Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
1 - 25 of 21
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
Bilateral Papilledema with Pseudotumor Cerebri | Chronic appearance of swelling in right eye. 29 year old woman. Bilateral papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Bilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Intracranial hypertension due to treatment of growth failure with thyroid medication. Clinical: symptoms: headache, signs: bilateral papill... | Image |
| 2 |
 |
A203 Disc Swelling with Big Blind Spot Syndrome | Slight inferior swelling in patient with grossly enlarged blind spot. 66 year old woman. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Unknown. Disease/ Diagnosis: Big blind spot syndrome. Clinical: symptoms: photopsias; blurred vision signs: disc swelling; white dots in the retina; enlarged blind spot on... | Image |
| 3 |
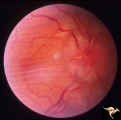 |
P52b Asymmetric Papilledema with Choroidal Folds | Right eye shows papilledema. Asymmetric papilledema with choroidal folds. Bilateral choroidal folds from elevated intracranial pressure. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/ Diagnosis: Chronic papilledema with choroidal folds. | Image |
| 4 |
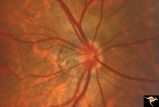 |
H48 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal-Nasal Hypoplasia | Bilateral nasal hypoplasia with absence of nasal nerve fiber layer and corresponding flag-like temporal field defect. Right eye. Same patient as H_49. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Nasal segmental disc hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congential anomaly. | Image |
| 5 |
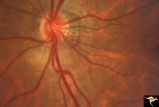 |
H49 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal-Nasal Hypoplasia | Bilateral nasal hypoplasia with absence of nasal nerve fiber layer and corresponding flag-like temporal field defect. Left eye. Same patient as H_48. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Nasal segmental disc hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congential anomaly. | Image |
| 6 |
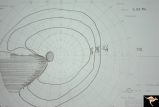 |
H42 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal, Nasal Hypoplasia | Visual field of patient in H_43. Flag-like temporal field defect from patient with nasal segmental disc hypoplasia. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Nasal segmental disc hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 7 |
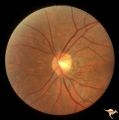 |
H43 Segmental Hypoplasia, Retinal, Nasal Hypoplasia | Nasal hypoplasia barely perceptible on disc. Nasal retinal nerve fibers are completely absent from 7:00 - 12:00. Anaotmy: Optic disc. Pathology: Nasal segmental disc hypoplasia. Disease/ Diagnosis: Congenital anomaly. | Image |
| 8 |
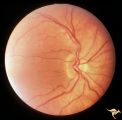 |
H15 Panhypoplasia | Moderate hypoplasia. Right eye. 14 year old boy. Good example of double ring sign. Same patient as H_16. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 9 |
 |
H16 Panhypoplasia | Moderate hypoplasia. Left eye. 14 year old boy. Good example of double ring sign. Same patient as H_15. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. | Image |
| 10 |
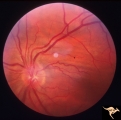 |
P52a Asymmetric Papilledema with Choroidal Folds | Left eye. Choroidal folds with no papilledema. Asymmetric papilledema with choroidal folds. Bilateral choroidal folds from elevated intracranial pressure. 52a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/ Diagnosis: Asymmetric - No papilledema with choroidal folds | Image |
| 11 |
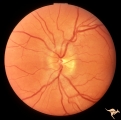 |
C116 Papillitis, Retrobulbar Neuritis | Demyelinative optic neuropathy with mild disc swelling. Note the mild disc margin blurring. The main focus of the neuritis lies behind the eye. 20/20 visual acuity. Anatomy: Optic disc; Optic nerve. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to inflammation; Acute demyelination. Disease/ Diagnosis: Acute sub-... | Image |
| 12 |
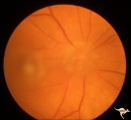 |
A401Disc Swelling, Vitreous Effects | Vitreopapillary haze. Cone of vitreous that has obscured the disc. Uveitis patient. Anatomy: Optic disc; Vitreous. Pathology: Vitreal contact with the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Vitreal traction on the disc? Clinical: Visual blurring in uveitis?¼igns: disc swelling; disc obscuration. | Image |
| 13 |
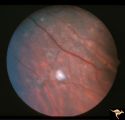 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Several small tuberous sclerosis lesions. Group with R1_D7a, c, d. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 14 |
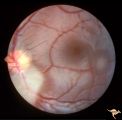 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Two moderate sized tuberous sclerosis lesions in the left eye. Group with R1_D7b, c, d. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 15 |
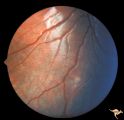 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | One small tuberous sclerosis lesion. Group with R1_D7a, b, c. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 16 |
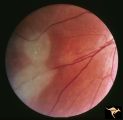 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Has two astrocytic hamartomas. Lower shows a few specs of calcification. Note how the tumor obscures the underlying retinal vessels. Left eye. Pair with R1_D4a. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 17 |
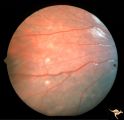 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Two very small tuberous sclerosis lesions. Group with R1_D7a, b, d. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: Patient had mental retardation and epilepsy. No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 18 |
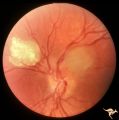 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Has two astrocytic hamartomas. One is calcified. Right eye. Pair with R1_D4b. Anatomy: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 19 |
 |
Bilateral Papilledema with Pseudotumor Cerebri | Left eye. Mild bilateral papilledema in a 7 year old boy. Cause of swelling unknown. Growth failure treated with thyroid medication. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Bilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Intracranial hypertension due to treatment of growth failure with thyroid medication. Clinica... | Image |
| 20 |
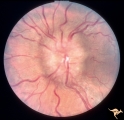 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Has papilledema. 27 year old white woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache. | Image |
| 21 |
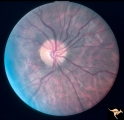 |
Unilateral Papilledema | Unilateral papilledema in pseudotumor cerebri. Right eye. Has no cup. 27 year old white woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Unilateral papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Idiopathic intracranial hypertiension, pseudotumor cerebri. Clinical: Woman, headache. | Image |
1 - 25 of 21
