Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh" Date: "1967"
1 - 25 of 22
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
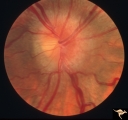 |
Bilateral Papilledema | Right eye. Bilateral Papilledema in a patient with hyperthyroidism. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Bilateral papilledema with hyperthyroidism. | Image |
| 2 |
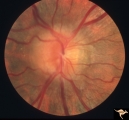 |
Bilateral Papilledema | Left eye. Bilateral Papilledema in a patient with hyperthyroidism. Woman. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Bilateral papilledema. | Image |
| 3 |
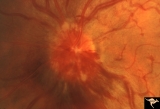 |
E01 Disc Swelling with Central Vein Occlusion | Left eye. Central retinal vein occlusion with disc swelling. Anatomyt: Optic disc; Retina. Pathology: Vasculitis. Disease/ Diagnosis: Disc swelling due to retinal vasculitis. | Image |
| 4 |
 |
Multifocal Choroidopathy | Multifocal choroidopathy in a patient with uveitis. Anatomy: Retina. Disease/Diagnosis: Uveitis, Multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 5 |
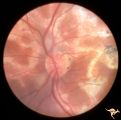 |
Multifocal Choroidopathy | Multifocal choroidopathy in a patient with uveitis. Anatomy: Retina. Disease/Diagnosis: Uveitis, Multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 6 |
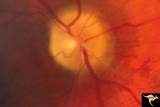 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Right eye 33 months after presentation. Atrophy appears about the same. Notice especially the narrowing of retinal arterioles. Visual loss is severe in both eyes. Papilledema due to brain tumor - 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Dis... | Image |
| 7 |
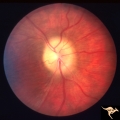 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Right eye at 27 months after presentation. Atrophy is more profound in both eyes. Papilledema due to brain tumor - 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema from acoustic neuronoma. | Image |
| 8 |
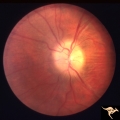 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Left eye at 25 months after presentation. Atrophy is more profound in both eyes. Papilledema due to brain tumor - 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema from acoustic neuronoma. | Image |
| 9 |
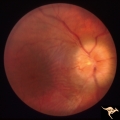 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Right eye 23 months after presentation. Atrophy is replacing papilledema in both eyes. Papilledema due to brain tumor - 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema from acoustic neuronoma. | Image |
| 10 |
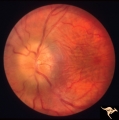 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Left eye 23 months after presentation. Atrophy is replacing papilledema in both eyes. Papilledema due to brain tumor - 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema from acoustic neuronoma. | Image |
| 11 |
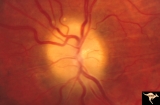 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Left eye. 3.5 years after presentation. Atrophy appears about the same. Note especially the narowing of retinal arterioles. Visual loss is profound in both eyes. Note the horizontal retinal folds. Papilledema due to brain tumor - 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. | Image |
| 12 |
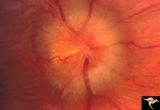 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Right eye at presentation. Papilledema due to acoustic neuronoma(tumor)- 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema from acoustic neuronoma. | Image |
| 13 |
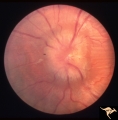 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Left eye at presentation. Papilledema due to acoustic neuronoma(tumor) - 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/Diagnosis: Papilledema from acoustic neuronoma. | Image |
| 14 |
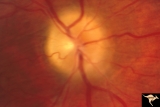 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Right eye 3.5 years after presentation. Atrophy appears about the same. Note especially the narrowing of retinal arterioles. Visual loss is prfound in both eyes. Note the horizontal retinal folds. Papilledema due to brain tumor - 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. | Image |
| 15 |
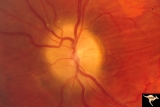 |
Papilledema due to Brain Tumor - Natural History | Left eye at 33 months after presentation. Atrophy appears about the same. Note especially the narrowing of retinal arterioles. Visual loss is severe in both eyes. Papilledema due to brain tumor - 3 year natural history. Patient refused treatment. Man. | Image |
| 16 |
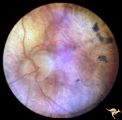 |
Retinal Degeneration Associated with Spastic Paraplegia | Retinal pigmentary degeneration concentrated around the optic discs in a patient with spastic paraplegia. Inverted retinitis pigmentosa where bone spicules are concentrated around the disc and maculae instead of the periphery. Left eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebellar spinal degenerative dise... | Image |
| 17 |
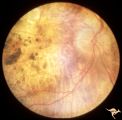 |
Retinal Degeneration Associated with Spastic Paraplegia | Retinal pigmentary degeneration concentrated around the optic discs in a patient with spastic paraplegia. Inverted retinitis pigmentosa where bone spicules are concentrated around the disc and maculae instead of the periphery. Right eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebellar spinal degenerative dis... | Image |
| 18 |
 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Atheromatous embolism in a patient who suffered sudden visual loss in his left eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Post cholesterol embolization. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: Sudden visual loss in left eye. | Image |
| 19 |
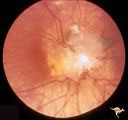 |
Tuberous Sclerosis | Tuberous Sclerosis. Astrocytic hamartoma of the optic disc. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Astrocytic hamartoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Tuberous sclerosis. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
| 20 |
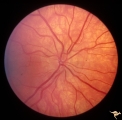 |
Unilateral Pseudopapilledema | PP_10b: shows albinotic fundus and a small crowded disc. PP_10a: left: pseudo papilledema with disc blurring, crowded disc. Optic disc is small in diameter. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Crowded disc. Clin... | Image |
| 21 |
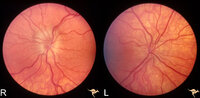 |
Unilateral Pseudopapilledema | PP_10a: Left: pseudo papilledema with disc blurring, crowded disc. Optic disc is small in diameter. PP_10b shows albinotic fundus and small crowded disc. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Elevated disc. Clinic... | Image |
| 22 |
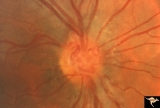 |
Venous Anomalies - Prepapillary Venous Convolutions (Congenital) | Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Disease/Diagnosis: Prepapillary venous convolutions - congenital. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
1 - 25 of 22
