Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 601 |
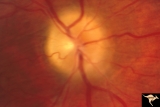 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Right eye 3.5 years after presentation. Atrophy appears about the same. Note especially the narrowing of retinal arterioles. Visual loss is prfound in both eyes. Note the horizontal retinal folds. Papilledema due to brain tumor - 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. | Image |
| 602 |
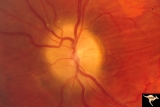 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Left eye at 33 months after presentation. Atrophy appears about the same. Note especially the narrowing of retinal arterioles. Visual loss is severe in both eyes. Papilledema due to brain tumor - 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. | Image |
| 603 |
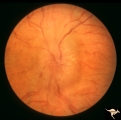 |
Papilledema with Choroidal Folds | Chronic papilledema with choroidal folds. Frontal astrocytoma. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Chronic papilledema. | Image |
| 604 |
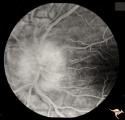 |
Papilledema with Choroidal Folds | Chronic papilledema with choroidal folds. Frontal astrocytoma. Flouroscein angiogram of choroidal folds. Man. | Image |
| 605 |
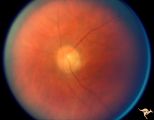 |
Paraneoplastic Retinopathy | Man with oat cell carcinoma of the lung with paraneoplastic retinopathy. Narrowed arterioles. Note absence of obvious retinal pigmentary degeneration. Cancer associated retinopathy syndrome (CAR Syndrome or Sawyer-Sellhorst Syndrome) (Ref: Sawyer, Sellhorst, Hoyt). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Oat c... | Image |
| 606 |
 |
Paraneoplastic Retinopathy | Man with oat cell carcinoma of the lung with paraneoplastic retinopathy. Narrowed arterioles. Note absence of obvious retinal pigmentary degeneration. Cancer associated retinopathy syndrome (CAR Syndrome or Sawyer-Sellhorst Syndrome) (Ref: Sawyer, Sellhorst, Hoyt). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Oat c... | Image |
| 607 |
 |
Paraneoplastic Retinopathy | Cancer associated retinopathy syndrome with extreme retino-arteriolar narrowing. CAR Syndrome. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Oat cell carcinoma of the lung with paraneoplastic retinopathy. Disease/Diagnosis: Cancer associated retinopathy. Clinical: Progressive visual loss, progressive night blindness,... | Image |
| 608 |
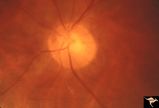 |
Paraneoplastic Retinopathy | Cancer associated retinopathy syndrome with extreme retino-arteriolar narrowing. CAR Syndrome. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Oat cell carcinoma of the lung with paraneoplastic retinopathy. Disease/Diagnosis: Cancer associated retinopathy. Clinical: Progressive visual loss, progressive night blindness,... | Image |
| 609 |
 |
Pigment Epithelial Hamartoma of Optic Disc | Optic disc tumor discovered incidentally in a 32 year old Asian woman who had no complaints about visual function in her involved left eye. Fundus slide shows granular elevation of left disc obscurring major disc vessels. Some of the granules has a shiny crystalline appearance. Near the vessel entra... | Image |
| 610 |
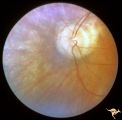 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy | Pigmentary retinopathy in a patient with peripheral neuropathy. Possible Refsums Syndrome. Optic disc shows some arteriole narrowing. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 611 |
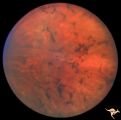 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy | Pigmentary retinopathy in a patient with peripheral neuropathy. Possible Refsums. Typical bone spicules in periphery. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 612 |
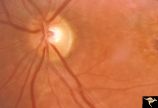 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 613 |
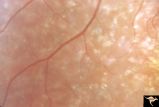 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 614 |
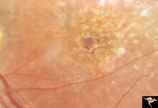 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 615 |
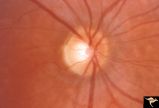 |
Pigmentary Retinopathy with Peripheral Neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) | Pigmentary retinopathy with peripheral neuropathy (Flecked Retinal Syndrome or Fundus Flavimaculatus) in a young woman. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Peripheral nerve degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa with hereditary peripheral degeneration. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 616 |
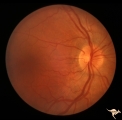 |
Post Papilledema | Right eye. Post Papilledema with minimal optic disc changes after treatment for temporal lobe glioma. Minimal optic disc haze. Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post Papilledema due to temporal lobe glioma. | Image |
| 617 |
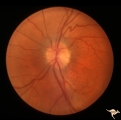 |
Post Papilledema | Left eye. Post Papilledema with minimal optic disc changes after treatment for temporal lobe glioma. Minimal optic disc haze. | Image |
| 618 |
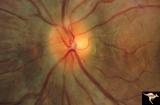 |
Post Papilledema Disc Blurring | Left eye. 8 year old boy. Post papilledema due to brain tumor. Note the entire peripapillary nerve fiber is blurred but the optic discs are barely elevated. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Brain tumor. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema. Clinical: Post papilledema due to brain tumor. | Image |
| 619 |
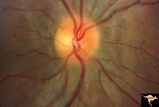 |
Post Papilledema Disc Blurring | Right eye. 8 year old boy. Post papilledema due to brain tumor. Note the entire peripapillary nerve fiber is blurred but the optic discs are barely elevated. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema due to brain tumor. | Image |
| 620 |
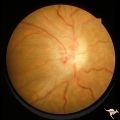 |
Post Papilledema Retinal Choroidal Bypass (Optociliary) | Right eye. Post papilledema retinal choroidal bypass (optociliary). Arterial venous malformation draining into saggital sinus causing papilledema and retinal choroidal collaterals. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with retinal choroidal bypass ves... | Image |
| 621 |
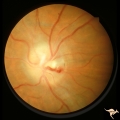 |
Post Papilledema Retinal Choroidal Bypass (Optociliary) | Left eye. Post papilledema retinal choroidal bypass (optociliary). Arterial venous malformation draining into saggital sinus causing papilledema and retinal choroidal collaterals. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with retinal choroidal bypass vess... | Image |
| 622 |
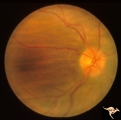 |
Post Papilledema with Choroidal Folds | Right eye. Post papilledema with choroidal folds due to brain tumor. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with choroidal folds. | Image |
| 623 |
 |
Post Papilledema, Secondary Optic Atrophy | Right eye. Post papilledema with chronic gliosis. arterial narrowing. ""high-water"" marks. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with optic atrophy. | Image |
| 624 |
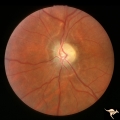 |
Post Papilledema, Secondary Optic Atrophy | Left eye. Post papilledema with chronic gliosis. arterial narrowing. "high-water" marks. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Post papilledema with optic atrophy. | Image |
| 625 |
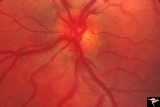 |
PP5b Crowded Disc | PP5a: left eye;PP5 b: left eye X 2 magnification; congenital disc blurring. Boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurred disc. Clinical: Blurred disc margin. Beautiful example of difficult differen... | Image |
| 626 |
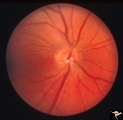 |
PP6a Crowded Disc with Glial Remnant | PP6a: 35 year old man. Right eye that has the glial remnant and blurred margins. PP6b: left eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc with glial remnant. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Crowded disc with glial remnant. Clinical: Man referred for ... | Image |
| 627 |
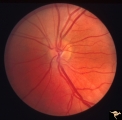 |
PP6b Crowded Disc with Glial Remnant | PP6a: right eye that has the glial remnant and blurred margins. PP6b: left eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Crowded disc. Clinical: Left eye is normal. | Image |
| 628 |
 |
PP7a Crowded disc | PP7a: right eye crowded disc with blurred margin. Note anomalous vascular pattern and glial tissue on the disc; PP7b- left disc is cupless disc and normal. 10 year old girl with gonadal dysgenesis and growth retardation. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Di... | Image |
| 629 |
 |
PP8a Crowded Disc with Significant Nasal Disc Blurring | Congenital nasal disc blurring. Myopic eyes. Thai girl patient. One wonders about vitreal adherence to the disc. PP 8a right eye. Pair with left eye in PP8b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurre... | Image |
| 630 |
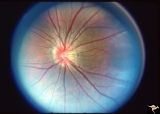 |
PP8b Crowded Disc with Significant Nasal Disc Blurring | Congenital nasal disc blurring. Myopic eyes. Thai girl patient. One wonders about vitreal adherence to the disc. PP 8b left eye. Pair with PP 8a right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurred d... | Image |
| 631 |
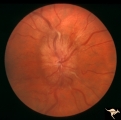 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Right eye. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. Papilladema has increased so that it has almost filled in the optic cup. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 632 |
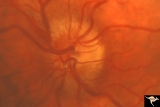 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Left eye at presentation. Early stage. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 633 |
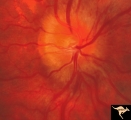 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Right eye at presentation. Early stage bilateral papilledema in a man. Note increased papilledema. Rapid progression of papilledema due to occipital metastatic melanoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Early stage bilateral papilledema. | Image |
| 634 |
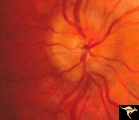 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Right eye at presentation. Early stage bilateral papilledema in a man. Rapid progression of bilateral papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema. | Image |
| 635 |
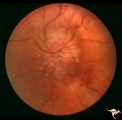 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Left eye one and a half months after presentation. Papilledema has increased and now hemorrhages have been added. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 636 |
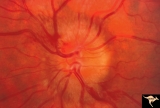 |
Progression of Papilledema due to Metastatic Melanoma | Left eye. 10 days after presentation. Papilledema has increased and bleeding is occurring at the disc margins. Rapid progression of papilledema due to metastatic occipital melanoma. | Image |
| 637 |
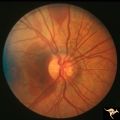 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) Right eye shows angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage. Patient was 25 year old man who developed a right sided carotid cavernous fistula. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrha... | Image |
| 638 |
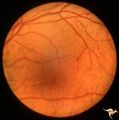 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Left eye. Peripheral retina shows characteristic sign of PXE called Peau d'orange. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage associated with carotid cavernous fistula. Clinical: Vi... | Image |
| 639 |
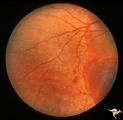 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Right eye. Peripheral retina shows characteristic sign of PXE called Peau d'orange. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage associated with carotid cavernous fistula. Clinical: V... | Image |
| 640 |
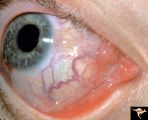 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) Conjunctival signs of carotid cavernous fistula of the right eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE). Disease/Diagnosis: PXE with angiod streaks with associated hemorrhage associated with carotid cavernous fistula. Clinical: Vision blurred in ri... | Image |
| 641 |
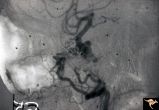 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) Lateral view of right internal carotid angiogram showing complete occlusion of the subcranial internal carotid artery with collateral formation (so called 'rete mirabile"") filling the supraclinoid carotid artery. Also shows evidence of the carotid cavernous fistula e... | Image |
| 642 |
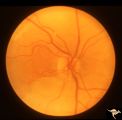 |
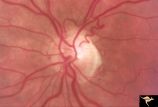
R3C4 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. This fundus shows two calcific emboli in the retinal arteriole tree. The embolus at the end of the disc has caused a retinal infarction and the embolus above the optic disc has also caused a retinal infarction. Note that these white emboli stick in the retinal vessel in mids... | Image |
| 643 |
 |
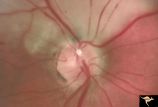
R3C5 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. There is a round gray embolus occluding the superior temporal branch of the retinal artery. Note that the blood column is absent in the superior temporal retinal artery for a short distance off of the disc margin. Note that two collateral branches now fill the distal tempora... | Image |
| 644 |
 |
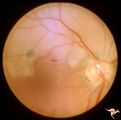
R3C6 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. There is a large calcium embolus totally occluding the superior branches of the central retinal artery. Note: calcium emboli of this type usually derive from the aortic valve. Close view of R3_C7. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Calcific aortic stenosis. Disease/ Diagnosis: Calc... | Image |
| 645 |
 |
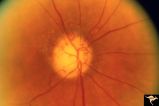
R3C7 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. This woman had aortic stenosis and a heart murmur. There is a large calcium embolus totally occluding the superior branches of the central retinal artery. Note: calcium emboli of this type usually derive from the aortic valve disease. Note superior retinal infarction. Far v... | Image |
| 646 |
 |
R3C8 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Histologic preparation of the optic nerve and papilla showing two red staining calcific emboli in the lumen of the central retinal artery. Calcific retinal emboli. Ocular pathology slide showing calcium embolus in the central retinal artery. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Calcific aortic stenosis. Dise... | Image |
| 647 |
 |
R3C9 Nettleship Collaterals: a Result of Calcific Embolization of the Central Retinal Artery | Result of calcific embolization of the central retinal artery. The embolus itself can not be seen within the tissue of the optic disc. Numerous chorio-retino collaterals are filling the branches of a central retinal artery. Such an eye is always blind. These collaterals indicate that the patient pro... | Image |
| 648 |
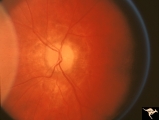 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Resolution of papilledema following optic nerve sheath decompression (ONSD) on November 1, 1974. Same eye as P_53a in January 1975. Atrophic, resolved disc. Note "high-water" marks. Visual acuity was 20/40. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilled... | Image |
| 649 |
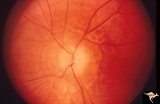 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Resolution of papilledema following optic nerve sheath decompression (ONSD) in November 1, 1974. Same eye as P_53a on December 1974. Atrophic. Note "high-water" marks. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Resolving papill... | Image |
| 650 |
 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Module developed papilledema. June 1974. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Resolving papilledema. | Image |
| 651 |
 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Resolution of papilledema following optic nerve sheath fenestration (ONSF) on November 1, 1974. Same eye as P_53a on November 7, 1974, one week following ONSF. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Resolving papilledema. | Image |
| 652 |
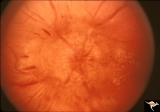 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Same eye as P_53a. Increased papilledema. August 1974. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Resolving papilledema. | Image |
| 653 |
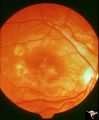 |
Retinal (Macular) Involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy | Retinal (macular) involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Chronic macular changes with bilateral blindness. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebral and retinal degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Clinical: Progressive visual loss and pro... | Image |
| 654 |
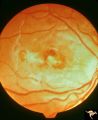 |
Retinal (Macular) Involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy | Retinal (macular) involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Acute macular changes with bilateral blindness. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebral and retinal degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Clinical: Progressive visual loss and progr... | Image |
| 655 |
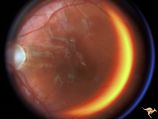 |
Retinal (Macular) Involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy | Retinal (macular) involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Note optic disc pallor. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebral and retinal degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Clinical: Progressive visual loss and progressive cerebral degenera... | Image |
| 656 |
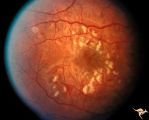 |
Retinal (Macular) Involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy | Retinal (macular) involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Note interesting microvascular changes associated with the retinal disease. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebral and retinal degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Clinical: Progr... | Image |
| 657 |
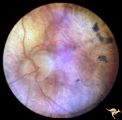 |
Retinal Degeneration Associated with Spastic Paraplegia | Retinal pigmentary degeneration concentrated around the optic discs in a patient with spastic paraplegia. Inverted retinitis pigmentosa where bone spicules are concentrated around the disc and maculae instead of the periphery. Left eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebellar spinal degenerative dise... | Image |
| 658 |
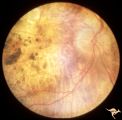 |
Retinal Degeneration Associated with Spastic Paraplegia | Retinal pigmentary degeneration concentrated around the optic discs in a patient with spastic paraplegia. Inverted retinitis pigmentosa where bone spicules are concentrated around the disc and maculae instead of the periphery. Right eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebellar spinal degenerative dis... | Image |
| 659 |
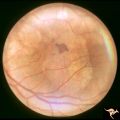 |
Retinal Pigmentary Degeneration with Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia | This 55 year old woman has pigmentary retinal degeneration with progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). (Kearns-Sayre Syndrome). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Mitochondrial disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). Clinical: Can't move eyes. | Image |
| 660 |
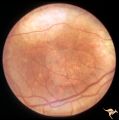 |
Retinal Pigmentary Degeneration with Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia | This 55 year old woman has pigmentary retinal degeneration with progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). (Kearns-Sayre Syndrome). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Mitochondrial disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). Clinical: Can't move eyes. | Image |
| 661 |
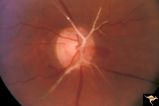 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Central retinal artery occlusion by soft atheromatous debris (mostly fibrin) causing blindness. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 662 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19c shows embolus has reached the bifurcation and a second embolus (below) is beginning its transit along the same path. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous v... | Image |
| 663 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19d shows progress along the same transit path for both emboli. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 664 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19a shows atheromatous embolus traveling up the arteriole. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 665 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19b shows embolus approaching the bifurcation. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 666 |
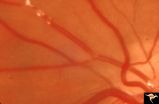 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Note shiny cholesterol plaques in retinal arterial. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Intraluminal cholesterol crystals. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 667 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Embolic occlusion of central retinal artery by white thrombis (probably fibrin.) Patient had a myocardial infarction. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Occlusion of a central retinal artery. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Sud... | Image |
| 668 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. White changes in the arteriolar wall are called plasma bleeding. They are produced by scratches in the endothelium from cholesterol embolization. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Plasma bleeding, Post cholesterol embolization. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atherom... | Image |
| 669 |
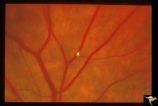 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Note the way the cholesterol emboli stick at arteriole bifurcation. Note second plaque hidden at the juncture below. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Intraluminal cholesterol crystals. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visua... | Image |
| 670 |
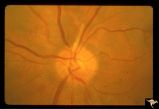 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Note shiny cholesterol plaques in retinal arterial. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Occlusion of the superior retinal arteriole at the level of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Inferior visual field loss from ... | Image |
| 671 |
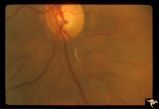 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Example of plasma bleeding in the arteriole wall secondary to cholesterol embolization. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Focal capillary bleeding. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Patient had several attacks of amaurosis fugax... | Image |
| 672 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Atheromatous embolism in retinal arteriole branch with associated minimal opacification. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Sudden inferior visual field loss. | Image |
| 673 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Atheromatous embolism in a patient who suffered sudden visual loss in his left eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Post cholesterol embolization. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Sudden visual loss in left eye. | Image |
| 674 |
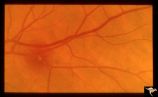 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Cholesterol embolization causing capillary bleeding. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Focal capillary bleeding. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 675 |
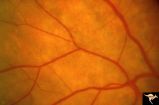 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Documentation of atheromatous embolus appearing at bifurcation during photographic session. R3_A18a shows no embolus and b shows new embolus. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease... | Image |
| 676 |
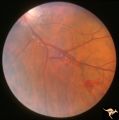 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Arteriole wall changes produced by a stuttering atheromatous embolus. Note the beaded track of the cholesterol embolus in the inferior retinal arteriole. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vasc... | Image |
| 677 |
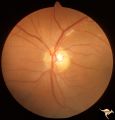 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization in the superior temporal arteriole. Atheromatous emboli. Also note an embolus more distally in the inferior temporal arteriole. Left eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Cli... | Image |
| 678 |
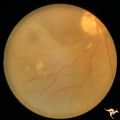 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Branch retinal artery occlusion from atheromatous debris. Note gray areas of retina including the macula indicating infarction. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Su... | Image |
| 679 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Documentation of atheromatous embolus appearing at bifurcation during photographic session. A shows no embolus and R3_A18b shows new embolus. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease... | Image |
| 680 |
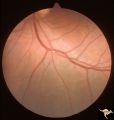 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Atheromatous emboli. Second view of inferior retinal arteriole with cholesterol embolus. Left eye. Pair with R3_A12a. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Transient ri... | Image |
| 681 |
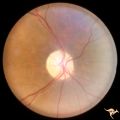 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Central retinal artery occlusion at the level of the optic disc. The embolus that caused it can not be seen. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 682 |
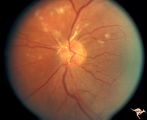 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Central retinal artery occlusion by soft atheromatous debris (mostly fibrin) causing blindness. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 683 |
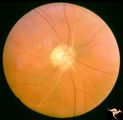 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Central retinal artery occlusion by soft atheromatous debris (mostly fibrin) causing blindness. All but one of the retinal arterioles have been converted to white strands. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Source of the embolic occlusion not determined. Disease/... | Image |
| 684 |
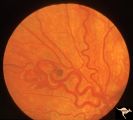 |
Retinocerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (Wyburn Mason Syndrome) | Retinocerebral arteriovenous malformation showing one major arteriovenous loop. (Cross reference with V12-28 this section). Cross reference with V12-28 this section, Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn Mason Syndrome. Clinical: Single arteriovenous l... | Image |
| 685 |
 |
Retinocerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (Wyburn Mason Syndrome) | Retinocerebral arteriovenous malformation showing multiple arteriovenous shunts, both small and large. (Cross reference with V12-28 this section). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn Mason Syndrome. Clinical: Arteriovenous loop in the inferior temporal r... | Image |
| 686 |
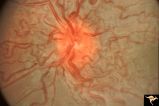 |
Retinocerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (Wyburn Mason Syndrome) | Florid arteriovenous malformation of the optic disc and surrounding retina, Caput medusa (Cross reference with V12-28 this section). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn Mason Syndrome. | Image |
| 687 |
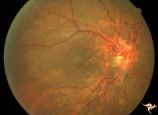 |
Retinocerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (Wyburn Mason Syndrome) | Retinocerebral arteriovenous malformation with optic atrophy and central extension up the optic nerve into the brain. Ipsilateral facial involvement. Man from Thailand. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn Mason Syndrome. Clinical: Asian man with an exten... | Image |
| 688 |
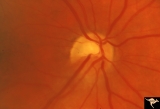 |
Segmental Atrophy - Altitudinal | Segmental optic atrophy - superior altitudinal. 55 year old man.1970. The cupping and the normal superior arteries are evidence against AION. Post ischemic, acquired. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic hemiatrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Segmental atrophy - altitudinal. Clinical: Inferior visual fiel... | Image |
| 689 |
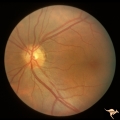 |
Segmental Atrophy - Altitudinal | Segmental Optic Atrophy Superiorly - Altitudinal. Cause unknown. There is a cup. 1973. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic hemiatrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Segmental atrophy - altitudinal. Clinical: Inferior visual field defect. | Image |
| 690 |
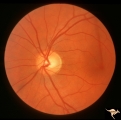 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy in an eye with temporal hemianopia. Wyburn-Mason Syndrome extending to the chiasm. Left eye 1975. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right sided chiasmal AVM. Disease/Diagnosis: Band atrophy due to chiasmal AVM and Wyburn-Mason Syndrome. Clinical: Blind right eye, temp... | Image |
| 691 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy from right optic tract injury. Red free filter. Left eye. Has temporal hemianopia with band atrophy. Note loss of nasal nerve fiber layer. Old right optic tract injury. 1972. Pair with IIA2C_9a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right optic tract injury. Disease/Diagno... | Image |
| 692 |
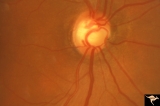 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy with horizontal cupping. Pituitary adenoma. Magnification of 14a. Pair with IIA2C_14a. 1975. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal compression from pituitary adenoma in a cupped disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Band atrophy and cupping. Clinical: Temporal hemianopia. | Image |
| 693 |
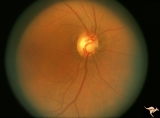 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy with horizontal cupping. Transverse cup. Pair with IIA2C_14b. 1975. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chiasmal compression from pituitary adenoma in a cupped disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Band atrophy and cupping. Clinical: Temporal hemianopia. | Image |
| 694 |
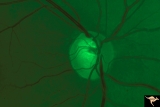 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy from right optic tract injury. Red free filter. Left eye. Has temporal hemianopia with band atrophy. Note loss of nasal nerve fiber layer. Old right optic tract injury. 1972. Pair with IIA2C_9b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right optic tract injury. Disease/Diagno... | Image |
| 695 |
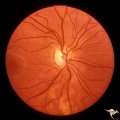 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy from right optic tract injury. This eye has a nasal hemianopia. Its disc shows temporal pallor with an intact nasal nerve fiber layer. Old right optic tract injury. 1986. Pair with IIA2C_8b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right optic tract injury. Disease/Diagnosis:... | Image |
| 696 |
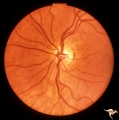 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy from right optic tract injury. Left eye. Has temporal hemianopia with band atrophy. Note loss of nasal nerve fiber layer. Old right optic tract injury. 1986. Pair with IIA2C_8a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right optic tract injury. Disease/Diagnosis: Homonymous h... | Image |
| 697 |
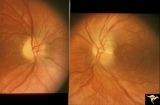 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy with papilledema. 1975. Patient had a right optic tract glioma. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Glioma of the right optic tract. Disease/Diagnosis: Twin peaks papilledema. Clinical: Left homonymous hemianopia. | Image |
| 698 |
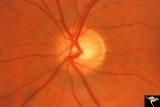 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Magnification of IIA2C_02a. Band atrophy in an eye with temporal hemianopia. Wyburn-Mason Syndrome extending to the chiasm. Left eye. 1975. Right eye in patient was blind. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Right sided chiasmal AVM. Disease/Diagnosis: Band atrophy due to chiasmal A... | Image |
| 699 |
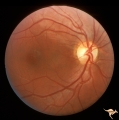 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (band) atrophy - Bilateral horizontal band atrophy secondary to old chiasmal trauma. Note the presence of arcuate nerve fibers and the absence of temporal and nasal nerve fibers. Note the sharp edged pallor of the nasal disc margin. Right eye. Pair with IIA2C_1b. 1985.... | Image |
| 700 |
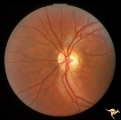 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (band) atrophy - Bilateral horizontal band atrophy secondary to old chiasmal trauma. Note the presence of arcuate nerve fibers and the absence of temporal and nasal nerve fibers. Note the sharp edged pallor of the nasal disc margin. Right eye. Pair with IIA2C_1a. 1985.... | Image |
