Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 176 |
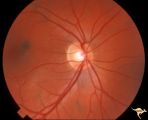 |
Neurofibromatosis-1 | Normal appearing optic disc with dark pigmented choroidal nevi. The patient had NF-1 and had a subclinical optic glioma on the left eye. This is the right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Choroidal nevus. Disease/Diagnosis: Neurofibromatosis type 1. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 177 |
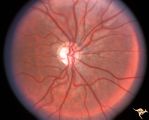 |
Neurofibromatosis-1 | Optic atrophy and hypoplasia of the optic disc associated with chiasmal glioma in a patient with NF-1. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal glioma; Optic atrophy; Hypoplasia. Disease/Diagnosis: Neurofibromatosis type 1. Clinical: Proptosis; Blindness. | Image |
| 178 |
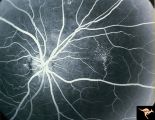 |
Neurofibromatosis-1 | Fluorescein angiogram defines the extent of the microvascular malformation. Pair with R1_E5b. (Ref: BJO 2002:86, p282-284). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Retinal microvascular malformations. Disease/Diagnosis: Neurofibromatosis type 1. Clinical: No visual symptoms. Imaging: Fluorescein angiogram. | Image |
| 179 |
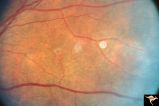 |
Neurofibromatosis-1 | Retinal microvascular malformations in NF-1. Fundus picture shows a somewhat larger vertically running corkscrew malformation between two temporal retinal veins. Pair with R1_E5a. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Retinal microvascular malformations. Disease/Diagnosis: Neurofibromatosis type 1. Clinical: ... | Image |
| 180 |
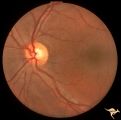 |
Neurofibromatosis-1 | Retinal microvascular malformations in NF-1 located between the disc and the macula. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Retinal microvascular malformations. Disease/Diagnosis: Neurofibromatosis type 1. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 181 |
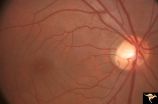 |
Neurofibromatosis-1 | Retinal microvascular malformations between optic disc and macula in NF-1. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Retinal microvascular malformations. Disease/Diagnosis: Neurofibromatosis type 1. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 182 |
 |
Neurofibromatosis-2 | CPERH (choroidal pigment epithelial retinal hamartoma) lesion in a patient with NF-2. Note the oblique superficial retinal traction folds running toward the center of the main lesion. 51 year old man. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Neurofibromatosis type 2. Clinical: Fiel... | Image |
| 183 |
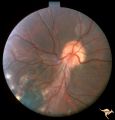 |
Neurofibromatosis-2 | Retinal tumor in NF-2 referred to as a CPERH (choroidal pigment epithelial retinal hamartoma). Patient, a 16 year old girl, had bilateral acoustic neurinomas. Pair with R1_F2b. Same eye. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Retinal hamartoma; Bilateral acoustic neurinoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Neuro... | Image |
| 184 |
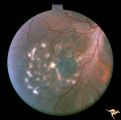 |
Neurofibromatosis-2 | Retinal tumor in NF-2 referred to as a CPERH (choroidal pigment epithelial retinal hamartoma). Patient, a 16 year old girl, had bilateral acoustic neurinomas. Pair with R1_F2a. Same eye. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Retinal hamartoma; Bilateral acoustic neurinoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Neuro... | Image |
| 185 |
 |
Neurofibromatosis-2 | This is the ocular fundus in a patient with NF-2 showing a preretinal membrane that extends from the temporal disc margin toward the macula. The optic disc shows low grade papilledema caused by one of the patient's acoustic neurinomas. The membrane has caused horizontal folds on the retinal surface.... | Image |
| 186 |
 |
P50 Chronic Papilledema with Subretinal Neo-Vascular Network | Chronic papilledema with subretinal neo-vascular network. Pseudotumor. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/ Diagnosis: Chronic papilledema with sub-retinal neovascular network. | Image |
| 187 |
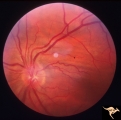 |
P52a Asymmetric Papilledema with Choroidal Folds | Left eye. Choroidal folds with no papilledema. Asymmetric papilledema with choroidal folds. Bilateral choroidal folds from elevated intracranial pressure. 52a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/ Diagnosis: Asymmetric - No papilledema with choroidal folds | Image |
| 188 |
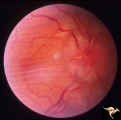 |
P52b Asymmetric Papilledema with Choroidal Folds | Right eye shows papilledema. Asymmetric papilledema with choroidal folds. Bilateral choroidal folds from elevated intracranial pressure. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/ Diagnosis: Chronic papilledema with choroidal folds. | Image |
| 189 |
 |
Pigment Epithelial Hamartoma of Optic Disc | Optic disc tumor discovered incidentally in a 32 year old Asian woman who had no complaints about visual function in her involved left eye. Fundus slide shows granular elevation of left disc obscurring major disc vessels. Some of the granules has a shiny crystalline appearance. Near the vessel entra... | Image |
| 190 |
 |
Post Papilledema, Secondary Optic Atrophy | Right eye. Post papilledema with chronic gliosis. arterial narrowing. ""high-water"" marks. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with optic atrophy. | Image |
| 191 |
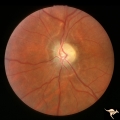 |
Post Papilledema, Secondary Optic Atrophy | Left eye. Post papilledema with chronic gliosis. arterial narrowing. "high-water" marks. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with optic atrophy. | Image |
| 192 |
 |
PP8a Crowded Disc with Significant Nasal Disc Blurring | Congenital nasal disc blurring. Myopic eyes. Thai girl patient. One wonders about vitreal adherence to the disc. PP 8a right eye. Pair with left eye in PP8b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurre... | Image |
| 193 |
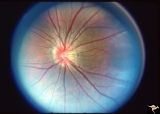 |
PP8b Crowded Disc with Significant Nasal Disc Blurring | Congenital nasal disc blurring. Myopic eyes. Thai girl patient. One wonders about vitreal adherence to the disc. PP 8b left eye. Pair with PP 8a right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurred d... | Image |
| 194 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19c shows embolus has reached the bifurcation and a second embolus (below) is beginning its transit along the same path. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous v... | Image |
| 195 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19d shows progress along the same transit path for both emboli. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 196 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19a shows atheromatous embolus traveling up the arteriole. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 197 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19b shows embolus approaching the bifurcation. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 198 |
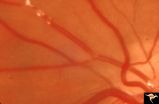 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Note shiny cholesterol plaques in retinal arterial. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Intraluminal cholesterol crystals. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 199 |
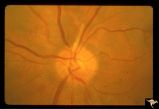 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Note shiny cholesterol plaques in retinal arterial. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Occlusion of the superior retinal arteriole at the level of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Inferior visual field loss from ... | Image |
| 200 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Atheromatous embolism in retinal arteriole branch with associated minimal opacification. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Sudden inferior visual field loss. | Image |
