Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 451 |
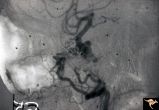 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) Lateral view of right internal carotid angiogram showing complete occlusion of the subcranial internal carotid artery with collateral formation (so called 'rete mirabile"") filling the supraclinoid carotid artery. Also shows evidence of the carotid cavernous fistula e... | Image |
| 452 |
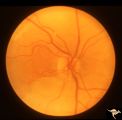 |
R3C4 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. This fundus shows two calcific emboli in the retinal arteriole tree. The embolus at the end of the disc has caused a retinal infarction and the embolus above the optic disc has also caused a retinal infarction. Note that these white emboli stick in the retinal vessel in mids... | Image |
| 453 |
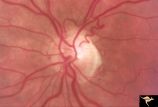 |
R3C5 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. There is a round gray embolus occluding the superior temporal branch of the retinal artery. Note that the blood column is absent in the superior temporal retinal artery for a short distance off of the disc margin. Note that two collateral branches now fill the distal tempora... | Image |
| 454 |
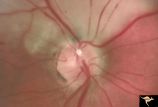 |
R3C6 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. There is a large calcium embolus totally occluding the superior branches of the central retinal artery. Note: calcium emboli of this type usually derive from the aortic valve. Close view of R3_C7. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Calcific aortic stenosis. Disease/ Diagnosis: Calc... | Image |
| 455 |
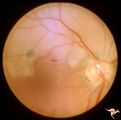 |
R3C7 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. This woman had aortic stenosis and a heart murmur. There is a large calcium embolus totally occluding the superior branches of the central retinal artery. Note: calcium emboli of this type usually derive from the aortic valve disease. Note superior retinal infarction. Far v... | Image |
| 456 |
 |
R3C8 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Histologic preparation of the optic nerve and papilla showing two red staining calcific emboli in the lumen of the central retinal artery. Calcific retinal emboli. Ocular pathology slide showing calcium embolus in the central retinal artery. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Calcific aortic stenosis. Dise... | Image |
| 457 |
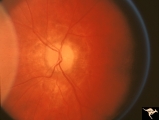 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Resolution of papilledema following optic nerve sheath decompression (ONSD) on November 1, 1974. Same eye as P_53a in January 1975. Atrophic, resolved disc. Note "high-water" marks. Visual acuity was 20/40. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilled... | Image |
| 458 |
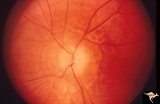 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Resolution of papilledema following optic nerve sheath decompression (ONSD) in November 1, 1974. Same eye as P_53a on December 1974. Atrophic. Note "high-water" marks. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Resolving papill... | Image |
| 459 |
 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Module developed papilledema. June 1974. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Resolving papilledema. | Image |
| 460 |
 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Resolution of papilledema following optic nerve sheath fenestration (ONSF) on November 1, 1974. Same eye as P_53a on November 7, 1974, one week following ONSF. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Resolving papilledema. | Image |
| 461 |
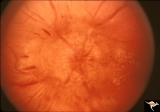 |
Resolution of Papilledema Following Optic Nerve Sheath Decompression (ONSD) | Left eye. 17 year old boy. Cryptococcal meningitis. Same eye as P_53a. Increased papilledema. August 1974. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Resolving papilledema. | Image |
| 462 |
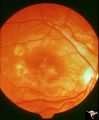 |
Retinal (Macular) Involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy | Retinal (macular) involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Chronic macular changes with bilateral blindness. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebral and retinal degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Clinical: Progressive visual loss and pro... | Image |
| 463 |
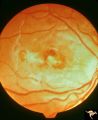 |
Retinal (Macular) Involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy | Retinal (macular) involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Acute macular changes with bilateral blindness. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebral and retinal degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Clinical: Progressive visual loss and progr... | Image |
| 464 |
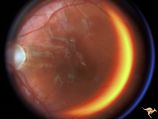 |
Retinal (Macular) Involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy | Retinal (macular) involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Note optic disc pallor. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebral and retinal degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Clinical: Progressive visual loss and progressive cerebral degenera... | Image |
| 465 |
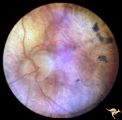 |
Retinal Degeneration Associated with Spastic Paraplegia | Retinal pigmentary degeneration concentrated around the optic discs in a patient with spastic paraplegia. Inverted retinitis pigmentosa where bone spicules are concentrated around the disc and maculae instead of the periphery. Left eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebellar spinal degenerative dise... | Image |
| 466 |
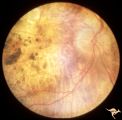 |
Retinal Degeneration Associated with Spastic Paraplegia | Retinal pigmentary degeneration concentrated around the optic discs in a patient with spastic paraplegia. Inverted retinitis pigmentosa where bone spicules are concentrated around the disc and maculae instead of the periphery. Right eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebellar spinal degenerative dis... | Image |
| 467 |
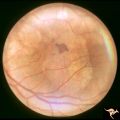 |
Retinal Pigmentary Degeneration with Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia | This 55 year old woman has pigmentary retinal degeneration with progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). (Kearns-Sayre Syndrome). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Mitochondrial disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). Clinical: Can't move eyes. | Image |
| 468 |
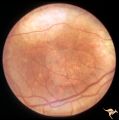 |
Retinal Pigmentary Degeneration with Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia | This 55 year old woman has pigmentary retinal degeneration with progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). (Kearns-Sayre Syndrome). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Mitochondrial disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Progressive external ophthalmoplegia (PEO). Clinical: Can't move eyes. | Image |
| 469 |
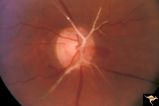 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Central retinal artery occlusion by soft atheromatous debris (mostly fibrin) causing blindness. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Blindness. | Image |
| 470 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19c shows embolus has reached the bifurcation and a second embolus (below) is beginning its transit along the same path. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous v... | Image |
| 471 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19d shows progress along the same transit path for both emboli. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 472 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19a shows atheromatous embolus traveling up the arteriole. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 473 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Series shows event in progress. R3_A19b shows embolus approaching the bifurcation. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Carotid atheromatous disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptom. | Image |
| 474 |
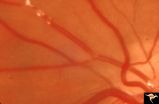 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Note shiny cholesterol plaques in retinal arterial. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Intraluminal cholesterol crystals. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 475 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Embolic occlusion of central retinal artery by white thrombis (probably fibrin.) Patient had a myocardial infarction. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Occlusion of a central retinal artery. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Sud... | Image |
