Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 701 |
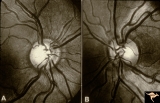 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy. Shows band atrophy in left disc with preserved upper and lower arcuate nerve fiber bundles. Right disc has thinning of both upper and lower arcuate nerve fiber bundles, temporal pallor, and an intact nasal nerve fiber layer. 1972. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Rig... | Image |
| 702 |
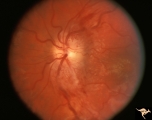 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy with ""Twin Peaks"" papilledema. Central band of the optic disc is completely atrophic and does not swell. ""Axons that are not there can not swell."" Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic tract injury. Disease/Diagnosis: Twin peaks papilledema. Clinical: Left homony... | Image |
| 703 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy with temporal hemianopia. 1983. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Atrophy of the chiasm or left optic tract. Disease/Diagnosis: Segmental band atrophy. Clinical: Right temporal field defect. | Image |
| 704 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy from Eight Optic Tract Injury | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy from right optic tract injury. This eye has a nasal hemianopia. Its disc shows temporal pallor with an intact nasal nerve fiber layer. Pair with IIA2C_7b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right optic tract injury. Disease/Diagnosis: Homonymous hemioptic atrophy. Clini... | Image |
| 705 |
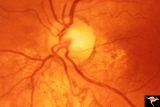 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy from Eight Optic Tract Injury | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy from right optic tract injury. Left eye. Has temporal hemianopia with band atrophy. Note loss of nasal nerve fiber layer. Four and a half months after injury from intracranial pressure catheter. Pair with IIA2C_7a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right optic tract in... | Image |
| 706 |
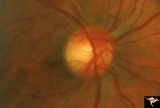 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Nutritional Amblyopia (alcohol) Discs show bilateral temporal pallor with hyperemia of the remaining disc tissue - Pair with IIA2_02b. 1971. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual lo... | Image |
| 707 |
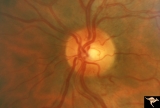 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Nutritional Amblyopia (alcohol) Discs show bilateral temporal pallor with hyperemia of the remaining disc tissue - Pair with IIA2_02a. 1971. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual lo... | Image |
| 708 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Nutritional amblyopia (alcoholic). 1985. Left eye. Pair with IIA2_03a. Anatomy: Optic disc.. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual loss. | Image |
| 709 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal pallor - Nutritional amblyopia (alcoholic). 1985. Right eye. Pair with IIA2_03b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual loss. | Image |
| 710 |
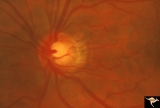 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Nutritional Amblyopia - Nerve fiber layer hemorrhage. Pair with IIA2_04b. 1970. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinincal: Central visual loss. | Image |
| 711 |
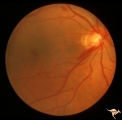 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal | Temporal - Nutritional Amblyopia - Nerve fiber layer hemorrhage. Pair with IIA2_04a. 1970. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from alcohol. Clinical: Central visual loss. | Image |
| 712 |
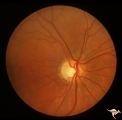 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Due to Thallium (Rat) Poisoning | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - due to thallium (rat) poisoning. Large bilateral central scotomas. 1972. Right eye. Pair with IIA1_01b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from thallium. Clinical: Decreased vision. | Image |
| 713 |
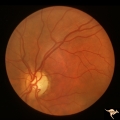 |
Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - Due to Thallium (Rat) Poisoning | Segmental Atrophy - Temporal - due to thallium (rat) poisoning. Large bilateral central scotomas. 1972. Left eye. Pair with IIA1_01a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Toxic optic atrophy from thallium. Clinical: Decreased vision. | Image |
| 714 |
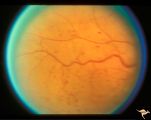 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Examples of Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy showing dilated and tortuous retinal veins and multiple capillary hemorrhages. This kind of retinopathy is produced by impaired arteriole circulation to the retina from various causes. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Ophthalmic artery venous malformati... | Image |
| 715 |
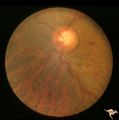 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Examples of Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy showing produced by a carotid-cavernous sinus fistula. Arteriole pressure was low in the retina and venous pressure was elevated. Note the characteristic dot and blot hemorrhages in the black and white photo (R3B2b). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Car... | Image |
| 716 |
 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Examples of Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy produced by a carotid-cavernous sinus fistula. Arteriole pressure was low in the retina and venous pressure was elevated. Note the characteristic dot and blot hemorrhages in this black and white photo. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: carotid-cavernous ... | Image |
| 717 |
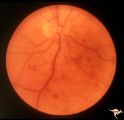 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy from macroglobulanemia. Note the dot and blot hemorrhages. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Macroglobulanemia. Disease/Diagnosis: Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy from macroglobulanemia. | Image |
| 718 |
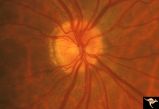 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy. Optic disc change in left eye (b) secondary to reduced carotid artery perfusion. Patient was an elderly man with a innominant artery occlusion. Note the reduced arteriole caliber in the left disc (b) compared to the right (a). Central retinal artery pressure ... | Image |
| 719 |
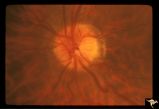 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy. Optic disc change in left eye (b) secondary to reduced carotid artery perfusion. Patient was an elderly man with a innominant artery occlusion. Note the reduced arteriole caliber in the left disc (b) compared to the right (a). Central retinal artery pressure ... | Image |
| 720 |
 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy (right eye) in a man with polycythaemia rubra vera. Hematological disease. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Hematological disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy secondary to polycythaemia. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 721 |
 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy (right eye) in a man with polycythaemia rubra vera. Hematological disease. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Hematological disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy secondary to polycythaemia. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 722 |
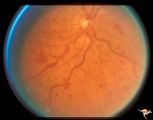 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Examples of Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy showing dilated and tortuous retinal veins and multiple capillary hemorrhages. This kind of retinopathy is produced by impaired arteriole circulation to the retina from various causes. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Ophthalmic artery venous malformati... | Image |
| 723 |
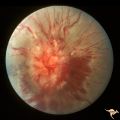 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis) with retinal evidence of central retinal vein occlusion. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Diffuse choroidal hemangioma; Glaucoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Sturge Weber Syndrome. Clinical: Port wine hemangioma of the face. | Image |
| 724 |
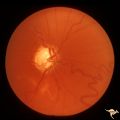 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis); Color of the retina is deep red (sometimes called tomato catsup) due to a four fold thickening of the choroidal vascular bed. Glaucomatous cupping of the optic nerve. Striking retinal venous vascular anomalies on the disc and in the retina. ... | Image |
| 725 |
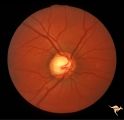 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis); Color of the retina is deep red (sometimes called tomato catsup) due to a four fold thickening of the choroidal vascular bed. Optic disc is cupped due to elevated intraocular pressure. (Secondary glaucoma) Patient had a major ""port wine"" m... | Image |
| 726 |
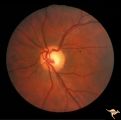 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Left eye is normal, without the deep red from thickened Choroid. Pair with R1_B1a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Diffuse choroidal hemangioma; Glaucoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Sturge Weber Syndrome. Clinical: Port wine hemangioma of the face. | Image |
| 727 |
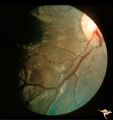 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Soft translucent lesion of tuberous sclerosis in the inferior temporal retina. Patient was 4 years old. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 728 |
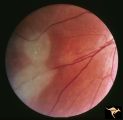 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Has two astrocytic hamartomas. Lower shows a few specs of calcification. Note how the tumor obscures the underlying retinal vessels. Left eye. Pair with R1_D4a. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 729 |
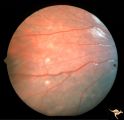 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Two very small tuberous sclerosis lesions. Group with R1_D7a, b, d. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 730 |
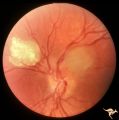 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Has two astrocytic hamartomas. One is calcified. Right eye. Pair with R1_D4b. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 731 |
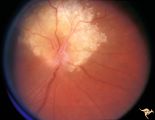 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Astrocytic hamartoma of the optic disc. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 732 |
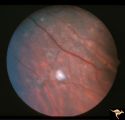 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Several small tuberous sclerosis lesions. Group with R1_D7a, c, d. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 733 |
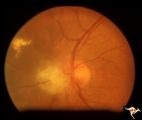 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Astrocytic hamartoma of the optic disc. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 734 |
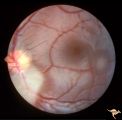 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Two moderate sized tuberous sclerosis lesions in the left eye. Group with R1_D7b, c, d. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 735 |
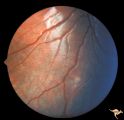 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | One small tuberous sclerosis lesion. Group with R1_D7a, b, c. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 736 |
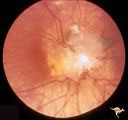 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Astrocytic hamartoma of the optic disc. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 737 |
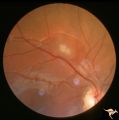 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Retinal lesion in tuberous sclerosis in the form of a translucent disc in the superior temporal area of the retina. Note the dense calcification in the center of the lesion. Note how the lesion obscures the details of the arterioles which pass through it. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamar... | Image |
| 738 |
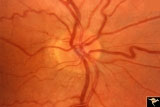 |
Unilateral Buried Drusen | PP20a: Right eye. Normal disc without optic cup.PP20b: Left eye. Buried drusen nasally and exposed drusen at the temporal margin. Boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Normally functioning eye with drusen. Right eye nor... | Image |
| 739 |
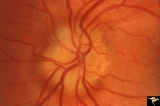 |
Unilateral Buried Drusen | PP20a: Right eye. Normal disc without optic cup.PP20b: Left eye. Buried drusen nasally and exposed drusen at the temporal margin. Boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc.. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc.. Clinical: Normally functioning eye with drusen. Right eye n... | Image |
| 740 |
 |
Unilateral Buried Drusen | PP23a: left eye; lumpy disc with buried drusen. PP23b: CT scan showing calcium (bright spot at optic nerve head on left). 10 year old boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Normally functioning eye with drusen. | Image |
| 741 |
 |
Unilateral Buried Drusen | PP23a: left eye; PP23b: CT scan showing calcium (bright spot at optic nerve head on left). 10 year old boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Unilateral drusen, only in the left eye. | Image |
| 742 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Has no optic cup. Disc is flat. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Transient monocular blindness (transient visual obscurations, amaurosis fugax); headache, sixth nerve palsy, ele... | Image |
| 743 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. This eye has papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Transient monocular blindness (transient visual obscurations, amaurosis fugax); headache, sixth nerve palsy, elevated i... | Image |
| 744 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema in Pseudotumor cerebri. Right eye. Has no cup. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache. | Image |
| 745 |
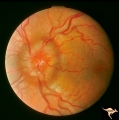 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Has chronic papilledema. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache. | Image |
| 746 |
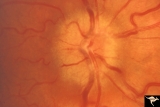 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema due to elevated intracranial pressure. Right eye. This eye has papilledema. Patient described transient monocular blindness with turning right eye. Asymmetric papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Iidiopathic intracranial hyper... | Image |
| 747 |
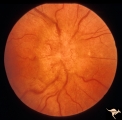 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye.Chronic Papilledema in right eye. Woman. Pseudo Foster Kennedy due to asymmetric papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri) causing pseudo Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: ... | Image |
| 748 |
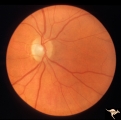 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Atrophic nerve right eye. Large falx meningioma. True Foster Kennedy Syndrome. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Meningioma causing Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: Visual loss one eye; Transient visual obscuration other eye. | Image |
| 749 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Has no optic cup. 24 year old obese woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopthatic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache, transient visual obscurations. | Image |
| 750 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Left eye has papilledema. Large falx meningioma. True Foster Kennedy Syndrome. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Meningioma causing Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: Visual loss one eye; transient visual obscuration other eye. | Image |
| 751 |
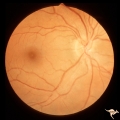 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Mild disc blurring. Obese woman complaining of headaches. Asymmetric papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Asymmetric papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Headache, obese woman. | Image |
| 752 |
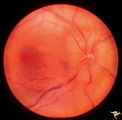 |
Unilateral papilledema | Unilateral papilledema in Pseudotumor cerebri in patient with elevated intracranial pressure. Right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Transient monocular blindness (transient visual ob... | Image |
| 753 |
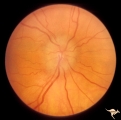 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema in Pseudotumor cerebri in patient with elevated intracranial pressure. Right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Transient monocular blindness (transient visual ob... | Image |
| 754 |
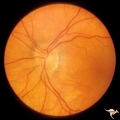 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema in Pseudotumor cerebri in patient with elevated intracranial pressure. Left eye. Has no optic cup. Disc is flat. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Transient monocular... | Image |
| 755 |
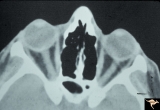 |
Unilateral Papilledema | CT scan showing equal thickening of the optic nerves. CT scan of no help in determining which eye has the papilledema. In this case, right eye has papilledema. Scan of patient depicted P_13a and P_13b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial... | Image |
| 756 |
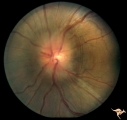 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Patient had tumor on right side. Right sided large meningioma. optociliary shunt at 10:00. Foster Kennedy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Meningioma of the brain. Clinical: Headache. | Image |
| 757 |
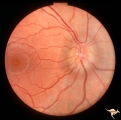 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Woman. Anomalous optic disc elevation in right eye only. This woman's case mimics unilateral papilledema from pseudotumor cerebri. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Anomalous disc elevation. Disease/Diagnosis: Pseudo papilledema. Clinincal: Mimic of papilledema; symptoms: headache; signs: a... | Image |
| 758 |
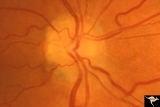 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema due to intracranial pressure. Left eye. This eye shows minor disc blur, inferiorly. No optic cup. Disc is flat. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Gaze evoked blindnes... | Image |
| 759 |
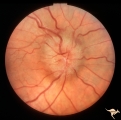 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Has papilledema. Patient has pseudotumor cerebri. 24 year old obese woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache, transient visual obscurations. | Image |
| 760 |
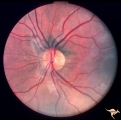 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Has no optic cup. Woman. Left optic disc is flat and cupless. This woman's case mimics unilateral papilledema from pseudotumor cerebri. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Anomalous disc elevation. Disease/Diagnosis: Pseudo papilledema. Clinical: Mimic of papilledema; symptoms: headache; signs... | Image |
| 761 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Low grade papilledema. Obese woman complaining of headaches. Asymmetric papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Asymmetric papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Headache, obese woman. | Image |
| 762 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Has slight disc blur. Asymmetric papilledema. 35 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Gaze evoked blindness. | Image |
| 763 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. This eye has papilledema. 35 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Gaze evoked blindness. | Image |
| 764 |
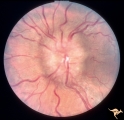 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Has papilledema. 27 year old white woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache. | Image |
| 765 |
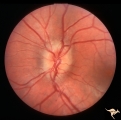 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Has papilledema. Patient has Pseudotumor cerebri. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache, transient visual obscuration. | Image |
| 766 |
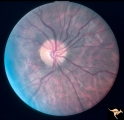 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema in pseudotumor cerebri. Right eye. Has no cup. 27 year old white woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertiension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache. | Image |
| 767 |
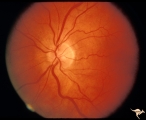 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Flat cupless disc. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri) causing pseudo Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: Visual loss in atrophic eye; obese. | Image |
| 768 |
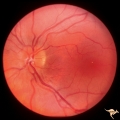 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema in Pseudotumor cerebri in patient with elevated intracranial pressure. Left eye. Has no optic cup. Disc is flat. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unliateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerbri). Clinical: Transient monocular ... | Image |
| 769 |
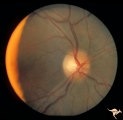 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Patient had tumor on right side. Right sided large meningioma. Disc edema due to tumor. 29 year old black woman. The right disc has mild temporal pallor. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Uninaleral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Meningioma of the brain. Clinical: Headache. | Image |
| 770 |
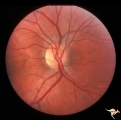 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Has no optic cup. Patient has pseudotumor cerebri. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache, transient visual obscurations. | Image |
| 771 |
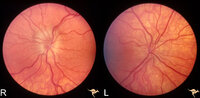 |
Unilateral Pseudopapilledema | PP_10a: Left: pseudo papilledema with disc blurring, crowded disc. Optic disc is small in diameter. PP_10b shows albinotic fundus and small crowded disc. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Elevated disc. Clinic... | Image |
| 772 |
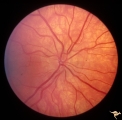 |
Unilateral Pseudopapilledema | PP_10b: shows albinotic fundus and a small crowded disc. PP_10a: left: pseudo papilledema with disc blurring, crowded disc. Optic disc is small in diameter. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Crowded disc. Clin... | Image |
| 773 |
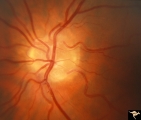 |
Vascular Complications of Drusen | PP34a: Right eye. Superior retinal vein drains into the choroid at 12:00. It has occluded between center of disc and 12:00. Note white ghost vessel. Note that other veins drain into the disc edge at 4:00. There is no evidence of a central retinal vein in the middle of the disc. PP34b: Visible drus... | Image |
| 774 |
 |
Vascular Complications of Drusen | PP34a: Right eye. Superior retinal vein drains into the choroid at 12:00. It has occluded between center of disc and 12:00. Note white ghost vessel. Note that other veins drain into the disc edge at 4:00. There is no evidence of a central retinal vein in the middle of the disc. PP34b: Visible drus... | Image |
| 775 |
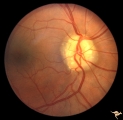 |
Vascular Complications of Drusen: Drusen Causing Loss of Superior Retinal Arterial Supply | PP32a: right; PP32b: left eye. Right eye is an obvious drusen disc. Patient had marked field defects. Left eye has occlusion of superior branch of the central retinal artery at 11:30 with the inferior retinal artery supplying collateral to the superior retina. Notice the branch of the inferior ret... | Image |
| 776 |
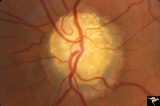 |
Vascular Complications of Drusen: Drusen Causing Loss of Superior Retinal Arterial Supply | PP32a: right; PP32b: left eye. Left eye has occlusion of superior branch of the central retinal artery at 11:30 with the inferior retinal artery supplying collateral to the superior retina. Notice the branch of the inferior retinal artery moves superiorly heading toward the upper retina. Drusen w... | Image |
| 777 |
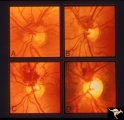 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Convolutions | Collection of prepapillary arterial congenital convolutions. Note: Typically involve the superior retinal arterioles. Purely arterial malformations (not arterial venous). Within the convolution in C, there are multiple tortuous loops. Not associated with cerebral vascular malformations and they do n... | Image |
| 778 |
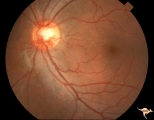 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Convolutions | Hemorrhage from prepapillary arterial convolutions has resolved. Abnormal vessels which were the source of the bleeding. 30 year old man. 3.5 months following hemorrhage. Same patient as V_10. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital prepapillary arterial convolutions with pre-retinal hemorrhage.... | Image |
| 779 |
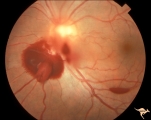 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Convolutions | Hemorrhage from prepapillary arterial convolutions. Note convolutions are inferior. 30 year old man. Same patient as V_11. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital prepapillary arterial convolutions with pre-retinal hemorrhage. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital arterial vascular anomaly. Clinical: Ac... | Image |
| 780 |
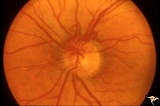 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Convolutions | Prepapillary arterial convolutions. Left eye. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital prepapillary arterial convolutions. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital arterial vascular anomaly. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 781 |
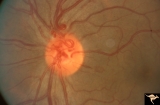 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Convolutions | Prepapillary arterial convolutions. Incidental finding in patient being treated for acute myelogenous leukemia. Note hemorrhage at about 4:00 off the disc related to the leukemia. Arterial loops are not related to leukemia. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital prepapillary arterial convolution... | Image |
| 782 |
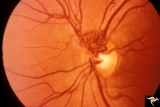 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Convolutions | Prepapillary arterial convolutions. 40 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital prepapillary arterial convolutions. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital arterial vascular anomaly. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 783 |
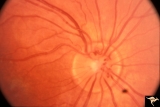 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Loop | Multiple prepapillary arterial loops involving superior and inferior retinal arterioles. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital prepapillary arterial loop. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital prepapillary arterial loop. Clinical: Asymptomatic. Patient presented with migraine. | Image |
| 784 |
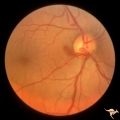 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Loop | Prepapillary arterial loop arising typically from the inferior retinal arterioles and projecting forward into the vitreous. 42 year old patient. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital prepapillary arterial loop. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital prepapillary arterial loop. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 785 |
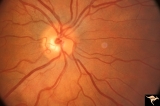 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Loop | Small central prepapillary arterial loop. 30 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital prepapillary arterial loop. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital prepapillary arterial loop. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 786 |
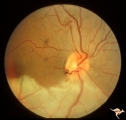 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Loop | Complication of prepapillary arterial loop causing occlusion of the inferior retinal arterial and resulting inferior retinal infarction. Appears to be a black thrombus in the apex of the arterial loop. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Arterial loop with retinal artery infarction. Disease/Diagnosis: B... | Image |
| 787 |
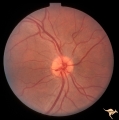 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Prepapillary Arterial Loop | Prepapillary arterial loops. 36 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital prepapillary arterial loop. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital prepapillary arterial loop. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 788 |
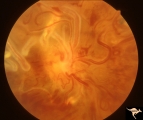 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Wyburn-Mason Syndrome in man with orbital cranial component. After embolization of the orbital and cranial component, the retinal malformation involuted further. Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Post-treatment. Close up view of the disc. October 21, 1992. Same patient as V_23 and V_25. Anatomy: ... | Image |
| 789 |
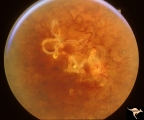 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Wyburn-Mason Syndrome in man with orbital cranial component. After embolization of the orbital and cranial component, the retinal malformation involuted further. Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Post-treatment. Wide angle view of slide V_24. October 21, 1992. Same patient as V_23 and V_24. Anat... | Image |
| 790 |
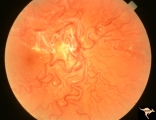 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Wyburn-Mason Syndrome in man with orbital cranial component. Pre-treatment. Retinal arteriovenous malformations, pre-involution. April 27, 1992. Same patient as V_24 and V_25. Anatomy: Optic disc; Brain. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation of retina and brain. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn-Mason syndr... | Image |
| 791 |
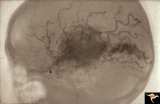 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Wyburn-Mason Syndrome. Angiogram showing extension of vascular malformation up the right optic nerve (arrow) through the thalamus and into the right visual cortex. References #3 and #73. Anatomy: Brain. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wy... | Image |
| 792 |
 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Partially involved. Same patient as V_27. Anatomy: Optic disc; Brain. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation of retina and brain. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn-Mason syndrome. Clinical: Blindness in the involved eye, proptosis. | Image |
| 793 |
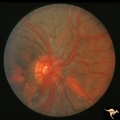 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn-Mason syndrome. Clinical: Cerebral symptoms, questionable seizures. | Image |
| 794 |
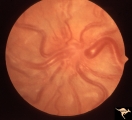 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Clinical: Reduced vision. | Image |
| 795 |
 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. 11 year old. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Clinical: Reduced visual function. | Image |
| 796 |
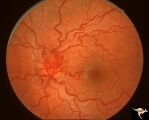 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations of disc and adjacent retina. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 797 |
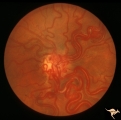 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations (Racemous angioma). Found in a 13 year old girl who had extension of this arteriovenous malformation up her right optic nerve into her thalamus and into her midbrain. Patient had large intra-cerebral AVM (Wyburn-Mason Syndrome). Patient died 10 years later of mass... | Image |
| 798 |
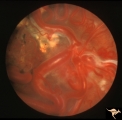 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations with no known cerebral component. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Clinical: Cerebral symptoms, questionable seizures. | Image |
| 799 |
 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Note ghost vessels, signs of involution within the malformation. Natural history is spontaneous involution of arterial loops within the malformation. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinal arteriovenous malf... | Image |
| 800 |
 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. Spontaneous involution. Bonnet-Dechaume-Blanc syndrome. Anatomy: Optic disc; Brain. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation of retina and brain. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn-Mason syndrome. Clinical: Blindness in the involved eye. | Image |
