Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh" Date: "1985"
1 - 25 of 14
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
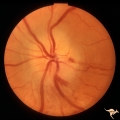 |
B105 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Pallid ischemic swelling. 48 year old woman, flight attendant. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 2 |
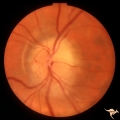 |
B107 Disc Swelling, Ischemic Papillopathies, AION | Pallid ischemic swelling. 41 year old man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: AION. Clinical: Viusal loss. | Image |
| 3 |
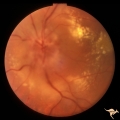 |
B401 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Male with blind eye. Marked peripapillary intraretinal exudate. April 1985. Same patient as B402, B407. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Radiation papillopathy; radiation optic neuropathy. Clinical: Visual loss after radiation therapy. | Image |
| 4 |
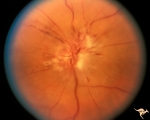 |
B402 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Radiation papillopathy with arterial narrowing, exudation and venous dilation in man with blind eye. May 1985. Same patient as B401, B407. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Radiation papillopahty; optic neuropathy. Clinical: Visual loss after radi... | Image |
| 5 |
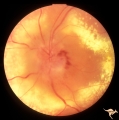 |
B407 Disc Swelling, Radiation Papillopathy | Man with blind eye. June 1985. Same patient as B401 and B402. Note the striking peripapillary intraretinal exudatation occurring at a slight distance from the disc. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to ischemia; Ischemic infarction. Disease/ Diagnosis: Radiation papillopathy; Opt... | Image |
| 6 |
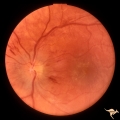 |
D201 Disc Edema with Systemic Hypertension | Left eye. Note generalized arterial narrowing. Low grade disc edema and multiple splinter hemorrhages. The patient had severe hypertension from kidney failure. Additional yellow intraretinal exudate at the macula. 20 year old male patient. Right eye. Pair with D2_02. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina; Ret... | Image |
| 7 |
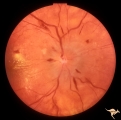 |
D202 Disc Edema with Systemic Hypertension | Right eye. Note generalized arteriole narrowing. Low grade disc edema and multiple splinter hemorrhages. The patient had severe hypertension from kidney failure. Additional yellow intraretinal exudate at the macula. 20 year old male patient. Pair with D2_01. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina; Retinal art... | Image |
| 8 |
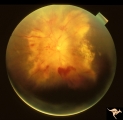 |
F108 Acute Disc Swelling | Chinese man with acute disc swelling. Blind in both eyes. Had large thalamic mass. (Lymphoma). Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Lymphoma. Disease/ Diagnosis: Lymphoma. | Image |
| 9 |
 |
H103 Occipital Hemianoptic Hypoplasia | Right eye. Congenital right homonymous hemianopia. Absent nerve fiber layer in right eye. Same patient as H_104. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Occipital hemianoptic hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital defect of the occipital lobe. | Image |
| 10 |
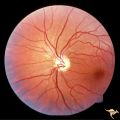 |
H104 Occipital Hemianoptic Hypoplasia | Left eye. Contrast with nasal nerve fiber in right eye, H_103. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Occipital hemianoptic hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital defect of the occipital lobe. | Image |
| 11 |
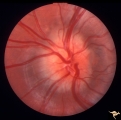 |
Unilateral Buried Drusen | PP23a: left eye; lumpy disc with buried drusen. PP23b: CT scan showing calcium (bright spot at optic nerve head on left). 10 year old boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Normally functioning eye with drusen. | Image |
| 12 |
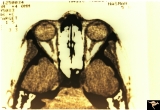 |
Unilateral Buried Drusen | PP23a: left eye; PP23b: CT scan showing calcium (bright spot at optic nerve head on left). 10 year old boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Unilateral drusen, only in the left eye. | Image |
| 13 |
 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. 11 year old. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Clinical: Reduced visual function. | Image |
| 14 |
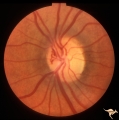 |
Venous Anomalies - Prepapillary Venous Convolutions (Congenital) | Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Disease/Diagnosis: Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
1 - 25 of 14
