Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 501 |
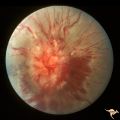 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis) with retinal evidence of central retinal vein occlusion. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Diffuse choroidal hemangioma; Glaucoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Sturge Weber Syndrome. Clinical: Port wine hemangioma of the face. | Image |
| 502 |
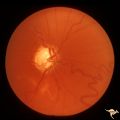 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis); Color of the retina is deep red (sometimes called tomato catsup) due to a four fold thickening of the choroidal vascular bed. Glaucomatous cupping of the optic nerve. Striking retinal venous vascular anomalies on the disc and in the retina. ... | Image |
| 503 |
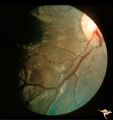 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Soft translucent lesion of tuberous sclerosis in the inferior temporal retina. Patient was 4 years old. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 504 |
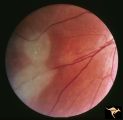 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Has two astrocytic hamartomas. Lower shows a few specs of calcification. Note how the tumor obscures the underlying retinal vessels. Left eye. Pair with R1_D4a. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 505 |
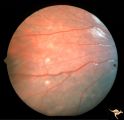 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Two very small tuberous sclerosis lesions. Group with R1_D7a, b, d. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 506 |
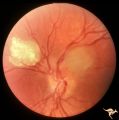 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Has two astrocytic hamartomas. One is calcified. Right eye. Pair with R1_D4b. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 507 |
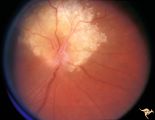 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Astrocytic hamartoma of the optic disc. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 508 |
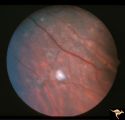 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Several small tuberous sclerosis lesions. Group with R1_D7a, c, d. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 509 |
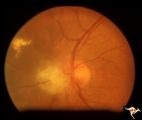 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Astrocytic hamartoma of the optic disc. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 510 |
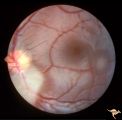 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Two moderate sized tuberous sclerosis lesions in the left eye. Group with R1_D7b, c, d. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 511 |
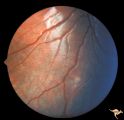 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | One small tuberous sclerosis lesion. Group with R1_D7a, b, c. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 512 |
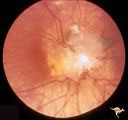 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Astrocytic hamartoma of the optic disc. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 513 |
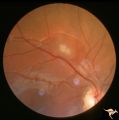 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Retinal lesion in tuberous sclerosis in the form of a translucent disc in the superior temporal area of the retina. Note the dense calcification in the center of the lesion. Note how the lesion obscures the details of the arterioles which pass through it. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamar... | Image |
| 514 |
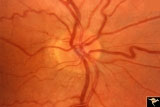 |
Unilateral Buried Drusen | PP20a: Right eye. Normal disc without optic cup.PP20b: Left eye. Buried drusen nasally and exposed drusen at the temporal margin. Boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Normally functioning eye with drusen. Right eye nor... | Image |
| 515 |
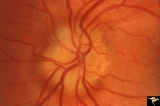 |
Unilateral Buried Drusen | PP20a: Right eye. Normal disc without optic cup.PP20b: Left eye. Buried drusen nasally and exposed drusen at the temporal margin. Boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc.. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc.. Clinical: Normally functioning eye with drusen. Right eye n... | Image |
| 516 |
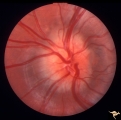 |
Unilateral Buried Drusen | PP23a: left eye; lumpy disc with buried drusen. PP23b: CT scan showing calcium (bright spot at optic nerve head on left). 10 year old boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Normally functioning eye with drusen. | Image |
| 517 |
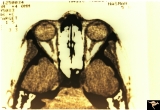 |
Unilateral Buried Drusen | PP23a: left eye; PP23b: CT scan showing calcium (bright spot at optic nerve head on left). 10 year old boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Unilateral drusen, only in the left eye. | Image |
| 518 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Has no optic cup. Disc is flat. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Transient monocular blindness (transient visual obscurations, amaurosis fugax); headache, sixth nerve palsy, ele... | Image |
| 519 |
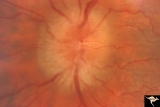 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. This eye has papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clinical: Transient monocular blindness (transient visual obscurations, amaurosis fugax); headache, sixth nerve palsy, elevated i... | Image |
| 520 |
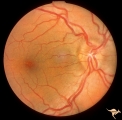 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema in Pseudotumor cerebri. Right eye. Has no cup. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache. | Image |
| 521 |
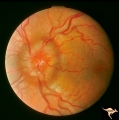 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Has chronic papilledema. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache. | Image |
| 522 |
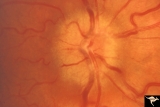 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema due to elevated intracranial pressure. Right eye. This eye has papilledema. Patient described transient monocular blindness with turning right eye. Asymmetric papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Iidiopathic intracranial hyper... | Image |
| 523 |
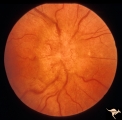 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye.Chronic Papilledema in right eye. Woman. Pseudo Foster Kennedy due to asymmetric papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri) causing pseudo Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: ... | Image |
| 524 |
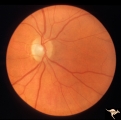 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Atrophic nerve right eye. Large falx meningioma. True Foster Kennedy Syndrome. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Chronic papilledema; optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Meningioma causing Foster-Kennedy Syndrome. Clinical: Visual loss one eye; Transient visual obscuration other eye. | Image |
| 525 |
 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Has no optic cup. 24 year old obese woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopthatic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache, transient visual obscurations. | Image |
