TO
Filters: Collection: "ir_eua"
| Title | Date | Subject | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1601 |
 |
Investigative approach to address thermoacoustic vibration in gas-fired heaters and boilers | 2022 | Industrial gas-fired boilers, furnaces and heaters occasionally encounter low-frequency vibrations generated by dynamic feedback between the burner (or burners) and acoustic modes in adjacent cavities in the main combustion chamber or ductwork. Feedback occurs when pressure pulses associated with ac... | |
| 1602 |
 |
Investor, Economic, Licensing, Regulatory and Reserve Valuation Issues | 2011-03-21 | underground coal gasification; UCG; valuation issues; financial modelling; UCG sites | UCG Training Course, March 21-22, 2011, Deloitte, London |
| 1603 |
 |
Ion chromatographic analysis of oil shale leachates | 1990-10-01 | ion chromatography; oil shale leachates; anions | Ion chromatography can be used for the rapid separation and determination of ions in aqueous solutions that would otherwise require a plethora of classical wet chemical techniques. Ion chromatography is finding increasing use in environmental analysis as well as the petroleum and fossil fuel industr... |
| 1604 |
 |
Is tar sand development part of our future? | 1995-04 | tar sand development; tar sand; oil production | What a difference a decade makes. It has been almost 10 years since the last of several attempts to produce oil from the tar sands at Asphalt Ridge near Vernal, Utah. The only activity since that time has been mining the tar sand for road repair and paving material. The problem is not availability, ... |
| 1605 |
 |
Isolation and characterization of surfactants from tar sand process water | 1994-05 | surfactants; tar sand process water; Utah tar sands; Asphalt Ridge; Whiterocks; characterization of surfactants; isolation of surfactants | A sublation technique was used to isolate soluble surfactants and accompanying species in the aqueous phase from the hot water processing of two Utah tar sands, Asphalt Ridge and Whiterocks. Many structural similarities for the isolated surfactants were observed from IR spectra, however, the amount ... |
| 1606 |
 |
Isothermal pyrolysis and char combustion of oil shales | 1988-02-03 | isothermal pyrolysis; char combustion; oil shale; hydrocarbon product formation; flash-pyrolysis oil | Yields and rates of hydrocarbons evolved during pyrolysis of oil shales have been measured with improved accuracy. Green River and New Albany oil shales were heated in a fluidized sand bed, and volatile pyrolysis products were transferred to a combustion tube and burned. Resulting H20 and C02 were d... |
| 1607 |
 |
Issues of fertility in Utah | 1988-08 | The recent decline in births in Utah has generated much interest. Local newspapers have reported the decline and speculated about possible reason, and demographic researchers have struggled to explain the trend. The question is why, after 15 years of increases, did births begin to decline in the ear... | |
| 1608 |
 |
Kerogen oil value enhancement research | 2002-05-22 | Kerogen; Kerogen oil; oil value enhancement; pure compounds; broad range concentrates; sweet refinery feedstock. | Three general categories of products from the Estonia Kukersite kerogen oil were defined: pure compounds, broad range concentrates, and sweet refinery feedstock. Product development and market research center on these three categories. Further attempts were made to identify and test chemical approac... |
| 1609 |
 |
Kinetic analysis of California oil shale by programmed temperature micropyrolysis | 1991-12-09 | oil shale; micropyrolysis | Three oil shales from California were examined by micropyrolysis for evolution behavior and pyrolysis kinetic parameters to understand hydrocarbon evolution. The samples consisted of one from the Los Angeles basin, and two from the Monterey formation. The two Monterey shales were distinguished by lo... |
| 1610 |
 |
Kinetic study of oil shale conversion | 2008-03-12 | oil shale pyrolysis; analysis of oil shale; associated reactors; oil shale; pyrolysis retorting; shale oil; TGA analysis | Analysis of oil shale pyrolysis and associated reactors designed and built to study kinetics, diffusion, mass transfer and stress effects. |
| 1611 |
 |
Kinetics of Colorado oil shale pyrolysis in a fluidized-bed reactor | 1985-05 | kinetics of Colorado oil shale pyrolysis; fluidized-bed reactor; oil shale pyrolysis; oil shale; hydrocarbon evolution | The hydrocarbon evolution data of Richardson et al. (1982) is reanalyzed to determine improved rate expressions for oil generation from Colorado oil shale under rapid pyrolysis conditions. Contributions from low molecular weight gases are subtracted from flame ionization detector data to obtain the ... |
| 1612 |
 |
Kinetics of cracking and coking of recycled heavy oil | 1993-05 | cracking and coking; recycled heavy oil kinetics; recycled heavy oil; heavy oil; cracking and coking methods; shale oil | In recycled solids processes, shale oil undergoes secondary cracking/coking reactions on the surface of the recycle solids used as the heat carrier. Heavy oil recycle uses these secondary reactions to advantage to convert the heavy oil fraction produced during primary pyrolysis reactions to lighter,... |
| 1613 |
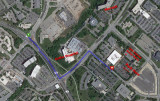 |
Komas (UUSAC) | University of Utah campus buildings | Aerial photograph of Komas including parking and entrance. It is shown in relation to the Ortho Hospital and Marriott Library. | |
| 1614 |
 |
KTIA corporate introduction | 2009-02-27 | KTIA; KTI; mines | Overview of KTIA's continuing oil sands development activities in Utah, presented at the 2009 Western U.S. Oil Sands Conference by Soung-Joon Kim, Chief Operating Officer, Korea Technology Industry America, Inc. |
| 1615 |
 |
Labor force participation rates | 1970 | ||
| 1616 |
 |
Laboratory and modeling investigation of a Colorado oil-shale block heated to 900°C | 1979-12 | modeling investigation; Colorado oil-shale block; oil shale; retorting; in-situ retort | A cylinder of oil-shale, 17.2 by 17.0 cm diameter, was heated in a retort from 23 to 900°C at a rate of 18°C h-1. Total mass loss, oil yield and evolution of individual products are monitored. A one-dimensional model is developed to simulate the heating of the cylinder of oil-shale and the chemist... |
| 1617 |
 |
Land and resource management issues relevant to deploying in-situ thermal technologies: Topical Report: October 1, 2009 to December 31, 2010 | 2011-01 | in-situ; oil shale; domestic energy source; oil sands | Utah is home to oil shale resources containing roughly 1.3 trillion barrels of oil equivalent and our nation's richest oil sands resources. If economically feasible and environmentally responsible means of tapping these resources can be developed, these resources could provide a safe and stable dome... |
| 1618 |
 |
Land and resource management topical report and produced water topical report | 2011-03-08 | water topical report; land management; resource management; oil sands; oil shale | |
| 1619 |
 |
Lands with wilderness characteristics, Resource Management Plan constraints, and land exchanges: Cross-jurisdictional management and impacts on unconventional fuel development in Utah's Uinta Basin | 2012-03 | Utah oil shale; oil sands; unconventional fuel resources; land exchanges; land rights | Utah is rich in oil shale and oil sands resources. Chief among the challenges facing prospective unconventional fuel developers is the ability to access these resources. Access is heavily dependent upon land ownership and applicable management requirements. Understanding constraints on resource acce... |
| 1620 |
 |
Lands with wilderness characteristics: Impacts on oil shale and oil sands development | 2012-05-15 | oil shale; oil sands development; LWC; BLM | Presentation describing the oil shale and sands development in Utah. |
| 1621 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale | 1983-08-09 | oil shale; oil shale project; pyrolysis; quarterly report. | Our general chemical kinetic model for oil shale pyrolysis has been further developed. The reactions included in tne model are primary pyrolysis of kerogen, vaporization of liquid oil, coking of liquid oil, hydrogenation of liquid oil, cracking of liquid oil, cracking of oil vapor, secondary and ter... |
| 1622 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale (May 1989) | 1989-05 | isothermal pyrolisis kinetics; dust; oil shale; oil generation; micropyrolysis | I. Isothermal Pyrolysis Kinetics. II. Dust. |
| 1623 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale (Nov 1987) | 1987-11 | oil shale; oil shale retorting system; water generation; pyrolysis of oil shales; water formation | I. Water Generation During Fischer Assay Pyrolysis of Oil Shales. II. Mixing Requirements of Solid-Recycle Oil Shale Retorting System. |
| 1624 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale (Oct 1988) | 1988-10 | Pyrolzer reactions; oil shale; pyrite decomposition; Green River Formation oil shale; water vapor concentrations in oil shale | I. Secondary Reactions in the Pyrolzer, H2S Release from Devonian Oil Shale. II. Pyrite Decomposition in Oil Shale. III. More on Organic/Inorganic Nitrogen in Green River Formation Oil Shale. IV. Fast and Accurate Measurements of Water Vapor Concentrations. V. References. |
| 1625 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Apr 1986) | 1986-04 | ammonia evolution; triple quadruple mass spectrometer; biomaker identification; oil shale; ammonia emissions | I. Ammonia Evolution. II. Development of the Use of a Triple Quadruple Mass Spectrometer as an On-Line Ammonia Monitor. III. Biomarker Identification by TQMS Improved by Artificial-Intelligence Tuning, IV. Products from Contact of Oil Shale with Reactive Gases. |
| 1626 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Aug 1983) | 1983-08-09 | oil shale pyrolysis; liquid oil; oil | Our general chemical kinetic model for oil shale pyrolysis has been further developed. The reactions included in the model are primary pyrolysis of kerogen, vaporization of liquid oil, coking of liquid oil, hydrogenation of liquid oil, cracking of liquid oil, cracking of oil vapor, secondary and ter... |
| 1627 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Feb 1985) | 1985-02 | retort modeling; Retort Oil Collection System; pyrolysis gas; oxidized oil shale; oil shale | I. Retort Modeling. II.Toulene to be Used in Retort Oil Collection System. III. Sulfur Species in Pyrolysis Gas by Triple Quadruple Mass Spectrometry. IV. Rate of Reaction of Oxidized Oil Shale with Hydrogen Sulfide. V. Visitors. |
| 1628 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Jul 1986) | 1986-07 | enthalpy relations; oil shale; chemical reaction modeling; generic pyrolysis modeling; heat capacities for oil shale | I. Enthalpy Relations for Oil Shale. II. Chemical Reaction Modeling. III. Generic Pyrolysis Modeling. |
| 1629 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Jun 1982) | 1982-06-04 | oil shale; retorted shale; retort modeling; oil hold up; fluidized-bed pyrolysis; saline zone oil shale; recycle chemistry | I. Fluidized-bed Combustion of Retorted Shale. II. Retort Modeling. III. Oil Holdup. IV. Fluidized-bed Pyrolysis. V. Saline Zone Oil Shale. VI. Biological Markers for Retort Diagnostics. VII. Recycle Chemistry. VIII. The Application of Triple Quadruple MS/MS (TQMS) to the Determination of Trace Sulp... |
| 1630 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Jun 1984) | 1984-06 | oil shale processing; solids-recycle retort system; sulfur gas analysis; oil shale; sulfur and nitrogen in oil shale; above ground retorting | I. Sulfur and Nitrogen in Oil Shale Processing. II Initial Operation of the Solids-Recycle Retort System. III. Sulfur Gas Analysis by Triple Quadruple Mass Spectrometry. IV. Retort Modeling. V. Publications and Presentations. VI. Visitors. |
| 1631 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Jun 1987) | 1987-06 | isomerization of alkenes; shale oil by kaolinite; oil shale enthalpy relations; fluid-bed pyrolzer; retorting; oil shale | I. Isomerization of Alkenes in the Shale Oil by Kaolinite. II. Oil Shale Enthalpy Relations. III. Simulation of Fluid-bed Pyrolzer/Lift-pipe Combustor Retort. IV. Yields from the Cross-swept, Packed-bed Pyrolzer Depend on Sweep, Run Conditions, and Shale Type |
| 1632 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Mar 1987) | 1987-03 | n-Butane pyrolysis; Ammonia from pyrolysis; Devonian oil shale; oil shale; dust | I. Dust. II. Pyrolysis of n-Butane. Ammonia from Pyrolysis of Devonian Oil Shale. |
| 1633 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (May 1985) | 1985-05 | oil shale; inorganic nitrogen; retort modeling | I. Determination of Inorganic Nitrogen in Shale II. Retort Modeling III. Reduced Volume Sampling System Installed on Triple Quadruple Mass Spectrometer IV. Visitors V. Publications |
| 1634 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Nov 1981) | 1981-11-02 | gas-combustion retort system; flowsheet data; retort model | A preliminary process flowsheet for a commercial-size, aboveground, countercurrent, gas-combustion retort system has been developed. Flowsheet data are based on an overall mass and energy balance code which uses the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory one-dimensional retort model in conjunction w... |
| 1635 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Nov 1983) | 1983-11 | oil shale; pyrolysis on sulfer gases; nitric oxide formation; sulfur gas production | I. Effect of Pyrolysis Conditions on Sulfur Gases. II. Nitric Oxide Formation During Combustion. III Process Modeling. |
| 1636 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Nov 1984) | 1984-11 | retort modeling; oil shale; sulfur containing gases; TQMS; recycle gas | I. Retort Modeling. II. Sulfur Containing Gases by Triple Quadruple Mass Spectrometer (TQMS), both Grab and On-Line Analysis. III. Visitors. |
| 1637 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project (Oct 1986) | 1986-10 | chemical reaction modeling; carbonate decomposition; oil shale; retorting process | I. Carbonate Decomposition Reaction Scheme and Kinetics. II. Chemical Reaction Modeling. |
| 1638 |
 |
Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory oil shale project review: METC third annual oil shale contractors meeting | 1988-07-20 | Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory; oil shale retorting alternatives; oil shale process development; oil shale | The Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory combines laboratory and pilot-scale experimental measurements with mathematical modeling of fundamental chemistry and physics to provide a technical base for evaluating oil shale retorting alternatives. Presented herein are results of four research areas of... |
| 1639 |
 |
LEED 2009 for healthcare: new construction and major renovations (UUSAC) | 2009 | Healthcare; University of Utah staff | Project checklist categories including: sustainable sites, water efficiency, energy and atmosphere, materials and resources, indoor environmental quality, innovation in design, and regional priority credits. |
| 1640 |
 |
Lessons learned from transient analysis of combustion equipment in the process industries | During gas flare operation, hydrocarbon gas is fed through a flare stack and ignited by a pilot. During the ignition process, flares generally produce significant amounts of smoke (see Figure 1) since enough mixing energy is not available to entrain surrounding air to completely burn the flare gas. ... | ||
| 1641 |
 |
LETC tar sand research - North Asphalt Ridge | 1985 | LETC tar sand research; North Asphalt Ridge; tar sand; in situ recovery methods; classifying tar sand deposits; in situ recovery process; tar sand deposits | This report describes work done by the United States Department of Energy's Laramie Energy Technology Center (LETC) from 1971 through 1982 to develop technology for future recovery of U.S. tar sands. The objectives of the program are: 1. To determine the feasibility of in situ recovery methods appli... |
| 1642 |
 |
Letter from Mario Capecchi to Chase Peterson dated September 28, 1981 | 1981-09-28 | University of Utah; Department of Human Genetics; History | This letter is a request for $49,977.00 to establish a small but highly skilled group whose goal would be to introduce purified genes into mouse embryos for the purpose of creating animal models for human genetic diseases and to test the feasibility of gene transfer therapeutic processes. |
| 1643 |
 |
Letter from the Senior Vice President for Academic Affairs to Deans and Department chairs | 2020-07 | Racism; Systemic racism; Research | Letter from the Senior Vice President for Academic Affairs to Deans and Department chairs addressing U.S. Department of Homeland Security's announcement of modifications to exemptions for non-immigrant students enrolled at high education institutions during the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| 1644 |
 |
Letter from the Senior Vice President for Academic Affairs to Students | 2020-07 | Racism; Systemic racism; Research | Letter from the Senior Vice President for Academic Affairs to students addressing U.S. Department of Homeland Security's announcement of modifications to exemptions for non-immigrant students enrolled at high education institutions during the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| 1645 |
 |
Liberal Education Program & Requirements | The liberal education program and requirements for the University of Utah. | ||
| 1646 |
 |
Libraries, Museums & Other Resources | Libraries; Museums; Higher education resources; University of Utah | The libraries, museum and other resources connected with the University of Utah. | |
| 1647 |
 |
Light-oils transformation to heavy oils and asphalts-assessment of the amounts of hydrocarbons removed and the hydrological-geological control of the process | 1987 | light-oils; heavy oils; asphalts; assessment; hydrocarbons; petroleum resources; oil alteration | Heavy oils frequently represent a residue left after removal of saturated and aromatic hydrocarbons by various alteration processes. They are characterized by a high content of asphaltenes and polar compounds and by higher sulfur content than the light oils from which they were derived. In the Dead ... |
| 1648 |
 |
Linc Energy: UCG towards commercialization | 2011-03-24 | Linc Energy; UCG; UCG commercialization; coal | 6th Annual International Conference & Workshop on Underground Coal Gasification, 23rd - 24th March 2011 |
| 1649 |
 |
List of SERDP publications and presentations | 2010 | SERDP; SERDP publications; SERDP presentations | Bibliography of SERDP publications |
| 1650 |
 |
Lithofacies and related hydrocarbon accumulations in Tertiary strata of the western and central Uinta Basin, Utah | 1975 | lithofacies; hydrocarbon accumulations; Tertiary strata; Uinta Basin; stratigraphy | Strata of Tertiary age in the Uinta Basin were deposited in an internally drained depression. They can be divided into (1) a central core of organic-rich open lacustrine claystone and mud-supported carbonate surrounded by (2) marginal lacustrine sandstone, claystone and mud- and grain-supported carb... |
| 1651 |
 |
Lithologic logs and correlation of coreholes P. R. Spring and Hill Creek oil-impregnated standstone deposits Uintah County, Utah | 1975-08 | lithologic logs; correlation of coreholes; P. R. Spring; Hill Creek; oil-impregnated sandstone deposits; Utah | This report of investigation presents the lithologic logs and correlation of 16 coreholes drilled in 1973 in the P. R. Spring and Hill Creek oil-impregnated sandstone deposits, southeast Uintah County, Utah. The program was conducted under Grant No. GO 122094 from the U. S. Department of the Interio... |
| 1652 |
 |
Local issues for Utah oil sands | 2008-02-22 | Utah oil sands; tar sand history; Western U.S. oil sands | Tar sand history in Uintah County. |
| 1653 |
 |
Los Alamos environmental activities/oil shale effluents | 1985-07 | oil shale effluents; oil shale resource; Los Alamos; health and environmental issues | Complex health and environmental issues will affect both the extent and rate of development of the nation's oil shale resource. Among these issues are concerns about land disruption, air and water contamination, waste disposal, and health and environmental problems associated with the refining and u... |
| 1654 |
 |
Low-temperature oil shale and tar sand extraction process | 1978-12-19 | low-temperature oil shale; low-temperature tar sand; extraction process; kerogen materials; crushed oil-shale; dekerosing; kerogen removal | Fertilizers and kerogen materials are extracted from crushed oil shale utilizing a low temperature dekerosing (kerogen removal) solvent phase followed by a second fertilizer extraction phase using water as solvent. Process control factors are effective in producing delamination of the crushed oil sh... |
| 1655 |
 |
Luncheon invitation (UUSAC) | 2013-09-18 | Luncheon; Staff Council | An invitation from President David W. Pershing and Dr. Sandi J. Pershing to the University of Utah Staff council to attend a luncheon at Eccles House. Included it a map and instructions for parking. |
| 1656 |
 |
Major tar sand and heavy oil deposits of the United States | 1985-07 | major tar sand; heavy oil deposits; heavy oil resources; tar sand resources; United States | This paper presents a current assessment of U.S. tar sand and heavy oil resources. It is based on an independent appraisal of all tar sand deposits with 100 million barrels in place or more and the construction of a heavy oil reservoir and data base of fields containing more than 20 million barrels ... |
| 1657 |
 |
Major tar sand deposits of Utah, United States: Recent field investigations | 1986-07-10 | tar sand deposits; field investigations; tar sand resource; resource evaluation | The results of field investigations at three major Utah tar sand deposits are presented along with representative core sections. A resource evaluation of the PR Spring deposit in the southeastern Uinta Basin includes stratigraphic cross sections and isopleth maps of significant reservoir engineering... |
| 1658 |
 |
Marketing Utah's non-conventional hydrocarbon resources | 2008-02-22 | oil sands development; oil sands; non-conventional hydrocarbon resources; hydrocarbon resources; marketing and production | Oil sands development--develop a resource that has market value. |
| 1659 |
 |
Marriott library circulation statistics 2011-2013 | 2014-07-28 | Circulation statistics; University Press | Circulation statistics for the Marriott Library and University of Utah Press for the years 2011-2013 |
| 1660 |
 |
Mass and heat transfer in crushed oil shale | 1993-07-30 | mass and heat transfer; crushed oil shale; packed beds | Past studies of heat and mass transfer in packed beds, which have disagreed substantially in their findings, have nearly all been done with beds of regular particles of uniform size, whereas oil-shale retorting involves particles of diverse shapes and widely ranging sizes. We have made 349 runs in w... |
| 1661 |
 |
Mathematical modeling of modified in situ and aboveground oil shale retorting | 1981-01 | mathematical modeling; modified in situ; aboveground oil shale retorting; oil shale | A one-dimensional mathematical model has been developed for simulating the chemicophysical processes involved in the vertical retorting of a rubblized bed of oil shale. Included in the present model are those processes believed to have the most important effects in either the hot-gas retorting mode ... |
| 1662 |
 |
McLennan samples: Skyline | 2012-04-06 | Skyline; tight rock analysis; porosity | |
| 1663 |
 |
Measured section, Green River Formation | 1977-09-05 | Green River Formation; Sunnyside Asphalt Quarry area | Sunnyside Asphalt Quarry area, Carbon Co., Utah, September 5-8, 1977, by Jock A. Campbell, assisted by Craig R. Dixon. |
| 1664 |
 |
Measures of agreement between computation and experiment: Validation metrics | 2005-08 | measures of agreement; computation and experiment; validation metrics; computational modeling; engineering design; performance estimation; safety assessment | With the increasing role of computational modeling in engineering design, performance estimation, and safety assessment, improved methods are needed for comparing computational results and experimental measurements. Traditional methods of graphically comparing computational and experimental results,... |
| 1665 |
 |
Mechanism and kinetics of lead capture by kaolinite in a downflow combustor | 2000 | mechanism and kinetics; lead capture; kaolinite; downflow combustor; postflame reaction; lead vapor | An 18 kW, 6 m long, gas-fired downflow combustor was used to examine the postflame reaction between lead vapor and kaolinite. Since the focus of this work was to evaluate the reaction with lead vapor, samples were extracted at a temperature above the metal dew point. The sample was rapidly diluted w... |
| 1666 |
 |
Mechanism of low-temperature water evolution from Green River Formation oil shale | 1989-04 | low-temperature water evolution; Green River Formation; oil shale; Mahogany Zone | The water evolved from Green River Formation oil shale (Mahogany Zone) at temperatures between 150 and 400°C as heated at the rate of 4°C/min results from analcime dehydration, and its rate of evolution is affected by the kinetics of dehydration, the transport of water inside and outside oil shale... |
| 1667 |
 |
Median residence and dispersion times for fluidization of crushed oil shale | 1983-03-24 | median residence and dispersion; fluidization of crushed oil shale; crushed oil shale | Median residence times and dispersions for crushed oil shale flowing downward through a fluidized bed were measured as a function of particle size, nominal residence time, and fluidizing gas velocity. For fluidized beds containing narrow particle-size distribution, it was found that median residence... |
| 1668 |
 |
Medicine in the Beehive State: Chapter 38: Human genetics | 1992 | University of Utah; Department of Human Genetics; History | This is a chapter on the history of the Department of Human Genetics at the University of Utah taken from the book, Medicine in the Beehive State, 1940-1990, edited by Henry P. Plenk and Trudy McMurrin. |
| 1669 |
 |
Metallopetroporphyrines as process indicators: Separation of petroporpyrins in Green River oil shale pyrolysis products | 1994-11 | product oils; LLNL hot-recycled-solids; HRS retorting process; metallopetroporphyrins; process indicators; petroporpyrins; Green River oil shale pyrolysis | Product oils from the LLNL Hot-Recycled-Solids (HRS) retorting process were separated to isolate and concentrate the metallopetroporphyrins. A modified column chromatography procedure developed previously for heavy crude oils and tar sand bitumens was used. The fractions were then examined by UV-vis... |
| 1670 |
 |
Metallopetroporphyrins as process indicators: mass spectral identification of Ni (ETIO) and Ni (DPEP) homologous series in Green River shale oil | 1994-12-05 | mass spectral identification; Green River shale oil; shale oil | Mass spectrometry (MS) of the porphyrin fraction of a demetallated shale oil from the LLNL Hot-Recycled-Solids retorting process exhibited homologous series of C25 to C33 (C28 maximum) for etio and C26 to C36 (C30 maximum) for DPEP (isocyclic) porphyrins, respectively. The sum of intensities after b... |
| 1671 |
 |
Method and apparatus for on-line monitoring of bitumen content in tar sand | 1984-02-21 | on-line monitoring of bitumen content; tar sand bitumen; tar sand; birumen content; bituminous sands processing; patent | An improvement in the processing of bituminous sands is described, whereby the concentration of bitumen in tar sand feed is measured by infrared light reflected from the tar sand surface. Near infrared is shone onto the surface of the incoming tar sand and reflected light is collected and passed thr... |
| 1672 |
 |
Method and apparatus for producing tar sand deposits containing conductive layers | 1991-08-27 | producing tar sand deposits; tar sand deposits; conductive layers in tar sand deposits; patent; method for producing tar sand deposits; apparatus for producing tar sand deposits | An apparatus and method are disclosed for producing thick tar sand deposits by preheating of thin, relatively conductive layers which are a small fraction of the total thickness of a tar sand deposit, with horizontal electrodes. The preheating is continued until the viscosity of the tar in a thin pr... |
| 1673 |
 |
Method and apparatus for producing tar sand deposits containing conductive layers having little or no vertical communication | 1991-10-29 | producing tar sand deposits; conductive layers in tar sand deposits; tar sand; vertical communication; patent | An apparatus and method are disclosed for producing thick tar sand deposits by preheating of thin, relatively highly conductive layers which are a small fraction of the total thickness of a tar sand deposit, with horizontal electrodes and steam stimulation. The preheating is continued until the visc... |
| 1674 |
 |
Method and apparatus for recovering viscous petroleum from tar sand | 1981-02-03 | patent; viscous petroleum recovery; tar sand; recovering viscous petroleum from tar sand; deviated steam injection well; pumping wells; fluidized petroleum recovery | A method of recovering viscous petroleum from tar sand formations utilizing a deviated steam injection well with pump-down (through the flow line) completion. The steam injection well may use side pocket mandrels with constant flow or orifice regulators to control steam injection rates into the surr... |
| 1675 |
 |
Method and apparatus for recovering viscous petroleum from thick tar sand | 1978-10-17 | viscous petroleum recovery; thick tar sand; closed-loop flow tath; production well; patent | Recovery of viscous petroleum such as from a thick tar sand formation is assisted using a closed-loop flow path formed in a production well extending from the earth's surface through a substantial portion of the formation for conducting hot fluid to reduce the viscosity of the petroleum in the forma... |
| 1676 |
 |
Method and apparatus for sampling a core of tar sand | 1983-02-08 | tar sand; core samples of tar sand; core sampling; patent | The invention provides a method and apparatus for sampling a frozen core of tar sand. The frozen core is first cut transversely along its length to form a pair of slabs of semi-circular cross-section. A longitudinal sample portion of substantially triangular cross-section is then cut from the centra... |
| 1677 |
 |
Method and apparatus for the solvent extraction of oil from bitumen containing tar sand | 1996-07-09 | solvent extraction of oil; tar sand bitumen; patent | A method and apparatus for extracting bitumen whereby tar sand containing bitumen components is contacted with a heated thinning oil mixture to reduce the tar sand viscosity and dissolve bitumen to form a lower viscosity feed slurry. The feed slurry is contacted with a light oil in a separator where... |
| 1678 |
 |
Method and appratus for extracting tar sand | 1983-11-22 | tar sand extraction; extraction method; patent; tar sand; extraction apparatus | Method and apparatus for separating coarse sand particles from fine sand particles in a slurry of sand and a solution such as results from the solvent extraction of tar sand, such method comprising causing flow of such slurry in a generally horizontal direction and then causing upward flow at a rate... |
| 1679 |
 |
Method for controlling flocculant addition to tar sand tailings | 1981-07-04 | flocculant addition to tar sand tailings; tar sand tailings; hot water extraction process; bitumen recovery; flocculation; vacuum filteration | The hot water extraction process for recovering bitumen from tar sand produces a large volume of solids-laden aqueous tailings as a waste product. The solids in the tailings stream may be flocculated by the addition of time and the components of the stream then separated into a water-free solids pha... |
| 1680 |
 |
Method for controlling sand in thermal recovery of oil from tar sands | 1978-09-19 | controlling sand; thermal recovery of oil; tar sands oil recovery; tar sands; oil recovery; patent; oil production | A method is disclosed for producing oil from a subterranean reservoir of tar sands as unconsolidated oil bearing sands. The method comprises basically (1) setting a screen in an open hole, the screen being large enough to pass a majority of the formation sand and small enough to retain a packing mat... |
| 1681 |
 |
Method for filtering solvent and tar sand mixtures | 1985-09-03 | filtering solvent; filtering tar sand mixtures; tar sand; paten | A method for filtering spent tar sands from a bitumen and organic solvent solution comprises separating the solution into two streams wherein the bulk of the coarser spent tar sand is in a first stream and has an average particle size of about 10 to about 100 mesh and the bulk of the finer spent tar... |
| 1682 |
 |
Method for recovering bitumen from tar sand | 1982-05-25 | bitumen recovery; tar sand | In recovering bitumen from tar sand by separation using an aqueous liquid, contamination of the aqueous phase with dispersed, finely divided solids is prevented by a mild heat treatment of the bituminous sand to reduce its water content before the sand is contacted with the aqueous liquid. |
| 1683 |
 |
Method for treating a tar sand reservoir to enhance petroleum production by cyclic steam stimulation | 1986-08-26 | tar sand drainage; patent; enhanced petroleum production; cyclic steam stimulation; tar sand treatment | A method for conditioning the virgin drainage area of a tar sand formation that is penetrated by a well for enhanced petroleum production by cyclic steam stimulation is described. The method comprises fracturing the drainage area by injection of liquid carbon dioxide. While carbon dioxide is still i... |
| 1684 |
 |
Method of extracting liquid and gaseous fuel from oil shale and tar sand | 1981-05-12 | liquid extraction; gaseous fuel; oil shale; tar sand; patent | Kerogen and other combustible matter can be extracted from an area of oil shale or tarsand by drilling boreholes in a selected pattern through the overlying soil and rock without removing it. Each borehole mouth is tightly closed by a cover provided with an air inlet pipe and a gas exhaust pipe. In ... |
| 1685 |
 |
Method of processing oil-shale or tar sand | 1982-03-16 | oil shale; tar sand; hydrogenating carbonization | Oil-shale or tar sand is subjected to hydrogenating carbonization and the residue is passed into a combustion zone wherein residual coke in the residue is reacted with oxygen. At least part of the heat produced in the combustion zone is used to heat the hydrogen to be used for the carbonization step... |
| 1686 |
 |
Method of producing tar sand deposits containing conductive layers | 1990-05-22 | tar sand deposits; conductive layers; patent | A method is disclosed for producing thick tar sand deposits by preheating of thin, relatively conductive layers which are a small fraction of the total thickness of a tar sand deposit. The thin conductive layers serve to confine the heating within the tar sands to a thin zone adjacent to the conduct... |
| 1687 |
 |
Method of recovering viscous petroleum from tar sand | 1976-11-30 | Patent; Viscous petroleum recovery; Tar sands | Recovery of viscous petroleum such as from tar sands is assisted using a substantially vertical passage from the earth's surface which penetrates the tar sand and has extending therefrom a lateral hole containing a flow path isolated from the tar sand for circulating a hot fluid to and from the vert... |
| 1688 |
 |
Method of recovering viscous petroleum from thick tar sand | 1977-02-22 | Patent; Viscous petroleum recovery; Thick tar sand | Recovery of viscous petroleum such as from thick tar sands is assisted using a closed-loop flow path formed in a well by concentric casing and tubular members extending from the earth's surface through a substantial portion of the formation for conducting hot fluid to reduce the viscosity of the pet... |
| 1689 |
 |
Method of recovery of bitumen from tar sand formations | 1977-01-18 | Patent; Bitumen recovery; Tar sand formation | A competent permeable communication zone connecting injection and production wells completed in a tar sand which communication zone will be rigid and will not tend to slump or heal may be developed by injecting a fluid in the injection well under such pressure so as to fracture the tar sand formatio... |
| 1690 |
 |
Method of reducing moisture and solid content of bitumen extracted from tar sand minerals | 2000-02-01 | Tar sand; Alkoxyalkylphenol alkoxylate surfactant; Recoverable hydrocarbon; Anionic and cationic flocculant; Bitumen; Moisture reduction | Tar sand is upgraded to produce a hydrocarbon having a low concentration of water and solids by contacting a bitumen/diluent mix with an alkoxyalkylphenol alkoxylate surfactant prior to separation of a recoverable hydrocarbon phase. The separation of the bitumen/diluent mix into a recoverable hydroc... |
| 1691 |
 |
Method of removing bitumen from tar sand for subsequent recovery of the bitumen | 1977-10-18 | Bitumen removal; Tar sand; Bitumen recovery; Sonicating; Sand granules | A method of removing bitumen from tar sand for subsequent recovery of the bitumen. The method comprises submerging tar sand in a sufficient amount of a circulating solvent in which the bitumen is soluble, and, while the tar sand is so submerged, sonicating within the solvent with a sufficient amount... |
| 1692 |
 |
Method of removing bitumen from tar sand utilizing ultrasonic energy and stirring | 1977-10-18 | Bitumen removal; Tar sand; Ultrasonic energy; stirring; Bitumen recovery | A method of removing bitumen from tar sand for subsequent recovery of the bitumen. The method comprises contacting tar sand with an excess of solvent in which the bitumen is soluble, said contacting being performed within a vessel wherein simultaneously the solvent is being stirred and ultrasonic en... |
| 1693 |
 |
Method of separating bitumen from tar sand with cold solvent | 1976-11-23 | Bitumen; Tar sand; Separation; Solvent extraction; Cold solvent | A method for separating bitumen from tar sand by solvent extraction with efficient separation of water from the recovered bitumen is disclosed. Tar sand may often be recovered by surface mining techniques. The tar sand is comprised of bitumen, water and sand including clays. The tar sand is contacte... |
| 1694 |
 |
Methodology for forecasting and allocating population, employment and land use along the Wasatch Front | 1970-09 | The report which follows presents a methodology for forecasting population, employment and land use patterns along the Wasatch Front. The methodology combines and mathematical model with a mapping analysis. Both are flexible and can be applied to transportation areas, counties, census tracts and tra... | |
| 1695 |
 |
Methods of tar sand bitumen recovery | 1992-09-01 | Bitumen recovery; Tar sand; Water displacement extraction; Patent | Methods for the recovery of bitumen from tar sands comprising the steps of mixing tar sand, solvent and a displacing amount of aqueous medium to form a mixture, followed by separating a bitumen-rich solvent phase from the mixture and recovering bitumen from the bitumen-rich solvent phase are disclos... |
| 1696 |
 |
Microstructural distribution of sulfur during the retorting and oxidation of oil shale | 1982-11 | Oil shale; Retorting; Combustion; Sulfur; Microstructural distribution | We report here the first direct observations of the mineralogical and chemical changes in oil shale caused by retorting and combustion. Electron microprobe and scanning electron microscopy techniques were used to examine a portion of the surface area of a sample in the raw shale state, the same area... |
| 1697 |
 |
Migration in Utah | 1988-08 | For many years Utah has been among the fastest growing states in the country. Although the primary reason for Utah's high growth is the rate of natural increase caused by Utah's high birth rate, migration is the other component of population change. This report examines some of the major sources of ... | |
| 1698 |
 |
Millennium synfuels project: Retort process characterization | 2008-03-12 | synefuels; retort process; retort process characterization; energy security; retorting technology; oil shale processing; hybrid energy system; HES | -Energy security issue has led to interest in coal-to-liquids technologies, -One approach use retorting technology commonly associated with oil shale processing, -Hybrid Energy System (HES) technology developed by: Millennium Synfuels, LLC - joint venture of Ambre Energy Pty, Ltd (Australia) and Oil... |
| 1699 |
 |
Mineral management plan: Glen Canyon National Recreation Area--Arizona and Utah | 1980-03 | A General Management Plan (GMP) for Glen Canyon National Recreation Area was prepared during the period 1973 - 1979 and was approved on November 21, 1979, after it and an accompanying final environmental statement (FES 79-23) had been released to the public. That Plan called for the preparation of a... | |
| 1700 |
 |
Mineral matter distribution during the hot water processing of Utah tar sand | 1991 | mineral matter distribution; hot water processing; Utah tar sand; tar sand; mineralogical analyses; Whiterocks deposit; bitumen separation | Mineralogical analyses of a U.S. tar sand sample from the Whiterocks deposit in the Uinta Basin, Utah, were performed by FTIR, XRD and XRF. The tar sand sample was subjected to the modified hot water process for the bitumen separation and the attendant distribution of constituent minerals into the b... |
