Collection of materials relating to neuro-ophthalmology as part of the Neuro-Ophthalmology Virtual Education Library.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
- NOVEL141
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_novel"
| Title | Creator | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
 |
Neuroblastoma | Shirley H. Wray, MD, PhD, FRCP | The patient is Case 27-1995 Case Records of the Massachusetts General Hospital (New Eng. J Medicine 1995, 333:579-586). The discusser was Dr. Elizabeth Engle, Associate Professor of Neurology, Harvard Medical School. The baby girl was born after a 30 week gestation, with a birth weight of 1.25 kg. T... | Downbeat Nystagmus; Paraneoplastic Opsoclonus; Neuroblastoma; Primary Position Downbeat Nystagmus; Ataxia; Paraneoplastic Downbeat Nystagmus |
| 102 |
 |
Treatment Outcomes of Ocular Manifestations in Wernicke's Encephalopathy: Case Report | Whitney Stuard Sambhariya, PhD, Medical Student; Melanie Truong-Le, DO, OD | The case of a 28- year-old woman with a past medical history of gastric sleeve who was reported to have blurry vision and presented to neuro-ophthalmology with double vision. On examination the patient had bilateral abducens palsy, alternating upbeat and downbeat nystagmus with a torsional component... | Wernicke's Encephalopathy; Ocular Manifestations; Neuro-ophthalmology; Abducens Palsy; Nystagmus; Double Vision; Blurry Vision |
| 103 |
 |
Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis | Shirley H. Wray, MD, PhD, FRCP | This 58 year old woman was referred to Dr. Robert Brown in March 1995 for evaluation of slurred speech. She remained under his care until her death. On examination she had signs of a pseudobulbar palsy: Dysarthria and dysphagia Diminished palatal movement with positive gag bilaterally Diminished rap... | Supranuclear Paralysis of Up and Downgaze Degeneration; Convergence Insufficiency; Slow Hypometric Horizontal Saccades;; Saccadic Breakdown of Horizontal Pursuit; Bulbar Palsy; Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis; Lou Gehrig's Disease; CNS -Degeneration; Superoxide Dismutase (SOD1) Gene |
| 104 |
 |
Management of Non-Organic Vision Loss | Aumer Shughoury, BA; Devin D. Mackay, MD | A description of the management of non-organic visual loss. | Non-Organic Vision Loss; NOVL |
| 105 |
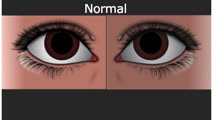 |
Normal Light Reflex and Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD) | Marshall Huang, 4th Year Medical Student | A Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect is an examination finding in patients who have an asymmetric pupillary reaction to light when it is shined back and forth between the two eyes. It is most commonly a sign of asymmetric optic nerve disease or damage but can also present in widespread asymmetric r... | Light Reflex; RAPD |
| 106 |
 |
Optic Disc Drusen | NANOS | Optic disc drusen are abnormal deposits of protein-like material in the optic disc - the front part of the optic nerve. Updated April 2020. | Optic Disc Drusen; Patient Brochure |
| 107 |
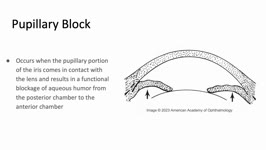 |
Pupillary Block | Sujata Dalal; James Brian Davis; Amanda Dean Henderson | Pupillary block occurs when the pupillary margin of the iris contacts the anterior surface of the lens. This creates a barrier for the outflow of aqueous humor from the posterior chamber to the anterior chamber and resultant increased pressure in the posterior chamber. This pressure can cause the ir... | Angle-Closure Glaucoma; Iris Bombe; Narrow Angle; Pupillary Block |
| 108 |
 |
Protecting Human Subjects in Biomedical Research | Lisa R. Latchney, MS, CCRC | PowerPoint discussion of the history and development of ethics regulations in health research. | Ethical Issues in Research; Consent |
| 109 |
 |
Age Related Macular Degeneration | Riya H. Patel; James Brian Davis; Amanda Dean Henderson | Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a degenerative disease of the retina that causes central vision loss, and it is the leading cause of blindness in the developed world. Age is a strong nonmodifiable risk factor for AMD. Patients may have genetic susceptibility to AMD from mutations in genes ... | AMD; AREDS2; Exudative; Geographic Atrophy; Macular Degeneration; Nonexudative |
| 110 |
 |
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) | Natali V. Baner, MD; Ali G. Hamedani, MD, MHS | PowerPoint providing an overview of the definition, clinical presentation and treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). | Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) |
| 111 |
 |
Cavernous Sinus Meningioma | Shirley H. Wray, MD, PhD, FRCP | This patient is a 46 year old woman from Portugal who was admitted to the Massachusetts General Hospital in September 1986 with ophthalmoplegia of the left eye (OS) and signs of aberrant reinnervation of the third nerve. She presented, in August 1985, with an episode of diplopia. The diplopia was su... | Ptosis; Unilateral Third Nerve Palsy; Aberrant Reinnervation of the Third Nerve; Paresis of Abduction; Sixth Nerve Palsy; Oculomotor Nerve; Cavernous Sinus Meningioma; Cavernous Sinus Syndrome; Unilateral Oculomotor Third Nerve Palsy; Unilateral Sixth Nerve Palsy |
| 112 |
 |
Migraine Visual Aura | Shirley H. Wray, MD, PhD, FRCP | The patient is a 9 year old right handed boy who developed headaches in 1993 at the age of 8. At that time he told his mother that he had bad headaches starting at the back of the head, usually bioccipital, spreading over the top of the head to his forehead. The headaches were short in duration last... | Migraine Visual Aura without Headache; Metamorphopsia; Macropsia - Hemi-macropsia; Alice in Wonderland Syndrome; Occipital Lobe; Visual Phenomena |
| 113 |
 |
Oculomasticatory Myorhythmia | Shirley H. Wray, MD, PhD, FRCP | This case, previously reported in 1986, is published courtesy of John Selhorst, M.D., Saint Louis University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO. (4) The patient is a 46 year old man who, over a period of six months, lost the ability to read and complained of excessive somnolence, occasional urinary i... | Somnolence; Supranuclear Paralysis of Up and Downgaze; Pendular Vergence Oscillations; Oculomasticatory Myorhythmia; Tropheryma Whippelii - Infection; CNS Whipple's Disease; Supranuclear Paralysis of Up and Downgaze Infection-Whipple's Disease; Oculomasticatory Myorhythmia (Whipple's) |
| 114 |
 |
The Mental Status Examination - Cognitive | James R. Bateman, MD, MPH; Victoria S. Pelak, MD | Introduction to the cognitive mental status examination. See accompanying videos: Executive function: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6bw1rp1, Limb-Kinetic apraxia: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s63c084b, Ideomotor apraxia: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s674... | Mental Status; Cognitive Function |
| 115 |
 |
Diagnostic Error of Neuro-ophthalmologic Conditions: State of the Science | Leanne Stunkel, MD; David E. Newman-Toker, MD, PhD; Nancy J. Newman, MD; Valérie Biousse, MD | Diagnostic error is prevalent and costly, occurring in up to 15% of US medical encounters and affecting up to 5% of the US population. One-third of malpractice payments are related to diagnostic error. A complex and specialized diagnostic process makes neuro-ophthalmologic conditions particularly vu... | Diagnostic Errors |
| 116 |
 |
Alexia Without Agraphia | Shirley H. Wray, MD, PhD, FRCP | The patient is a 69 year old left handed man with a history of hypertension, insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and atrial fibrillation. Treated with coumadin, adjusted to keep the INR between 2 and 3. On the morning of admission he awoke at 4 a.m., sat momentarily on the side of the bed and then s... | Pure Alexia; Color Anomia; Right Homonymous Hemianopia; Alexia Without Agraphia; Infarct of the Left Visual Cortex and Splenium of the Corpus Callosum; Disconnection Syndrome; Occipital Infarct |
| 117 |
 |
The Mental Status Examination | James R. Bateman, MD, MPH; Victoria S. Pelak, MD | Introduction to the mental status examination. See accompanying videos: Executive function: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6bw1rp1, Limb-Kinetic apraxia: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s63c084b, Ideomotor apraxia: https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s67410xj | Mental Status |
| 118 |
 |
Anatomy of the Oculomotor Nerve (CN III) | Lucas E. Morgan, MS4; Nicholas A. Koontz, MD; Devin D. Mackay, MD | A detailed overview of the anatomic course of CN III, including a detailed pathway description and labeled MRI images, gross anatomy pictures, and structural models. | CN III; Third Cranial Nerve; Oculomotor Nerve; Anatomy; MRI |
| 119 |
 |
Thalamic Infarct | Shirley H. Wray, MD, PhD, FRCP | The patient is a 64 year old man with no major past medical history who, on the day of admission, suddenly developed loss of vision in both eyes and then was unable to open his eyes on his own unless he used his hands. Holding his eyelids open his vision was very blurry. Within minutes he lost consc... | Somnolence; Bilateral Ptosis; Supranuclear Paralysis of Downgaze; Vertical Oculocephalic Reflex Normal; Absent Convergence; Horizontal Gaze Evoked Nystagmus; Top of the Basilar Syndrome; Artery of Percheron; Thalamic Infarct; Supranuclear Paralysis of Downgaze Infarct; Thalamus Infarct; Downgaze Pal... |
| 120 |
 |
Bilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia | Shirley H. Wray, MD, PhD, FRCP | This patient was seen at the Yale Eye Center at the age of 37. She had a long history of multiple sclerosis. At age 22, she had an acute attack of optic neuritis in the left eye which recovered fully within three weeks. Some months later she had a recurrent episode in the same eye, which also recove... | Bilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia; Pendular Horizontal Oscillations; Lid Nystagmus; Upbeat Nystagmus; Botulinum Toxin Therapy; Multiple Sclerosis; Horizontal Pendular Nystagmus; Gaze Evoked Upbeat Nystagmus; Abducting Nystagmus |
| 121 |
 |
Dementia: Overview and Classification | Molly Cincotta, MD; Whitley Aamodt, MD; Ali G. Hamedani, MD, MHS | PowerPoint providing a broad overview of dementia, including definition, clinical findings, work up, diagnosis, classification, and management. | Dementia |
| 122 |
 |
Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy) | NANOS | Hereditary Optic Neuropathy - A hereditary optic neuropathy is caused by a genetic variant (or mutation) that causes dysfunction of the neurons (nerve cells) which form the optic nerve. The optic nerve sends information from the back of the eye to the vision center in the brain.The two most common t... | Hereditary Optic Neuropathy; Patient Brochure |
| 123 |
 |
Paraneoplastic Opsocolonus | Shirley H. Wray, MD, PhD, FRCP | This patient is the index case of the Anti-Ri antibody, published in Annals of Neurology in 1988 (4). The Anti-Ri antibody is recognized to be a paraneoplastic marker in patients with breast and gynecological malignancies (10). The history of this case is particularly important because she was initi... | Opsoclonus; Ocular Flutter; Oscillopsia; Saccadic Oscillations; Paraneoplastic Cerebellar Syndrome; Adenocarcinoma of the Breast; Anti-Ri Antibody; Paraneoplastic Opsoclonus; Paraneoplastic Ocular Flutter; Saccadomania |
| 124 |
 |
Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody Associated Disease (MOGAD) Revisited | Zahir Sheikh; Michael Gilhooley | The purpose of this presentation is to review the varied clinical manifestations of MOGAD for the neurology and neuro-ophthalmology providers. | Demyelinating; MOG; MOGAD; Myelin |
| 125 |
 |
Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act of 2008 | Senate and House of Representatives of the United States of America in Congress | Law to prohibit discrimination on the basis of genetic information with respect to health insurance and employment. | Genetics |
