A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
+ HIT, + Skew, Unidirectional Nystagmus: Central Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Wallenberg Syndrome | This is a 45-year-old woman who presented to the ED with acute prolonged vertigo and vertical diplopia. She was seen as an outpatient 1 month after her ED visit, and double vision and balance were improving by that time. Her HINTS testing showed the following (seen in the video): 1) Head Impulse - A... | Image/MovingImage |
| 2 |
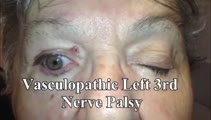 |
3rd Nerve Palsy With Preserved 4th Nerve Function | 80-yo-woman with a left vasculopathic 3rd nerve palsy (minimal pupil involvement of about 1 mm relative mydriasis OS - other etiologies ruled out and resolved as expected over months). Although the inferior rectus is paretic, intact superior oblique muscle function can be demonstrated by asking the ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 3 |
 |
6th Nerve Palsy as Initial Presentation of Metastatic Lung Cancer | A video describing 6th nerve palsy as initial presentation of metastatic lung cancer. | Image/MovingImage |
| 4 |
 |
A 'Canal Jam' During Head Impulse Testing in a Patient With Horizontal Canal BPPV | A 70-year-old man reported brief episodes of positional vertigo. Ten years prior, he had undergone gamma knife radiosurgery for a vestibular schwannoma at the left cerebellopontine angle. Video head impulse testing (vHIT) showed reduced gains and corrective saccades in the planes of the left horizon... | Image/MovingImage |
| 5 |
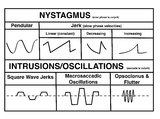 |
A Comparison of Nystagmus and Saccadic Intrusions/Oscillations | Nystagmus can be classified into pendular and jerk waveforms, where both are generated by a slow, pathologic phase. Corrective phase (the position reset mechanism) differs. In pendular nystagmus, the eyes move back and forth with about the same velocity and amplitude, similar to that of a pendulum... | Image |
| 6 |
 |
A flowchart approach to nystagmus/intrusions | In tandem with the flowchart, the following added clues should be used to help with etiology: i) vector [horizontal, vertical, torsional]; ii) binocular or monocular; iii) spontaneous or provoked [e.g., BPPV]; iv) change with monocular viewing or gaze direction; v) rest of history, neurologic, and o... | Image |
| 7 |
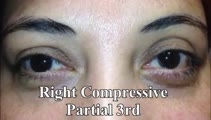 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the 3rd Nerve | Aberrant regeneration in two patients: 1) a young woman with a right cavernous sinus meningioma with subsequent development of aberrant regeneration demonstrated by eyelid elevation OD in attempted downgaze (i.e., some fibers that were supposed to innervate the right IR were misrouted to the right l... | Image/MovingImage |
| 8 |
 |
Abnormal Active Head Impulse Testing Recorded Asynchronously in Bilateral Vestibular Loss | This is a video of patient with the subacute onset of head movement-dependent oscillopsia due to bilateral vestibular loss (with obvious bilaterally abnormal head impulse test (HIT) at the bedside), in addition to central ocular motor signs including saccadic smooth pursuit and gaze-evoked nystagmus... | Image/MovingImage |
| 9 |
 |
Abnormal Head Impulse Test in Vestibular Neuritis 1 Week After Onset | This is a 25-year-old woman who experienced the acute vestibular syndrome due to right-sided vestibular neuritis 1 week prior to this video. Left-beating nystagmus (LBN) was only noted in left gaze, but with fixation-removed, there was clear LBN in primary position that increased with head-shaking a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 10 |
 |
Abnormal Visually-Enhanced VOR in Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome (CANVAS) | A 67 year old woman presented with 1 year of progressive numbness, gait instability, and oscillopsia when walking or with head movements. Examination showed excessive square-wave jerks, bilateral horizontal gaze-evoked nystagmus, impairment of the visually-enhanced vestibular ocular reflex (vVOR - s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 11 |
 |
Acquired Elliptical Pendular Nystagmus Suppressed by Blinks and Saccades | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 70-year-old man who experienced the gradual onset of oscillopsia over weeks about 3 months prior to this video recording. Examination demonstrated elliptical pendular nystagmus which was atypical for infantile n... | Image/MovingImage |
| 12 |
 |
Active Head Impulse Test | Active head impulse test (HIT): instruct the patient to fix their eyes on the camera and turn their head 20o to the right/left, and then make a rapid movement toward the midline to align their head with the camera again, keeping their eyes fixed on the camera throughout. A simple instruction is to a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 13 |
 |
Acute Vestibular Neuritis With Unidirectional Nystagmus and Abnormal Video Head Impulse Test | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is 45-year-old man who presented to the emergency department (ED) 2 days prior to this video recording with acute onset prolonged vertigo, nausea, head motion intolerance, unsteadiness and spontaneous nystagmus, cons... | Image/MovingImage |
| 14 |
 |
The Acute Vestibular Syndrome in MS Due to Middle Cerebellar Peduncle/Root Entry Zone Lesion | This is a 13 year-old girl with relatively abrupt onset vertigo and oscillopsia. On exam, there was primarily right-beating nystagmus in primary gaze with a slight upward (upbeat) component, giving the nystagmus an oblique appearance. The upward component and lack of a clear torsional component acut... | Image/MovingImage |
| 15 |
 |
The Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Dysarthria, Dysphagia, Dysphonia, Hemi-ataxia, and Saccadic Dysmetria Due to the Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman with the acute onset of vertigo, dysarthria, dysphagia and dysphonia/hoarseness (nucleus ambiguus), ptosis and imbalance. Her examination localized to a left lateral medullary (Wallenberg) synd... | Image/MovingImage |
| 16 |
 |
Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Ocular Tilt Reaction Due to Bacterial Labyrinthitis | This is a patient who initially presented with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus) and right sided hearing loss, and was diagnosed with bacterial labyrinthritis. Her HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central etiolo... | Image/MovingImage |
| 17 |
 |
Acute Vestibular Syndrome With Skew Deviation and Positive Head Impulse Test Due to a Demyelinating Lesion | This is a patient who initially presented with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS, e.g., acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus). ; See https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=187730 for additional history. ; Her HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) testing indicated a central e... | Image/MovingImage |
| 18 |
 |
The Acute Vestibular Syndrome with Skew Deviation, Gaze-evoked Nystagmus, and Bilaterally Abnormal Head Impulse Testing Due to AICA Stroke | This is a 60-year-old man with the acute onset of prolonged vertigo and nystagmus, consistent with the acute vestibular syndrome (AVS). HINTS (Head Impulse, Nystagmus, Test of Skew) exam demonstrated a central pattern: 1) Head impulse test (HIT) was abnormal to the right and to the left. An abnormal... | Image/MovingImage |
| 19 |
 |
The Affected-Ear-up 90 degree Maneuver (HC-Canalithiasis) | The Affected-Ear-up 90 degree Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal-canalithaisis. 1. The patient starts in a supine position. 2. The patient rotates their head 90 degrees towards the unaffected side. 3. The patient sits up. | Text |
| 20 |
 |
The Affected-Ear-up 90 degree Maneuver (HC-Canalithiasis) (Video) | The Affected-Ear-up 90 degree Maneuver is used to treat horizontal canal-canalithaisis. 1. The patient starts in a supine position. 2. The patient rotates their head 90 degrees towards the unaffected side. 3. The patient sits up. | Image/MovingImage |
| 21 |
 |
Alternating Hypertropias - Bilateral 4th Nerve Palsies and Alternating Skew Deviation | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are two patients with alternating hypertropias. The first is a 70-year-old woman with a diagnosis of cerebellar ataxia, neuropathy, vestibular areflexia syndrome (CANVAS). In the video, both spontaneous downbeat... | Image/MovingImage |
| 22 |
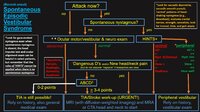 |
An Approach to the Patient with (Recent Onset) Spontaneous Episodic Vestibular Syndrome | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A vascular etiology should always be on the differential diagnosis of the recent onset of the spontaneous (unprovoked) episodic vestibular syndrome (EVS), especially in the older population and when vascular risk factors ... | Image |
| 23 |
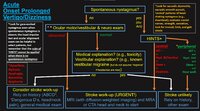 |
An Approach to the Patient with Acute Onset Prolonged Vertigo | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: A vascular etiology should always be on the differential diagnosis of the acute onset prolonged vertigo, especially in the older population and when vascular risk factors are present. However, young patients can suffer fr... | Image |
| 24 |
 |
Anterior Canal - BPPV: Deep Head Hanging | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Regardless or whether it is thought that the patient has right or left anterior canal (AC) involvement, the deep head hanging maneuver is performed in the same way. • First the patient is placed in the long-sitting posi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 25 |
 |
Anterior Canal BPPV | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Although the anterior canal (AC) variant of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is rare, mainly owing to its orientation relative to gravity (which makes otoconial debris much less likely to enter it), it can occu... | Image/MovingImage |
