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, and Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome) Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) Figure | CANVAS (Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, and Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome) is a genetic condition consisting of slowly progressive late-onset ataxia, bilateral vestibulopathy, sensory neuropathy, chronic cough, and autonomic dysfunction. While the term vestibular areflexia typically implies bilateral... | Vestibulo-ocular Reflex and Head Impulse Testing - Abnormal; Video Head Impulse Test |
| 59 |
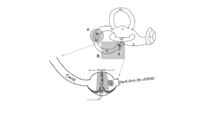 |
Atypical PC BPPV Variant Figures | Figure 1: Atypical posterior canal BPPV variants The labyrinth consists of the cochlea (C), two otolithic organs including utricle (U) and saccule (S), and three semicircular canals including anterior canal (AC), horizontal canal (HC), and posterior canal (PC). A. If otoconia are located within the ... | BPPV |
| 60 |
 |
Neuro-Ophthalmic Features and Pseudo-MG Lid Signs in Miller Fisher Syndrome (Figure 1) | This is a 51-year-old woman who presented with imbalance, acute onset dizziness and diplopia that developed over three days following two weeks of upper respiratory infection and bacterial conjunctivitis. When she was initially seen as an outpatient, nystagmus was noted to the right and left, and a ... | Abnormal VOR; Miller Fisher Syndrome; Myasthenia Gravis; Acute Vestibular Syndrome; Jerk Nystagmus; Gaze Evoked Nystagmus |
